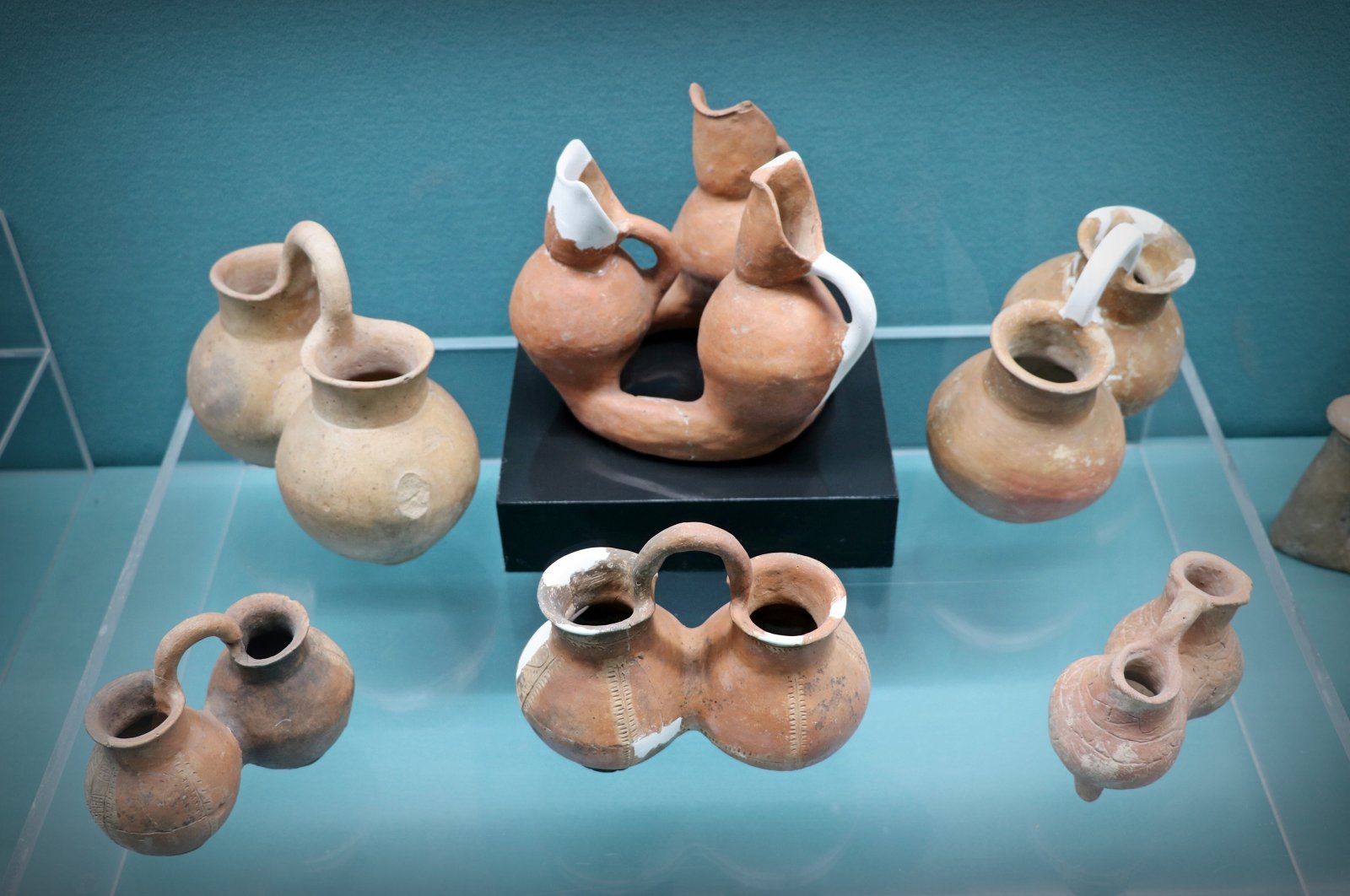
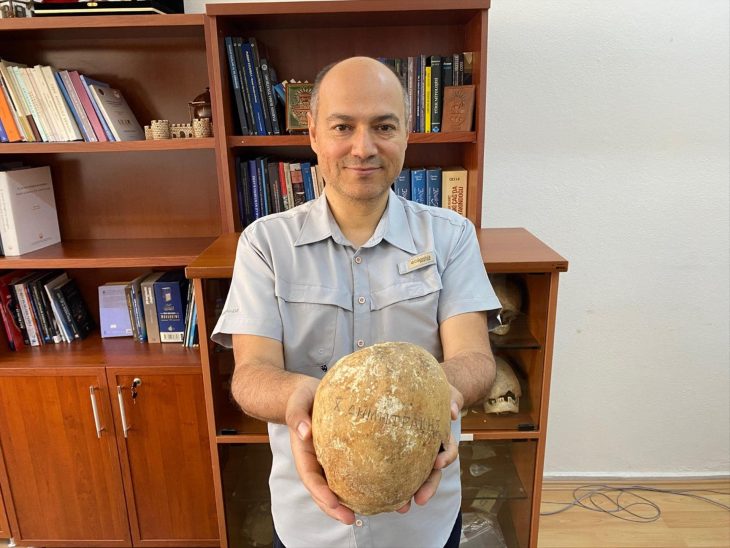
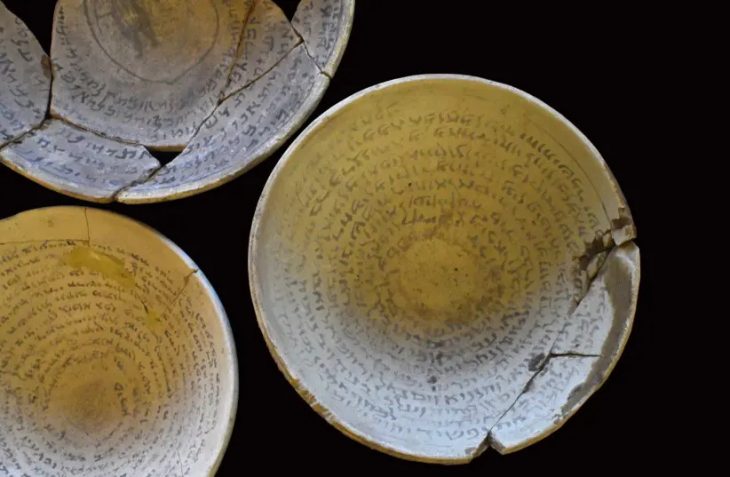
