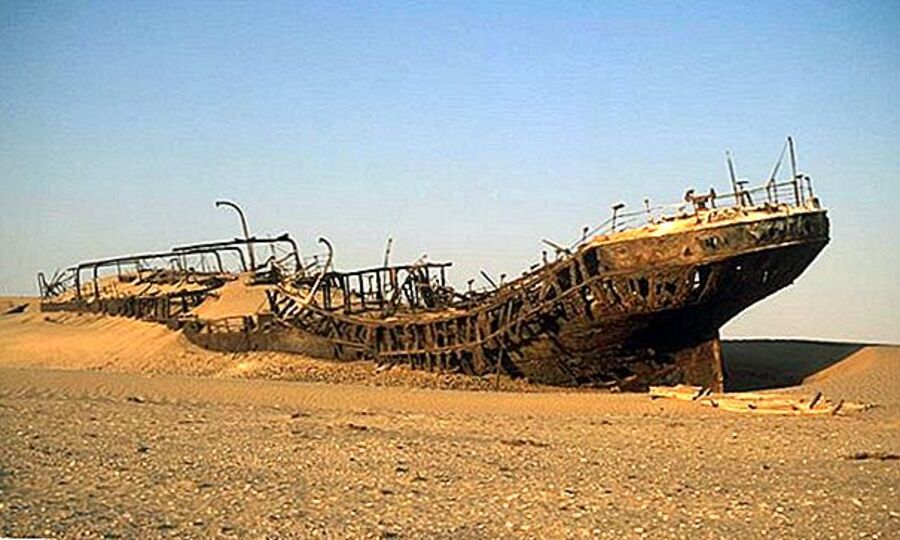
In a remarkable archaeological discovery, the Bom Jesus (The Good Jesus), a Portuguese ship that sank over 500 years ago, has been found in the desert of Namibia, revealing a treasure trove of gold coins and other valuable artifacts. The ship, which set sail from Lisbon on March 7, 1533, was lost at sea during a violent storm while en route to India.
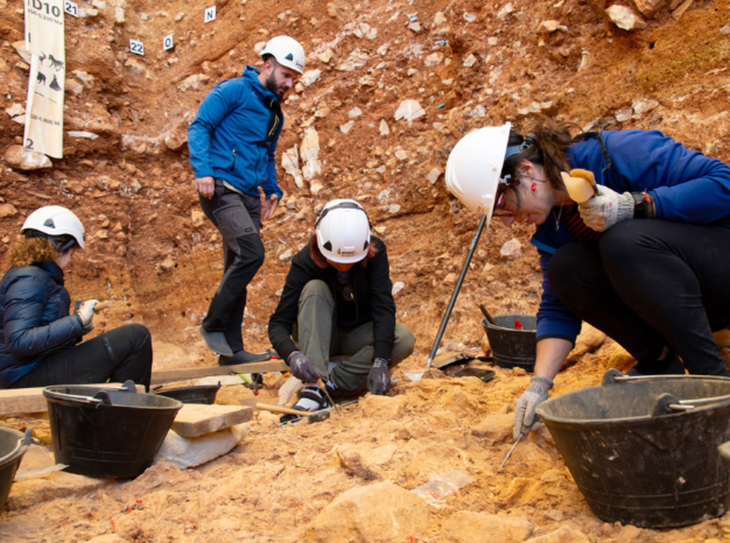
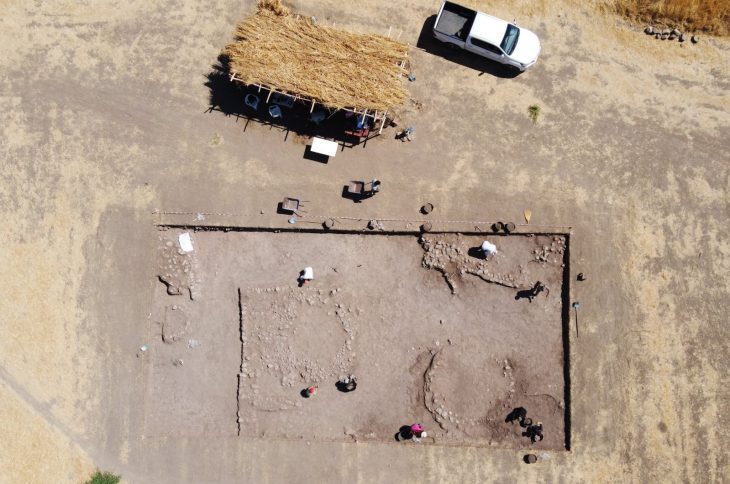
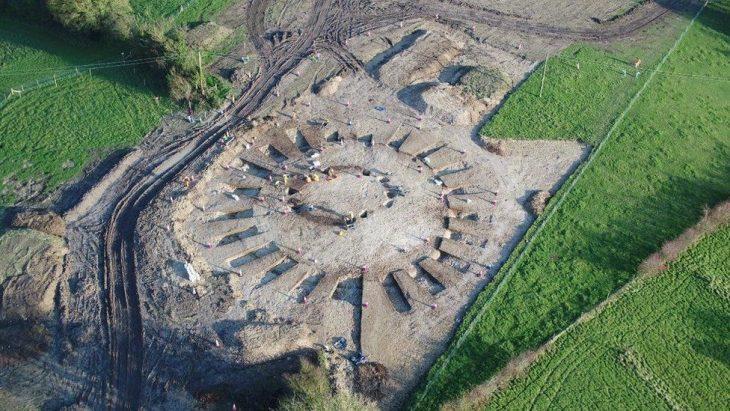
