Over 13,000 artifacts, including gold coins and Baltic amber, discovered in one of Central Europe’s largest Celtic settlements.
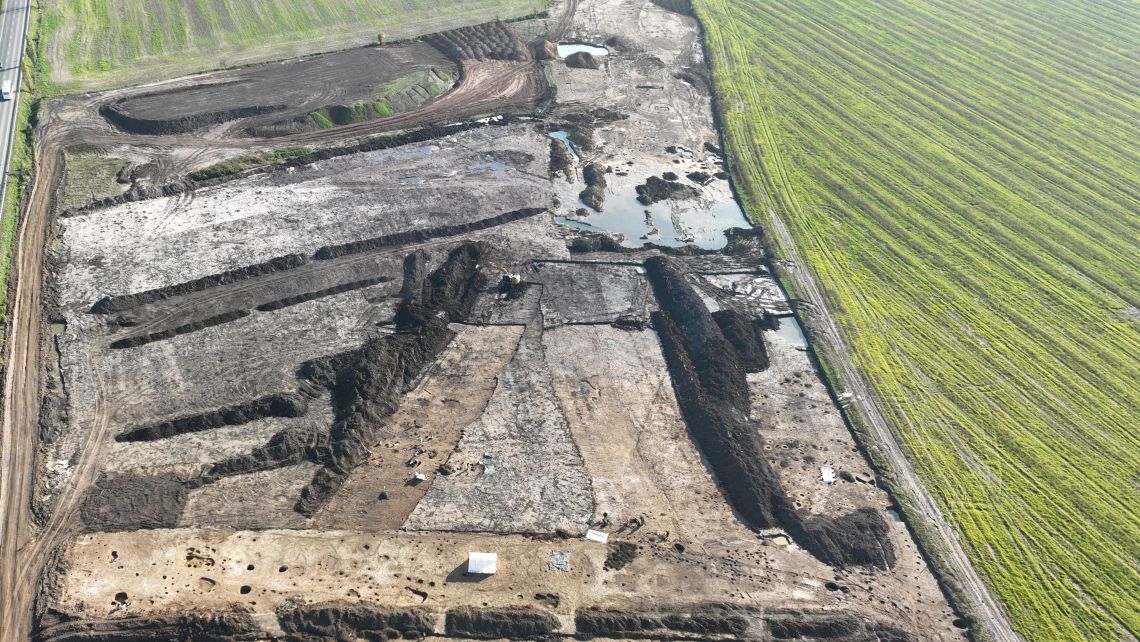
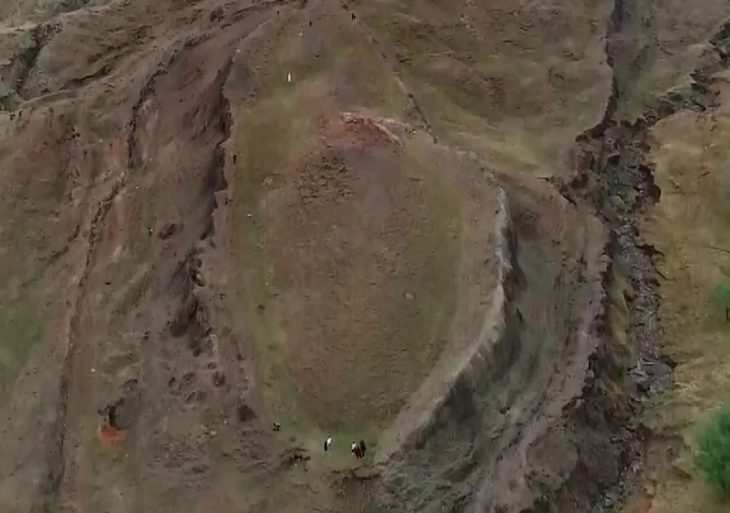
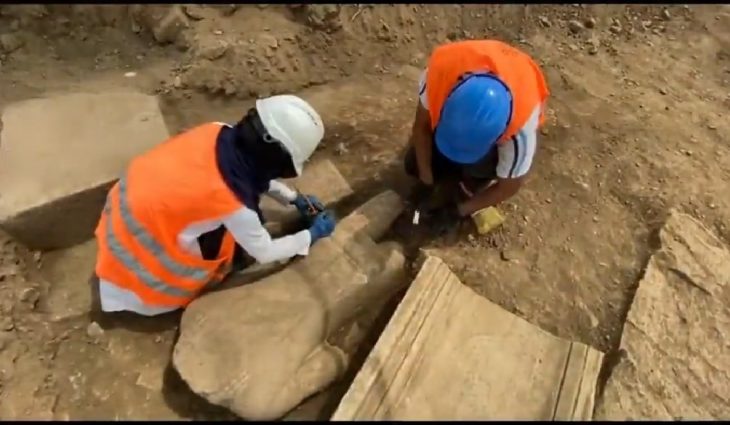
A groundbreaking archaeological discovery in eastern Bohemia has unveiled an ancient Celtic settlement of remarkable scale and significance, dating back more than 2,200 years to the La Tène period. Unearthed near Hradec Králové during pre-construction excavations for the D35 motorway, the site has been described by experts as one of the most important finds in Czech history.
