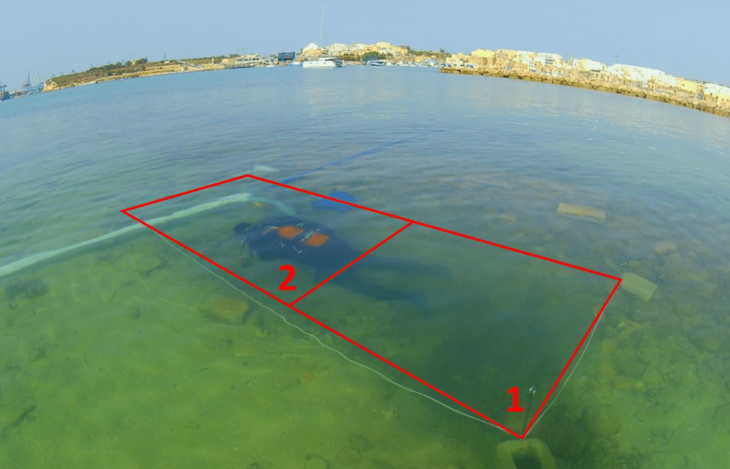
A recent underwater exploration off the coast of Colombia has uncovered compelling new evidence that may confirm the identity of one of the most legendary shipwrecks in maritime history — the 18th-century Spanish galleon San José.
The study, published in the journal Antiquity, details how researchers used a remotely operated vehicle (ROV) to investigate a wreck believed to be the San José, a royal treasure ship sunk in 1708 during a battle with the British Navy. The galleon was transporting an enormous cargo of silver, gold, and other precious goods from the Americas to Spain when it went down in the Caribbean Sea.
The Royal Treasure Fleet and the San José
Between the 1500s and 1700s, Spain operated powerful treasure fleets that ferried riches from its colonies in the Americas back to Europe. One such fleet, the Tierra Firme Fleet, linked Spain with modern-day Colombia and Peru. Its flagship, the San José, held a monopoly on transporting royal wealth and was considered one of the most important vessels in the Spanish colonial fleet system.
The exact location of the San José wreck remained a mystery for centuries — until 2015, when the Colombian government announced the discovery of a possible match off its Caribbean coast. However, a lack of detailed analysis meant its true identity could not be confirmed at the time.
A High-Tech Approach to an Age-Old Mystery
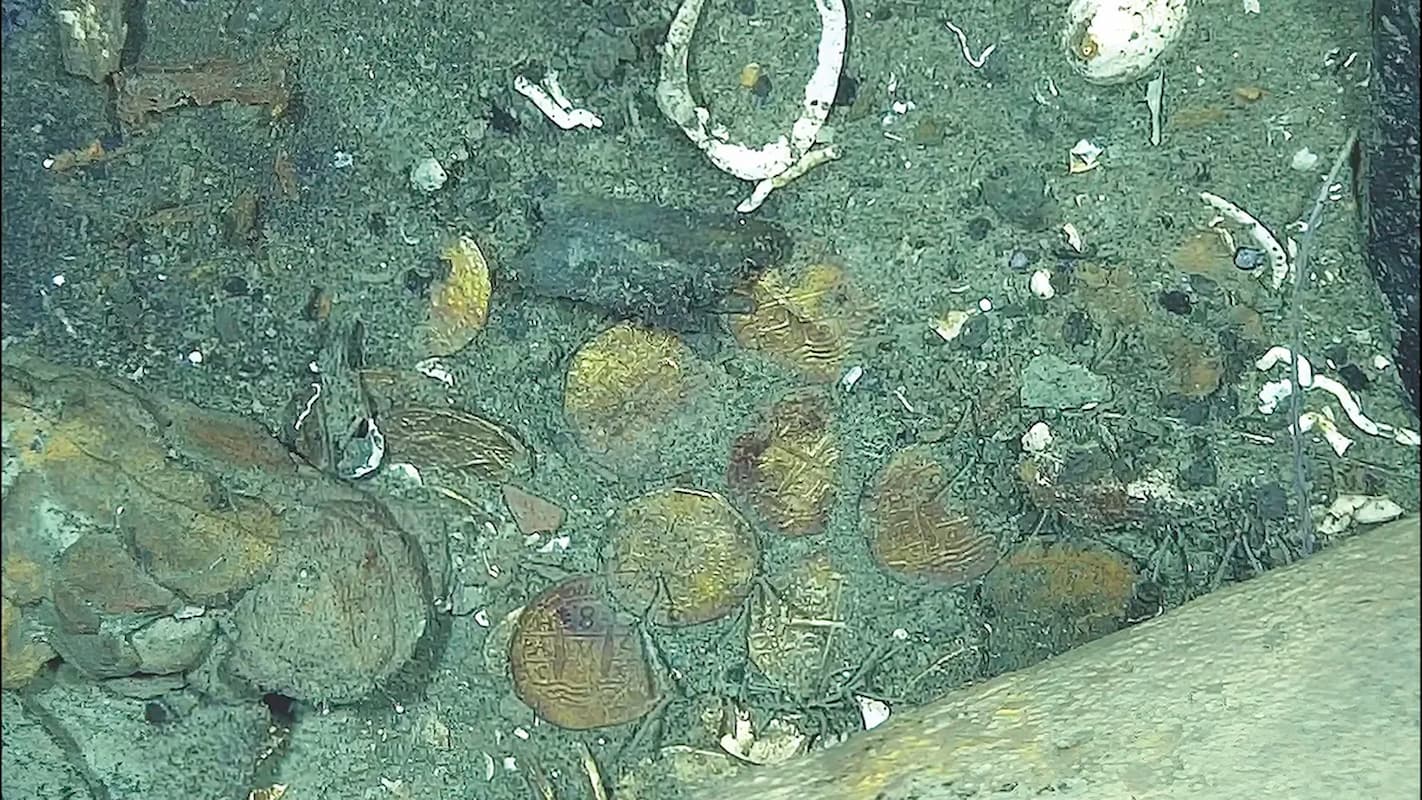
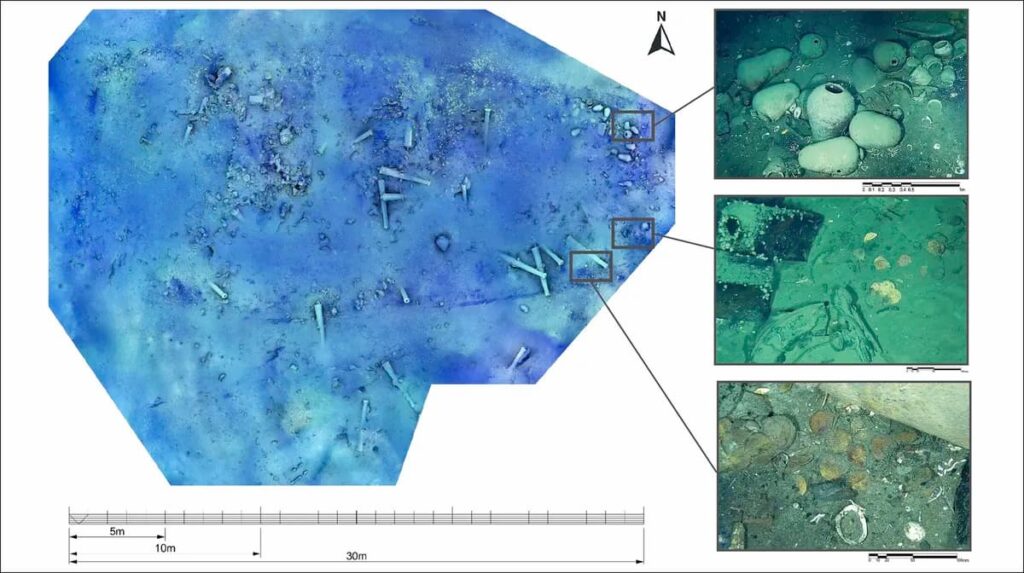
To investigate further, researchers from the Colombian Institute of Anthropology and History (ICANH) and the Admiral Padilla Naval Cadet School deployed a high-resolution ROV to examine the site without disturbing the fragile wreck. The vehicle captured detailed imagery of artifacts, with special attention on coins found scattered around the remains.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