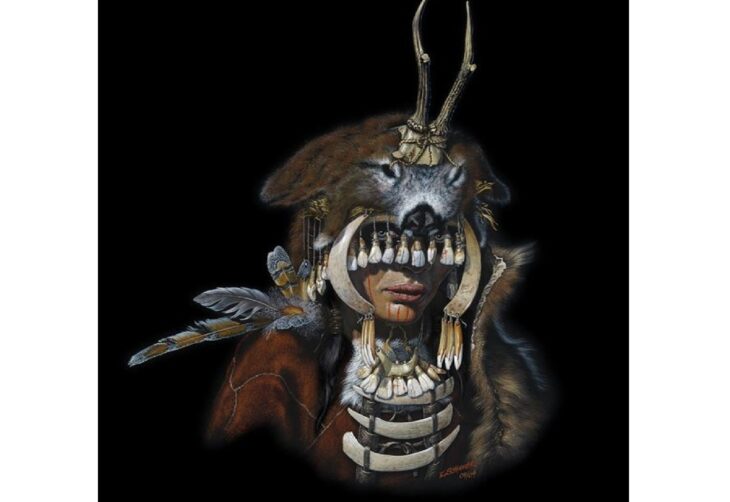
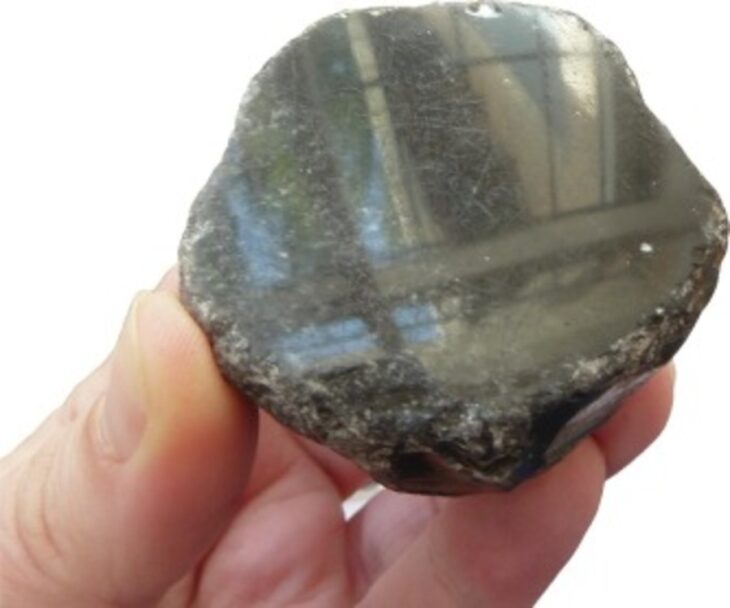
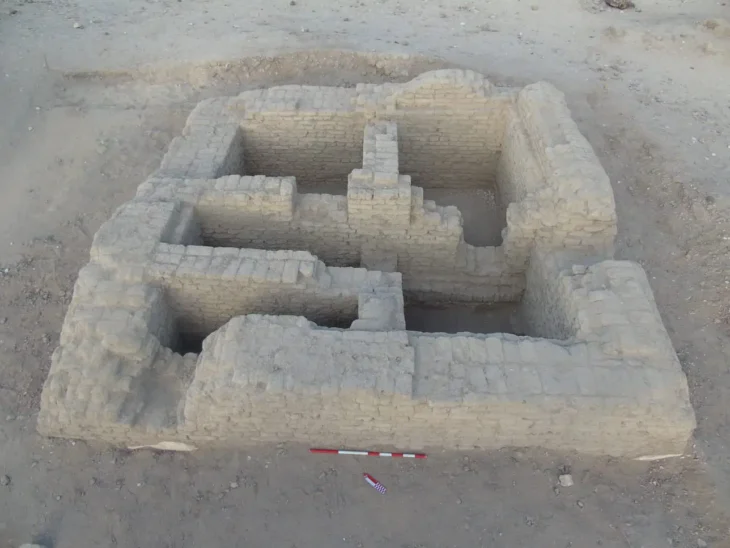
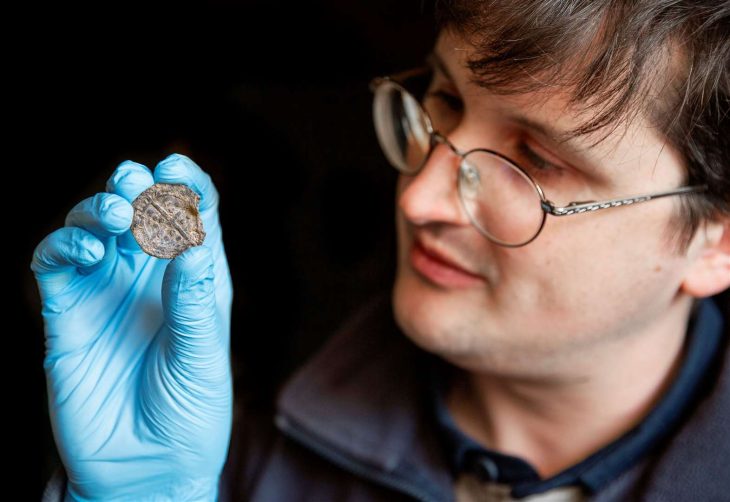