Although the settlement was first identified in 2024 during preliminary motorway surveys near Hradec Králové, full-scale archaeological research only began recently.
An Ancient Celtic Center with Regional Influence
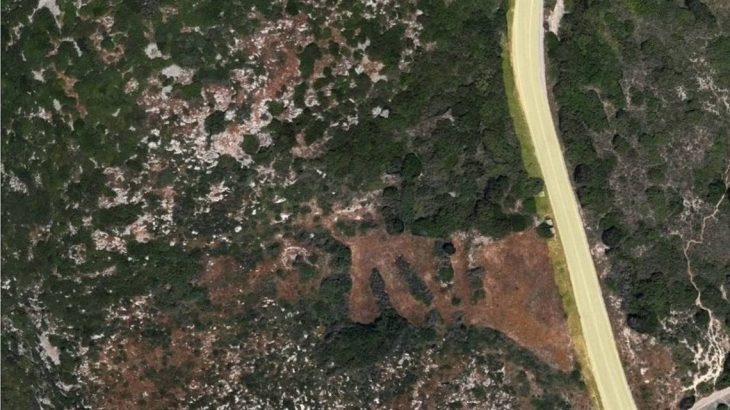
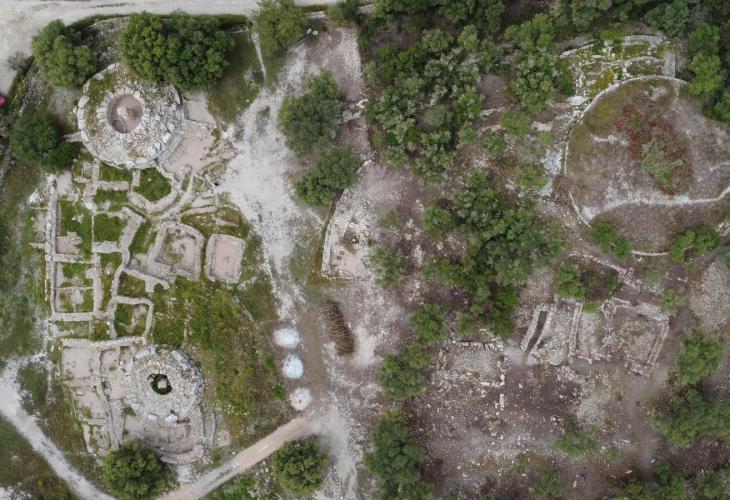
Covering approximately 25 hectares (250,000 square meters), the settlement is attributed to the Boii tribe, the Celtic people after whom Bohemia is named. According to archaeologists from the University of Hradec Králové, the Museum of Eastern Bohemia, and Archaia Praha, this “open agglomeration” functioned as a central hub for commerce, manufacturing, and administration in the 2nd century BCE, before mysteriously vanishing in the 1st century BCE.
