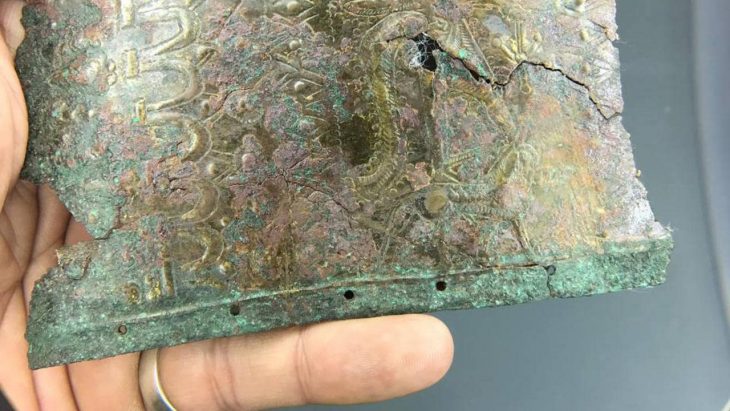
Numerous bronze ornaments have been discovered in Poland’s Chełmno region (Kuyavian-Pomeranian Voivodeship).
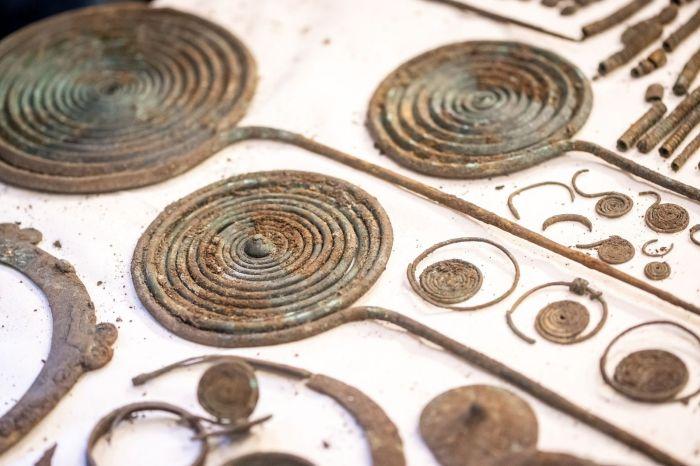
Archaeologists report that dozens of bronze ornaments, including necklaces, bracelets, greaves, decorative pins, and numerous human bones, were discovered. Scientists believe these are most likely objects used in sacrificial rituals 2,500 years ago.
People threw these treasures into a lake around 2500 years ago. Today, however, the site is a drained peat bog that has been converted to farmland.
The discovery was made by members of the Kuyavian-Pomeranian Group of History Seekers (Kujawsko-Pomorskiej Grupy Poszukiwaczy Historii), who conducted searches using metal detectors.
Once metal detectors discovered something of value was hidden at the site, excavations led by Wojciech Sosnowski at the WUOZ in Toruń began in January. They were attended by researchers from the Institute of Archeology of the Nicolaus Copernicus University in Toruń and the services of the Wdecki Landscape Park.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
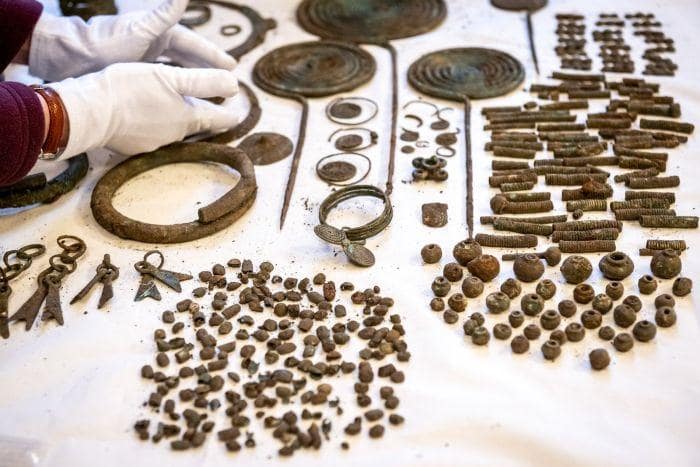