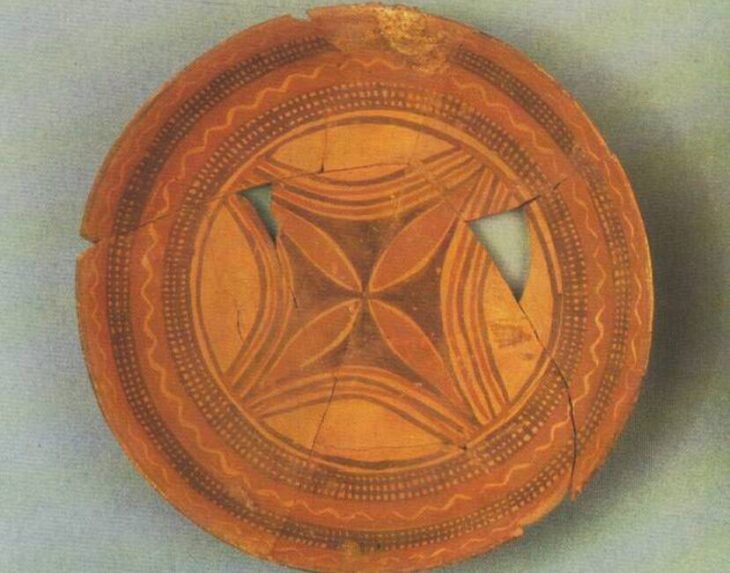
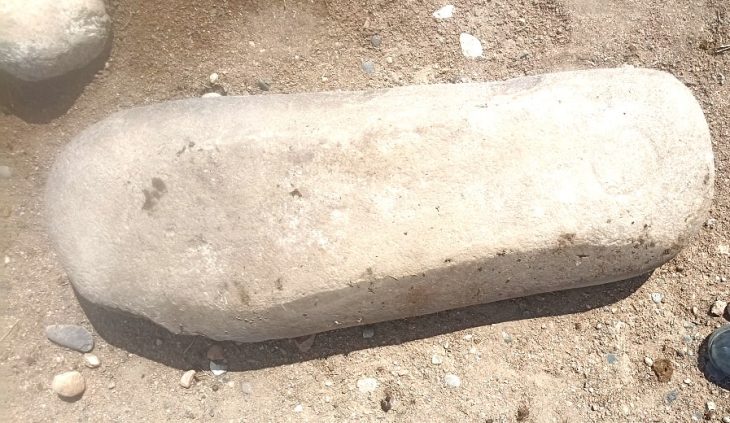
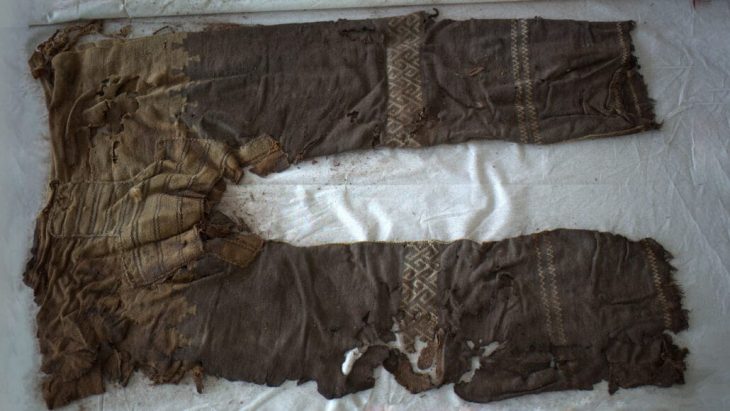
Approximately 14,500 artifacts have been unearthed during rescue excavations carried out over 33 years at Seyitömer Mound in Turkey’s western Kütahya province.