“This is undoubtedly a very important location with economic and social functions,” said archaeologist Matouš Holas, who helped lead the multi-institutional excavation. Notably, there are no signs of violent destruction, suggesting the settlement’s decline may have been gradual or influenced by economic or environmental changes.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
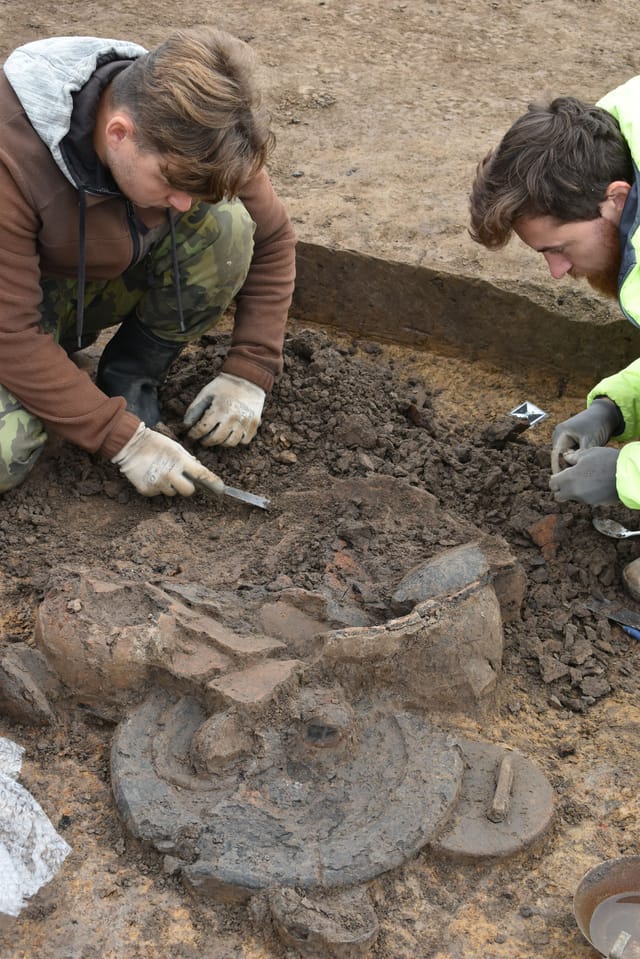