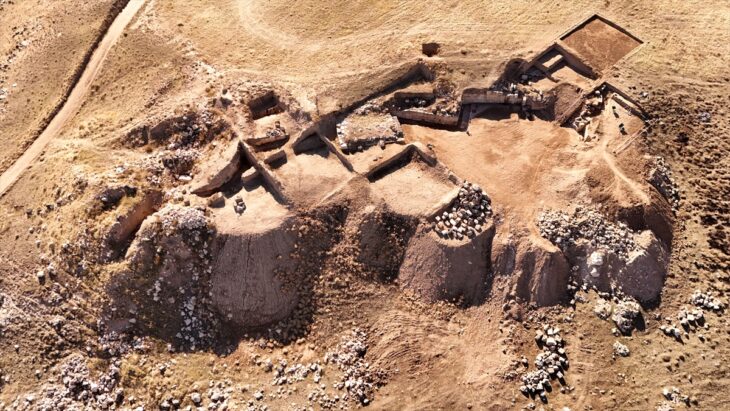
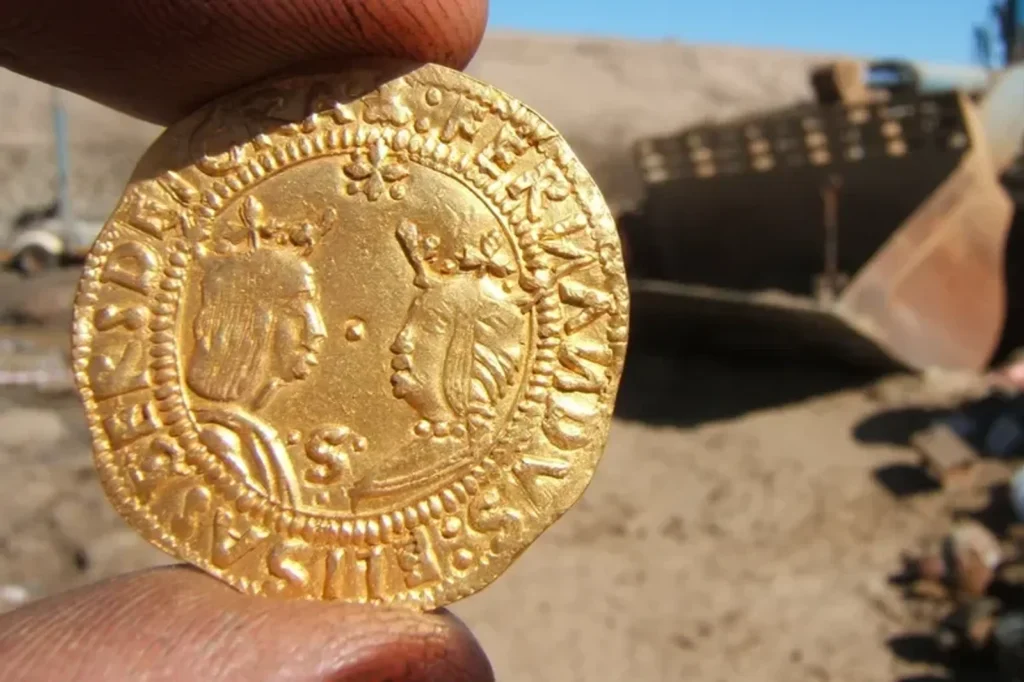
The remains of the Bom Jesus were uncovered in 2008 by diamond miners who were conducting operations near the Namibian coast. The shipwreck, which had been hidden beneath the sands for centuries, contained approximately 2,000 gold coins and tens of thousands of pounds of copper ingots, all remarkably well-preserved. This discovery has not only shed light on the maritime history of the era but also on the trade routes that were vital for the Portuguese Empire.