Seyitömer Mound, which dates back to 3,000 B.C., is located in the Çelikler Seyitömer Elektrik Üretim AŞ work area, 26 kilometers away from the city center.
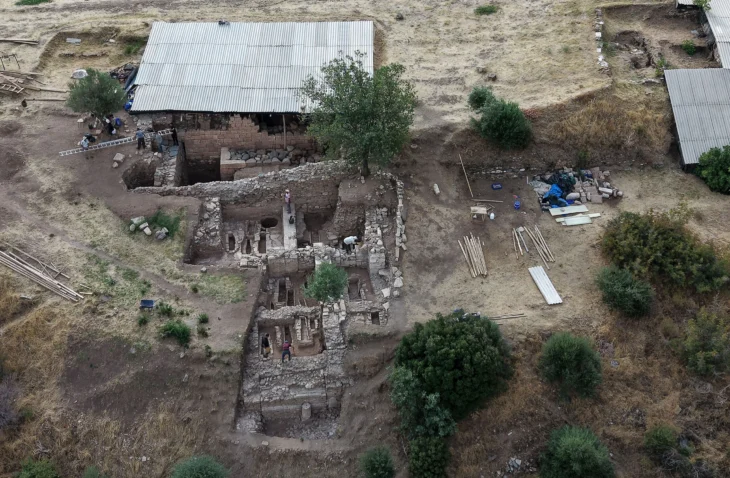
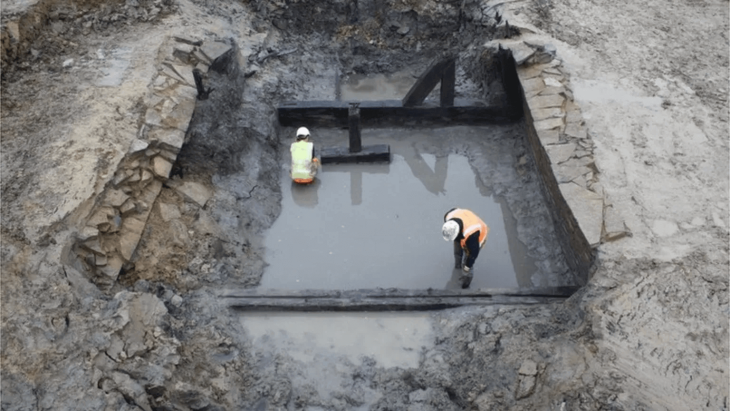
The rescue excavation on the mound, the original height of which was 26 meters, width 140 and length 150 meters, was initiated by Eskişehir Museum Directorate in 1989 in order to bring 12 million tons of lignite under it into the economy.
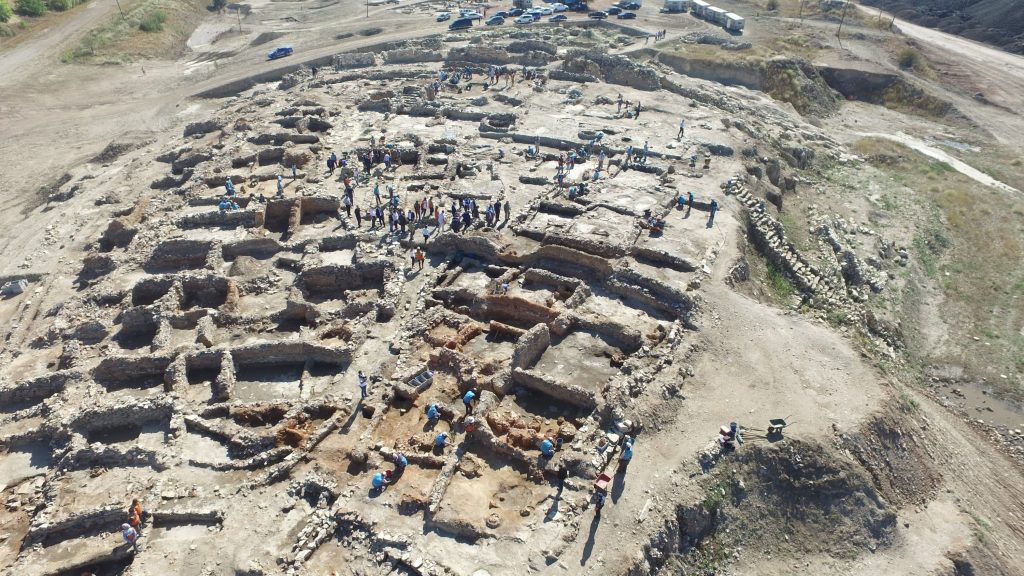

The mound was excavated by the Afyonkarahisar Museum Directorate between the years 1990 and 1995. The excavations got transferred to the DPU Archeology Department in 2006. The excavation team consisting of academic staff, students and workers continued working under the presidency of the head of the department.
