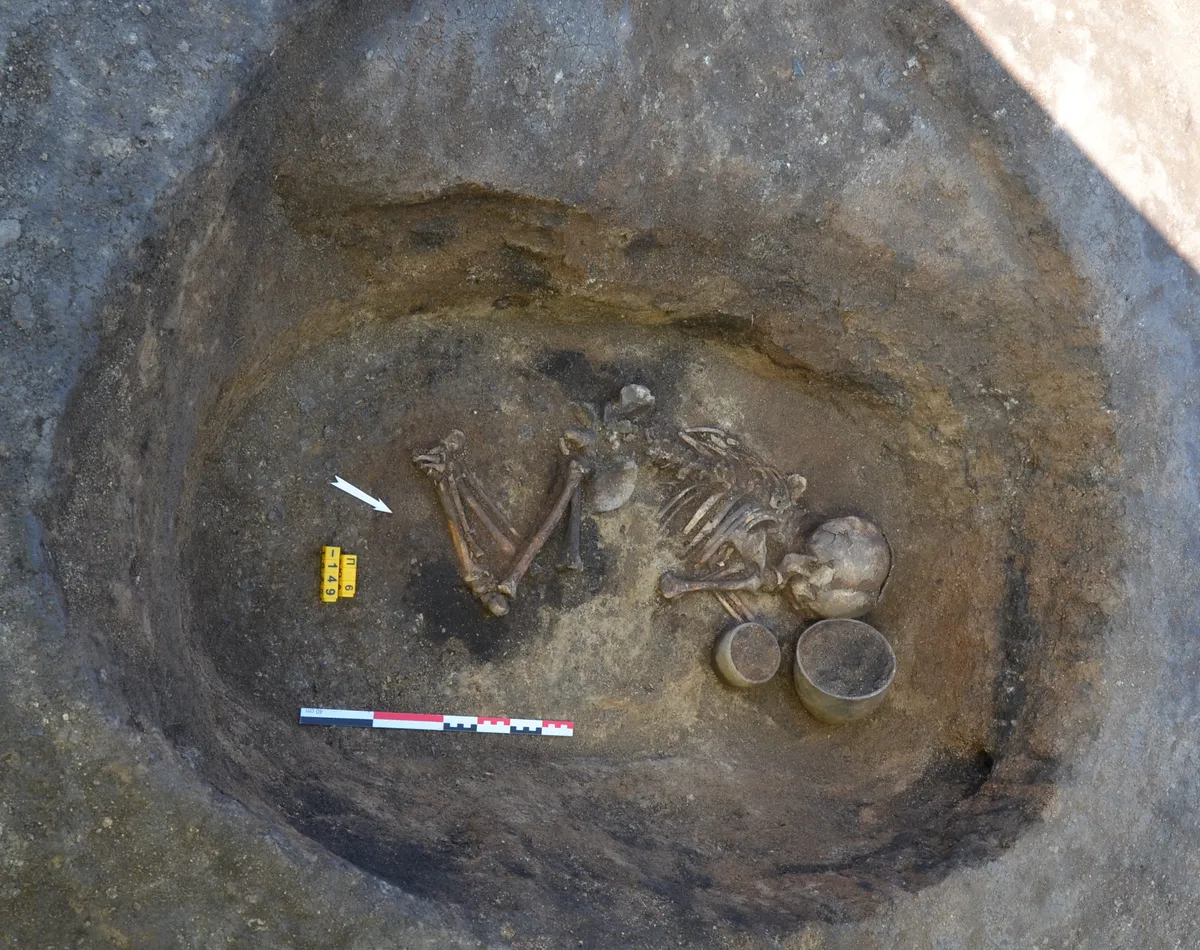
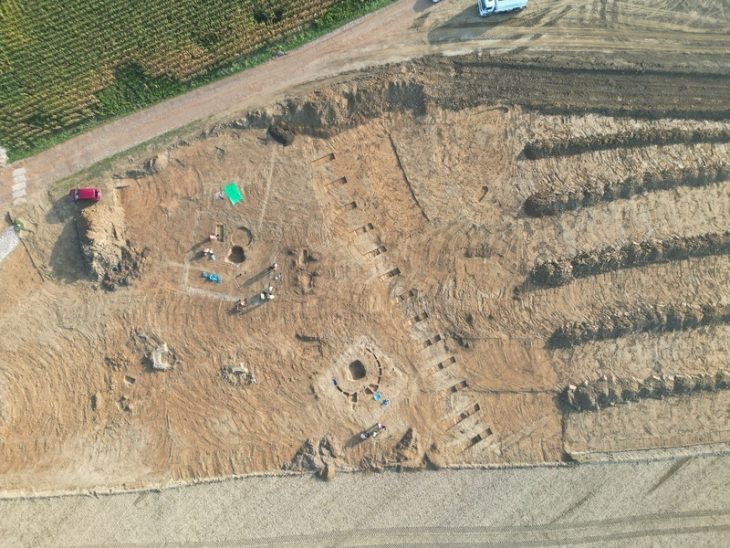
A Bronze Age family living 3,800 years ago in the Southern Urals may have taken a flexible approach to marriage, with most men allowed only one wife while a select few enjoyed the company of multiple women. Researchers discovered that the oldest of six brothers had the luxury of a second wife after analyzing the genomes of 32 ancient relatives who were all interred in the same burial mound.
