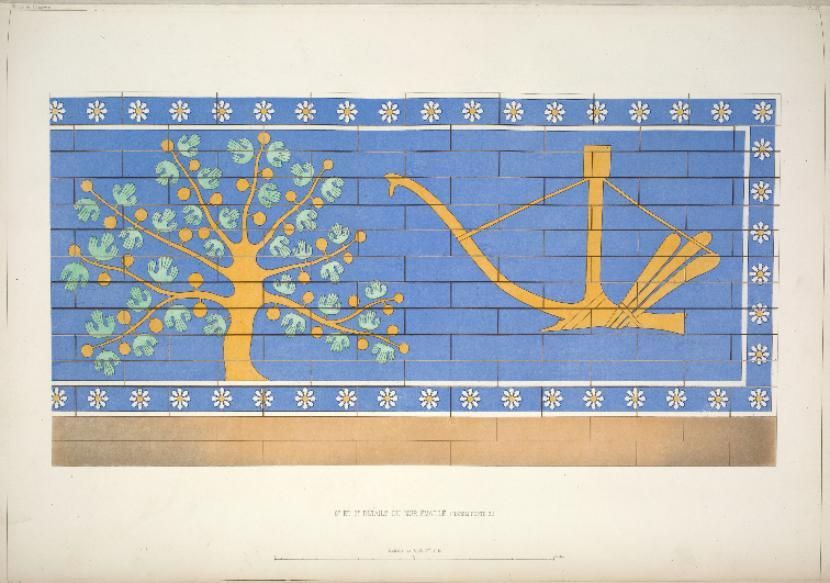
A new interpretation of a set of temple symbols that have puzzled scholars for more than a century has been put forth by an Assyriologist. The ancient symbols, found in a 2,700-year-old temple in the city of Dur-Šarrukin in present-day Khorsabad, Iraq, include a lion, an eagle, a bull, a fig tree and a plough.
The ancient city of Dūr-Šarrukīn, meaning “fortress of Sargon” was home to King Sargón II, ruler of Assyria from 721-704 BCE. He was revered as a great king who established the Sargonid Dynasty, which lasted for an additional century before the collapse of the Neo-Assyrian Empire. He was a patron of the arts and especially enjoyed erecting monuments.
The ancient symbols tend to appear in the same sequence consisting of a lion, eagle, bull, fig tree and a plough and these symbols were prominently displayed on temples throughout the ancient city. French excavators who visited the site at the end of the 19th century were the ones who first documented and shared them with the public.
Since their rediscovery, many researchers have attempted to interpret their meaning. Some believe they are like Egyptian hieroglyphs, some sort of expression of imperial power, or may even spell out the king’s name. But how these connections could be made remained a conundrum.
An Assyriologist from Trinity College Dublin named Dr. Martin Worthington has offered a convincing analysis of these symbols that has the potential to completely change our perception of ancient Mesopotamian iconography.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
In his recent article in the Bulletin of the American Schools of Oriental Research, Dr. Worthington put forth a groundbreaking hypothesis: the sequence of five symbols may spell out Sargon’s name (šargīnu), while also representing specific constellations.
“The study of ancient languages and cultures is full of puzzles of all shapes and sizes, but it’s not often in the Ancient Near East that one faces mystery symbols on a temple wall,” Dr. Worthington explained in a statement.
What is more, according to Dr Worthington, each of the five symbols can also be understood as a constellation. Thus, the lion represents Leo, and the eagle Aquila (our own constellations are largely inherited from Mesopotamia, via the Greeks, so many of them are the same). The fig-tree stands in for the hard-to-illustrate constellation ‘the Jaw’ (which we don’t have today), on the basis that iṣu ‘tree’ sounds similar to isu‘jaw’.

“The effect of the five symbols, was to place Sargon’s name in the heavens, for all eternity – a clever way to make the king’s name immortal. And, of course, the idea of bombastic individuals writing their name on buildings is not unique to ancient Assyria…”
Although Dr. Worthington admits that his theory cannot be proven beyond a reasonable doubt, the fact that it holds true for both the longer three-symbol sequence and the five-symbol sequence suggests it is more than just a coincidence.
As he noted, the chances of such a connection being accidental are, quite literally, “astronomical”.
Cover Photo: Late 19th-century drawings of the eagle and bull symbols published by French excavator Victor Place. From New York Public Library.