Thanks to these studies in Seyitömer, artifacts belonging to six different periods, including the Roman and Hellenistic periods, the Iron Age, the Middle Bronze Age, and the third and second periods of the Early Bronze Age, were introduced to Anatolian archaeology.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
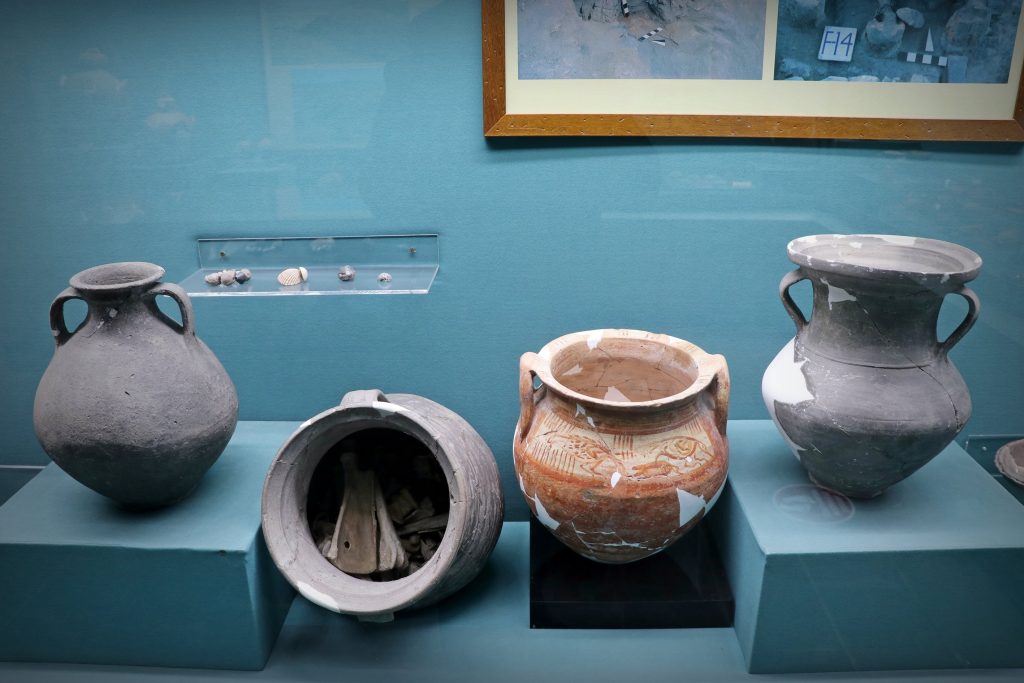

Approximately 14,500 artifacts have been unearthed during rescue excavations carried out over 33 years at Seyitömer Mound in Turkey’s western Kütahya province, Provincial Culture and Tourism Director Zekeriya Ünal said.
Informing that the Archaeology and Mine Museum is being constructed in Kütahya, Ünal also added that most of the unearthed artifacts will be on display at this museum.
Cover Photo: In this photo provided artifacts found in Seyitömer Mound are seen in Kütahya, western Turkey. (AA Photo)