Treasure Trove of Artifacts: Gold, Silver, Ceramics, and Amber
A remarkable total of over 13,000 bags of artifacts have been uncovered from the site—an extraordinary amount for a Celtic settlement in Central Europe.
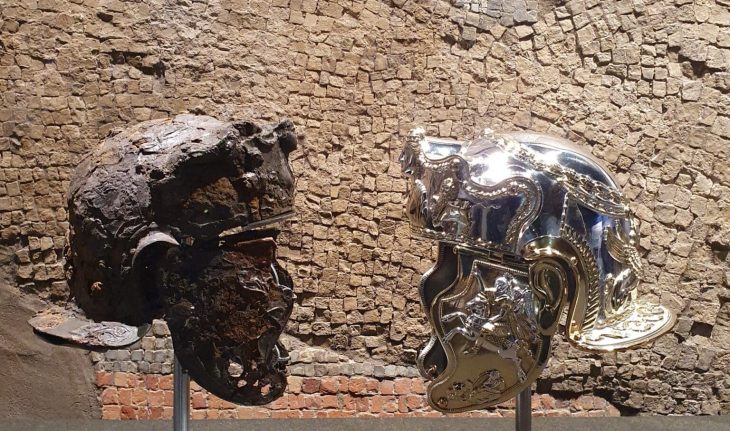
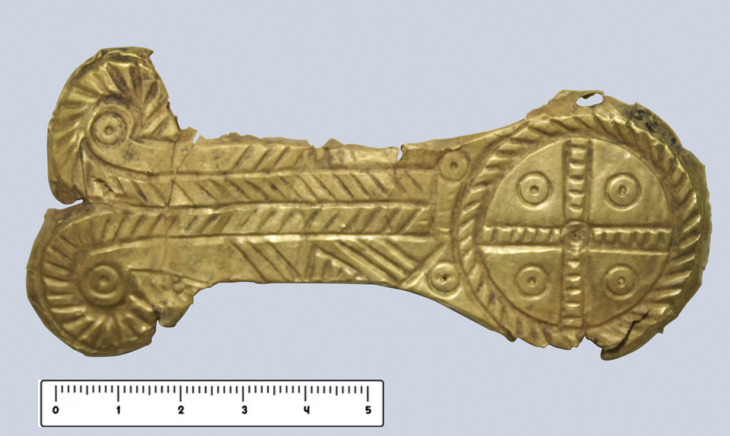
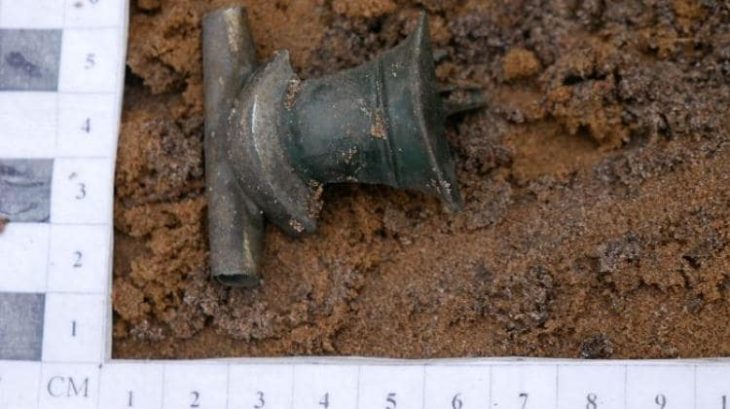
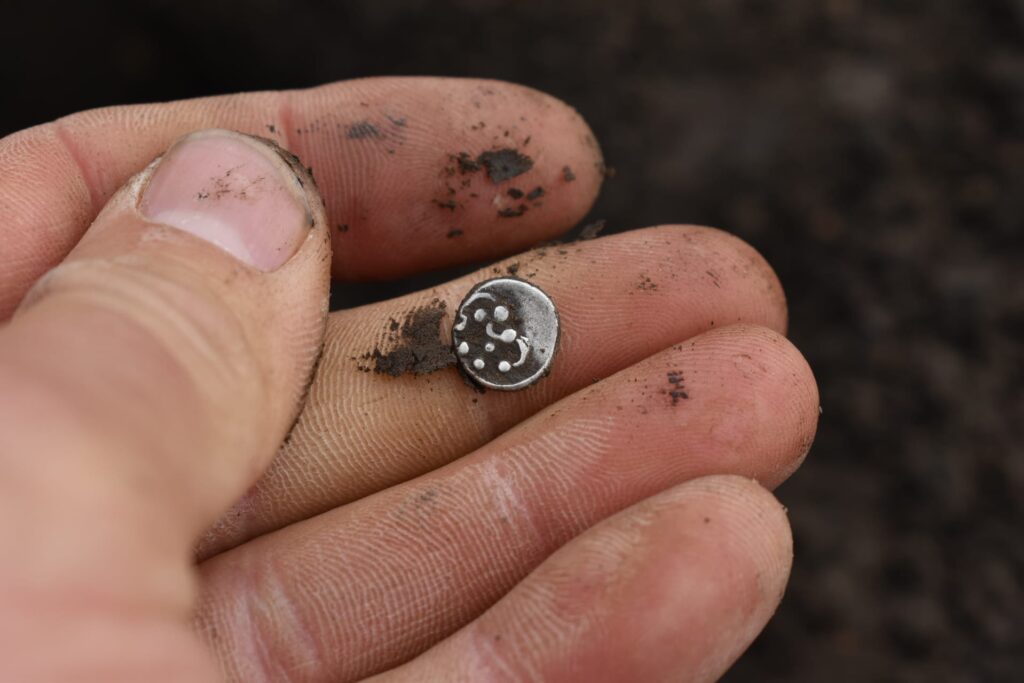
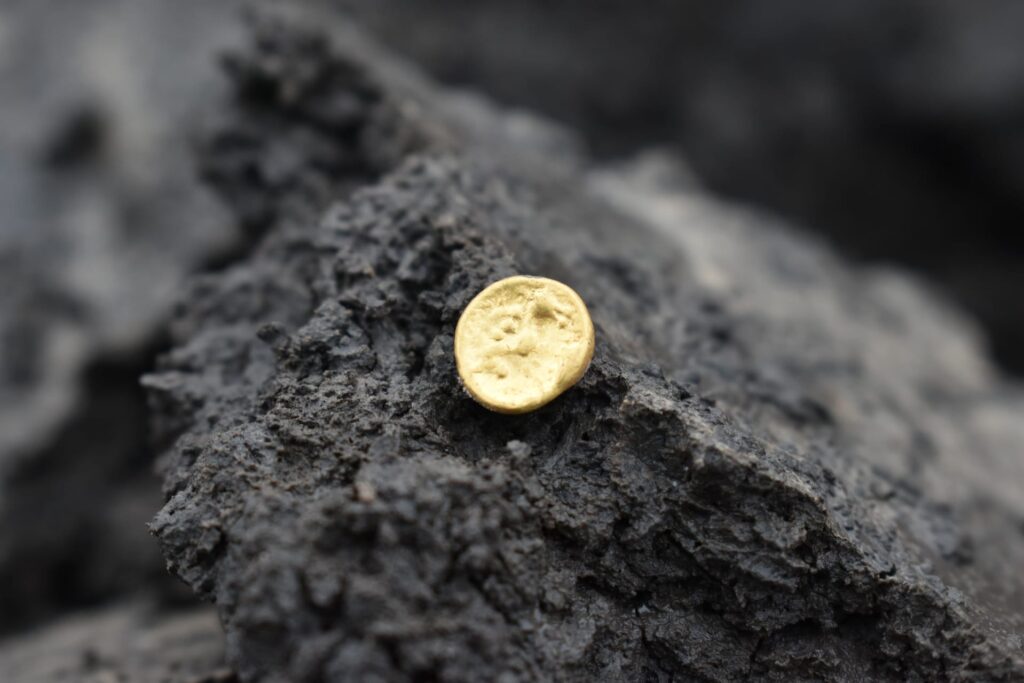