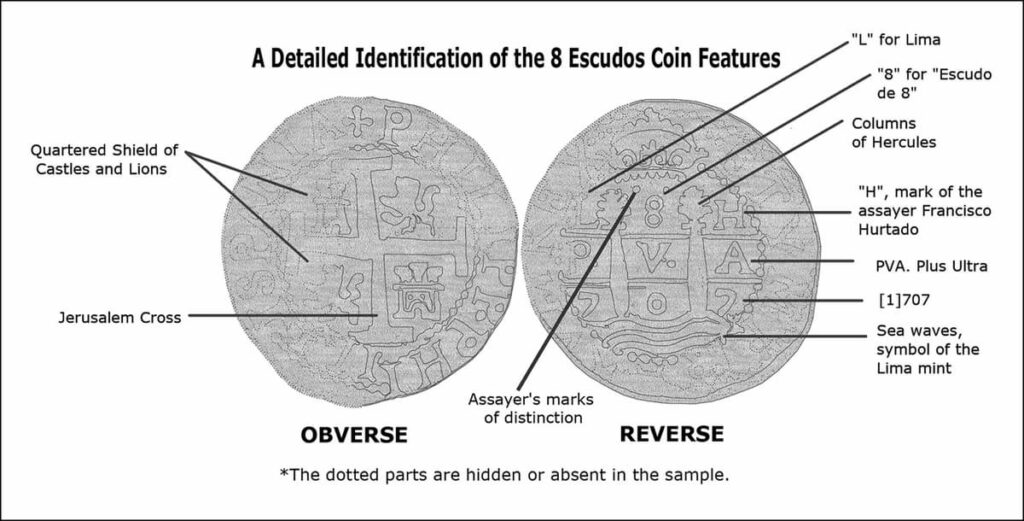
Using advanced photogrammetry techniques, the team created 3D reconstructions of the coins — known as macuquinas, crude hand-hammered coins widely used in Spanish America. These coins bore mint marks and heraldic symbols that indicated they were produced in 1707 at the Lima Mint in present-day Peru.
This precise dating is crucial. “The ship could not have sunk before 1707 if the coins minted that year were onboard,” explained lead researcher Daniela Vargas Ariza. Historical documents confirm that the San José was transporting silver from Peru to Spain in 1708, aligning perfectly with the artifacts’ origin.
Closer Than Ever — But Not a Final Confirmation
While the findings strongly support the theory that the wreck is indeed the San José, researchers caution that the evidence is not yet conclusive. “Coins are key chronological markers, especially in shipwreck contexts,” Vargas Ariza emphasized. Still, further analysis is needed to rule out alternative possibilities and definitively confirm the vessel’s identity.
The discovery underscores not only the technological advances in underwater archaeology but also the enduring historical significance of colonial-era shipwrecks. As the investigation continues under the guidance of the Colombian government, the world watches in anticipation for final confirmation of one of the greatest shipwreck mysteries in history.
Vargas Ariza, D., Jaramillo Arango, A., Aldana Mendoza, J. A., Del Cairo Hurtado, C., & Sarmiento Rodriguez, J. D. (2025). The cobs in the archaeological context of the San José Galleon shipwreck. Antiquity, 1–6. doi:10.15184/aqy.2025.10095