As a result of the plowing, many ancient objects were found scattered loosely on the ground. Scientists discovered three deposits filled with whole or damaged ornaments and bronze items used in all likelihood for ceremonial purposes. The research team recovered necklaces, bracelets, greaves, horse harnesses, and pins with spiral heads.
The discovery of rare organic raw material artifacts like rope fragments and fabrics of antler tools in bronze sheet frames delighted archaeologists. It is unusual to find organic raw materials that have remained well-preserved in such wet conditions.
Most of the monuments, according to the researchers, should be associated with representatives of the Lusatian culture community.
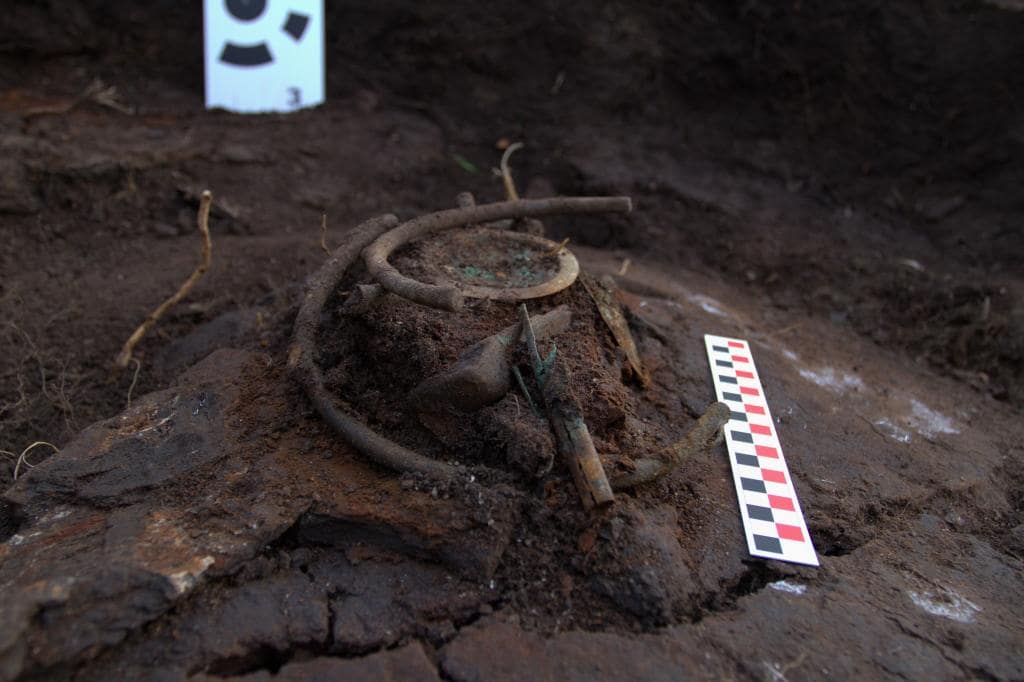

The Lusatian culture was widespread in the Bronze Age and early Iron Age (12th–4th century BC) in the Oder River and Vistula River basins, and extended east to the Buh River. The name is derived from the Sorbian region of Lusatia (Lausitz), now in eastern Germany, where monuments of the culture were first discovered and studied.
Some items, however, are not indigenous to this region and should be correlated with the Scythian civilization and its influences from the region of present-day Ukraine.
Numerous human bones were discovered by scientists among dozens of other artifacts, which supports the theory that this was a location where people and objects were sacrificed.
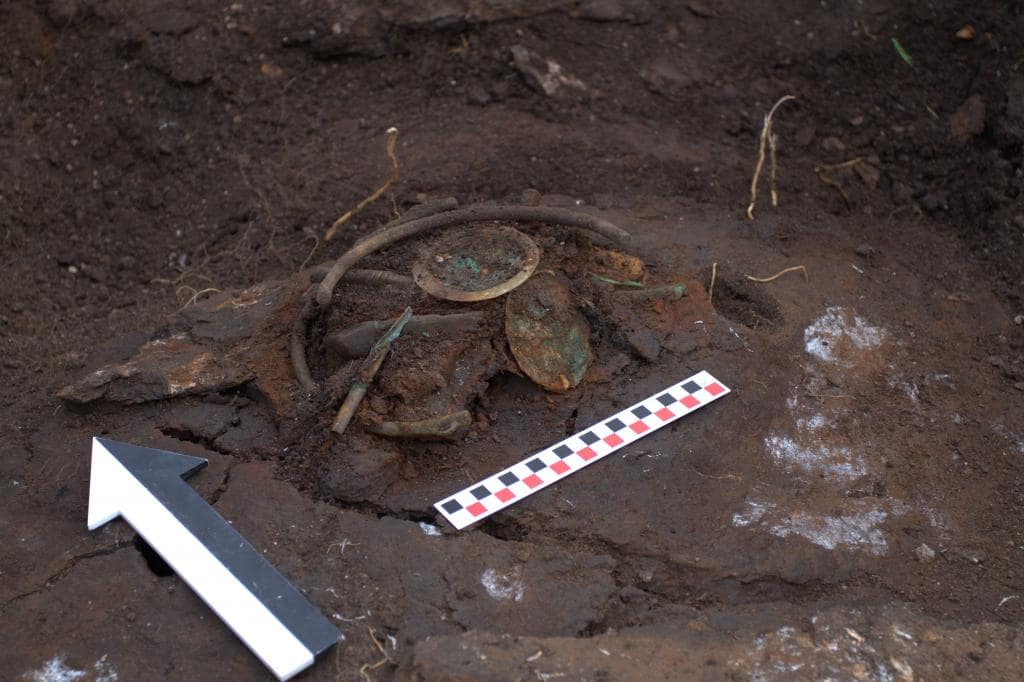

The research team explained that it was a time of increasing unrest related to the penetration into Central and Eastern Europe of groups of nomads from the Pontic Steppe. Local communities found themselves on the threshold of sudden changes. To postpone the rapid changes associated with the appearance of new neighbors, locals began to practice various rituals, including sacrifices.
Archaeologists have not revealed the exact location of the discovery for security reasons. At the same time, they plan further research within the dried-up lake.
Cover Photo: PAP/Tytus Żmijewski