Among the most notable finds are numerous gold and silver coins, some of which were likely minted directly at the site, pointing to a sophisticated local economy.
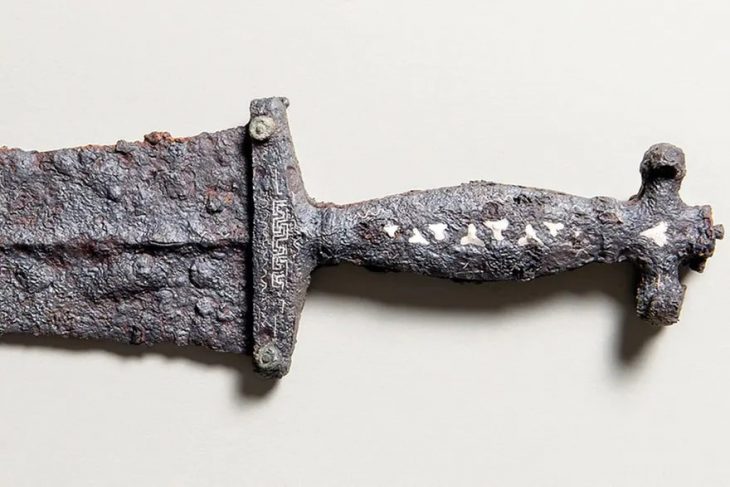
Archaeologists also discovered coin molds, further supporting evidence of on-site coin production. In addition to currency, the settlement yielded luxury ceramics, metal vessels, and fragments of mirrors—items that reflect both everyday life and the wealth and cultural complexity of the community.