Dr. Dieter Noli, chief archaeologist at the Southern Africa Institute of Maritime Archaeological Research, noted that the coastline is notorious for storms, making the discovery of a shipwreck unsurprising. However, the find was particularly significant when a treasure chest filled with gold coins was unearthed, confirming the ship’s identity as the Bom Jesus. The coins, which date back to the early 16th century, provide invaluable insights into the economic conditions and trade practices of the time.

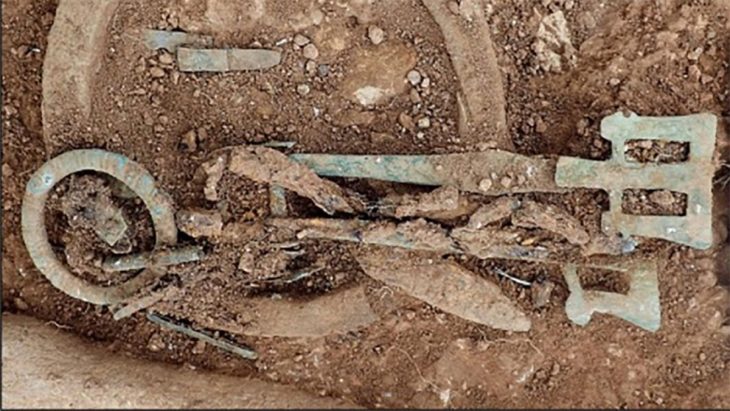
Further excavations revealed an array of artifacts, including bronze bowls, cannons, navigational instruments, and even a musket estimated to be over 500 years old. The ship’s cargo also included silver coins and elephant tusks, highlighting the extensive trade routes of the time. These findings suggest that the Bom Jesus was not just a vessel for transporting goods but also a crucial part of the larger narrative of exploration and commerce during the Age of Discovery.
Experts believe the Bom Jesus sank after being pulled too close to shore during a storm, causing it to collide with a rock and capsize. As the coastline receded over the centuries, the ship re-emerged in the desert, where it was eventually discovered. The preservation of the ship and its cargo is attributed to the unique environmental conditions of the Namibian desert, which have protected the artifacts from the ravages of time.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Despite the significant value of the find, the Namibian government retains ownership of the ship and its contents, as it was classified as a “ship of state” belonging to the King of Portugal. However, the Portuguese government has generously allowed Namibia to keep the treasure. This decision reflects a spirit of cooperation and mutual respect between the two nations, emphasizing the importance of cultural heritage.
Today, the Bom Jesus stands as the oldest and most valuable shipwreck ever discovered off the western coast of Sub-Saharan Africa, with ongoing discussions about the potential establishment of a museum to showcase the remarkable artifacts recovered from this historic site. Such a museum would not only serve as a tribute to the ship’s storied past but also as an educational resource for future generations, highlighting the rich maritime history of the region.
Cover Image Credit: The Bom Jesus was laden with treasures like gold and copper ingots. Public Domain