32 individuals from a burial site in the southern Ural region show close kinship relations / Only women came from other areas
Researchers Jens Blöcher and Joachim Burger from Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz (JGU) have analyzed the genomes of skeletons from an extended family from a Bronze Age necropolis in the Russian steppe. The 3,800-year-old Nepluyevsky burial mound was excavated several years ago and is located on the geographical border between Europe and Asia. Using statistical genomics, the family and marriage relationships of this society have now been deciphered.
The kurgan (burial mound) investigated was the grave of six brothers, their wives, children and grandchildren. The presumably oldest brother had eight children with two wives, one of whom came from the Asian steppe regions in the east. The other brothers showed no signs of polygamy and probably lived monogamously with far fewer children.
Fascinating snapshot of a prehistoric family
“The burial site provides a fascinating snapshot of a prehistoric family,” explains Blöcher, lead author of the study. “It is remarkable that the first-born brother apparently had a higher status and thus greater chances of reproduction. The right of the male firstborn seems familiar to us, it is known from the Old Testament, for example, but also from the aristocracy in historical Europe.”
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
The genomic data reveal even more. Most women buried in the kurgan were immigrants. The sisters of the buried brothers, in turn, found new homes elsewhere. Burger, senior author of the study, explains, “Female marriage mobility is a common pattern that makes sense from an economic and evolutionary perspective. While one sex stays local and ensures the continuity of the family line and property, the other marries in from the outside to prevent inbreeding.”
The genomic diversity of the prehistoric women was higher than that of the men
Accordingly, the Mainz population geneticists found that the genomic diversity of the prehistoric women was higher than that of the men. The women who married into the family thus came from a larger area and were not related to each other. In their new homeland, they followed their husbands into the grave. From this the authors conclude that in Nepluyevsky there was both “patrilineality,” i.e., the transmission of local traditions through the male line, and “patrilocality,” i.e., the place of residence of a family is the place of residence of the men.
“Archaeology shows that 3,800 years ago, the population in the southern Trans-Ural knew cattle breeding and metalworking and subsisted mainly on dairy and meat products,” comments Svetlana Sharapova, archaeologist from Ekaterinburg and head of the excavation, adding, “the state of health of the family buried here must have been very poor. The average life expectancy of the women was 28 years, that of the men 36 years.”
In the last generation, the use of the kurgan suddenly stopped and almost only infants and small children were found. Sharapova adds, “it is possible that the inhabitants were decimated by disease or that the remaining population went elsewhere in search of a better life.”
Multiple partners and many children for the putative firstborn son
“There is a global connection between different family systems and certain forms of life-style and economy,” says Blöcher. “Nevertheless, human societies are characterized by a high degree of flexibility.” He adds, “in Nepluyevsky, we find evidence of a pattern of inequality typical of pastoralists: multiple partners and many children for the putative firstborn son and no or monogamous relationships for most others.”
The authors find additional genomic evidence that populations genetically similar to Neplujevsky society lived throughout most of the Eurasian steppe belt. Burger comments, “It is quite possible that the local pattern we found is relevant to a much larger area.” Future studies will show to what extent the “Neplujevsky” model can be verified at other prehistoric sites in Eurasia.
The study was carried out in cooperation with archaeologists from Ekaterinburg and Frankfurt A.M. and was published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz
Cover Image credit: Svetlana Sharapova
