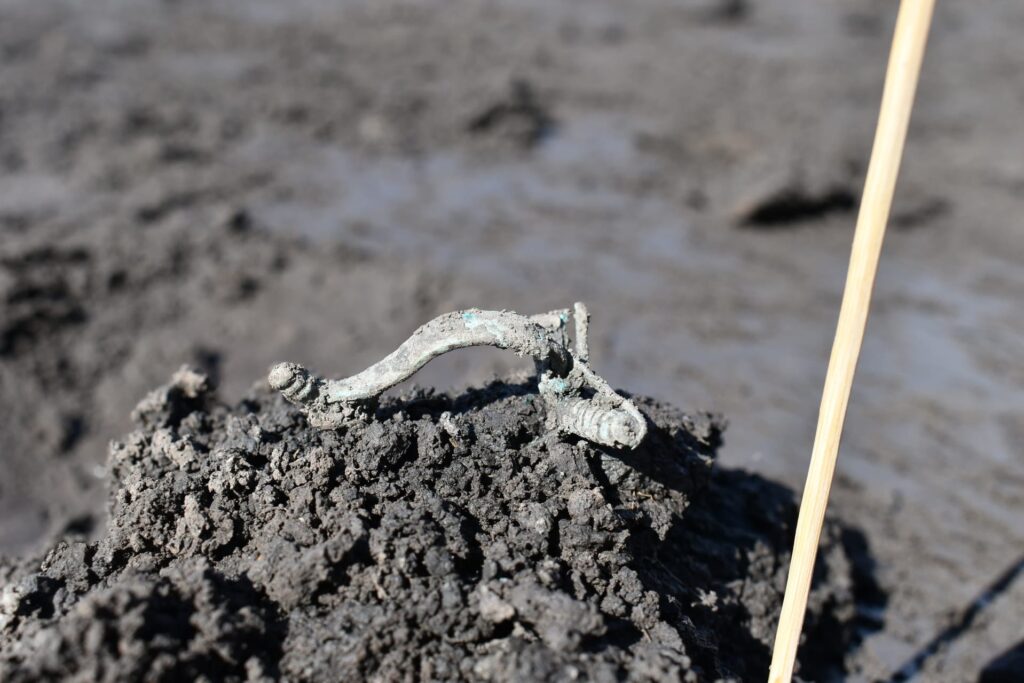
Baltic amber, evidence of long-distance trade
One especially rare object is a ceramic shard engraved with the image of a horse—an artifact rarely seen across the continent.
“The presence of amber, luxury pottery, and local coin production indicates that this was not a typical rural village,” said Tomáš Mangel, archaeologist at the University of Hradec Králové. “It was clearly integrated into the Amber Road, a key trade route connecting the Baltic to the Mediterranean.”

A Snapshot of Celtic Urbanization
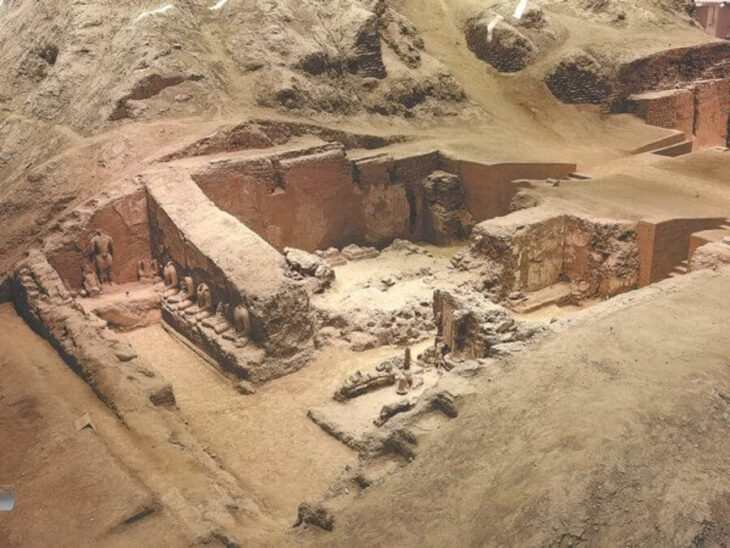
Researchers have identified pottery kilns, glass processing facilities, and possibly religious sanctuaries, suggesting a complex and stratified society. The site offers an unparalleled view into La Tène culture, a hallmark of the Iron Age known for advanced metalwork, elite warrior classes, and long-distance cultural exchange.
According to Miroslav Novák from the Museum of Eastern Bohemia, the site’s importance is “comparable to major Celtic centers in the central Danube region or southern Germany.”
The La Tène Period
The La Tène period (circa 450 BCE to the Roman conquest) marks a significant phase of the European Iron Age, characterized by the flourishing of Celtic culture across much of Central and Western Europe.
Named after the archaeological site of La Tène in Switzerland, this era is noted for its advanced metalwork, distinctive art styles, and the development of complex social structures including tribal elites and warrior classes.
The period also saw increased trade and cultural exchanges, with settlements like the one discovered near Hradec Králové playing vital roles in regional economies and long-distance trade networks such as the famous Amber Road.

Preserved by Time, Revealed by Teamwork
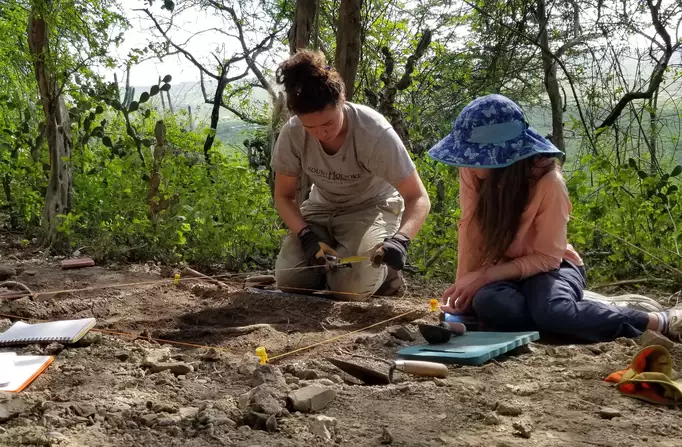
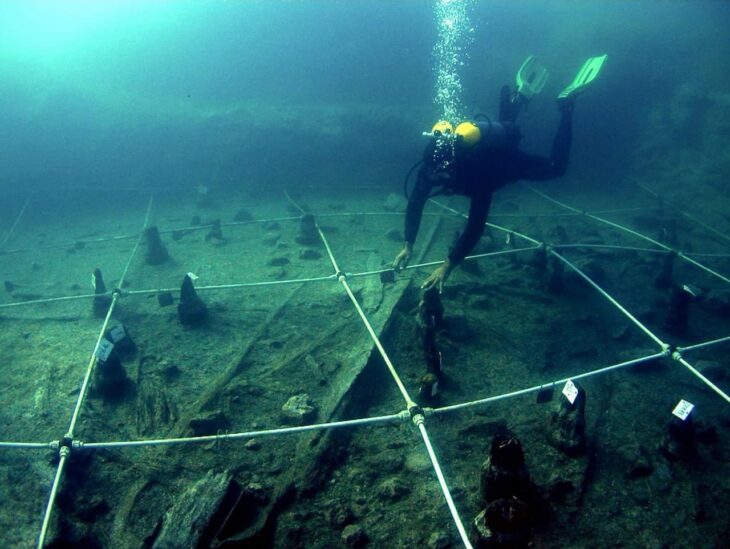
Remarkably well-preserved due to minimal modern agricultural activity and protection from illegal metal detecting, the site also benefited from an innovative collaboration with amateur detectorists. Selected from over 300 applicants, a small team worked under expert supervision for three years to ensure thorough coverage.
Next Steps in Research
Although the excavation phase concluded in early 2025, analysis is just beginning. Artifacts are now being catalogued and studied at the Museum of Eastern Bohemia, with a small exhibition planned in the near future. A more comprehensive showcase will follow once full evaluation is complete.

“This discovery allows us to study ancient Celtic life with exceptional clarity,” said Holas. “It may fundamentally reshape our understanding of early European trade networks and settlement structures in what is now the Czech Republic.”
Cover Image Credit: Archaeologists made the discovery while conducting survey work on the route of a planned motorway in the north of the country. Credit: x.com/AstronomiconEu