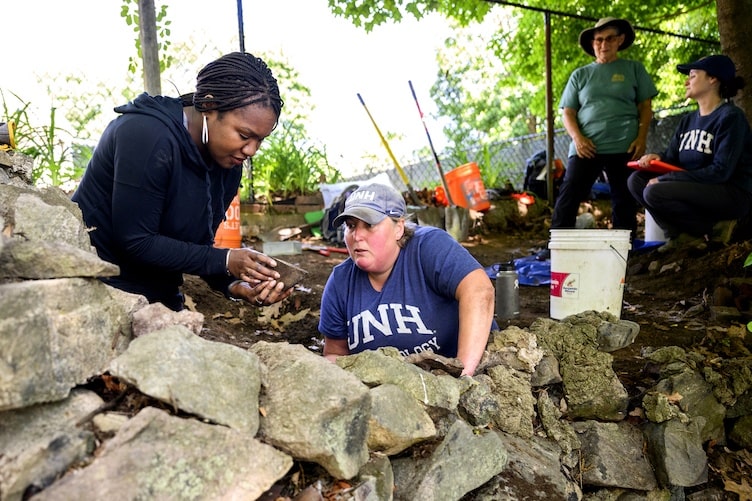
Archaeologists from the University of New Hampshire (UNH) and a historian from Northeastern University believe they might have found the home of a leader in New England’s Black community dating back to the 1700s. King Pompey was an enslaved African who gained his freedom and became one of the first Black property owners in colonial New England.
Pompey Mansfield’s home has been a historical enigma. The find, which is situated near the Saugus River, may offer a unique window into the life of this well-known esteemed community leader.
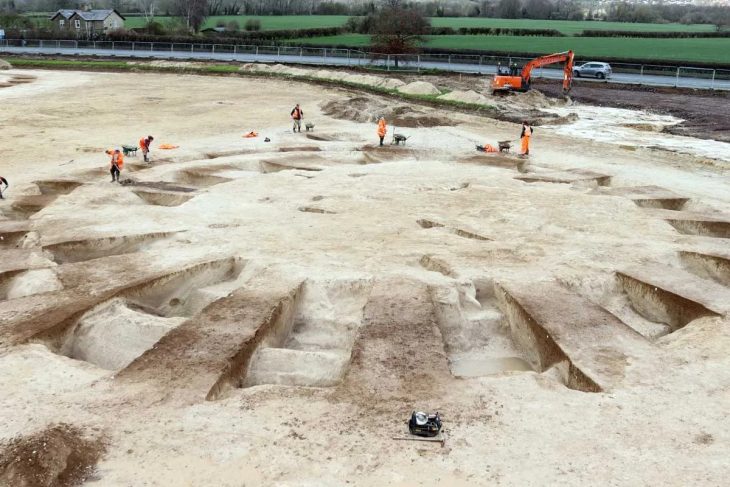
The archeologists said they spent months before the dig trying to pinpoint where “King” Pompey Mansfield lived more than 260 years ago.
Archaeologists at the University of New Hampshire and Kabria Baumgartner, dean’s associate professor of history and African studies at Northeastern University worked together to locate Pompey’s homestead, where he lived with his wife Phylis (or Phebe) over 260 years ago.
“We are thrilled,” said Meghan Howey, professor of anthropology and director of the University of New Hampshire’s Center for the Humanities. “I’m extremely confident this is a foundation from the 1700s and everything that points to this being the home of King Pompey is very compelling.”
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
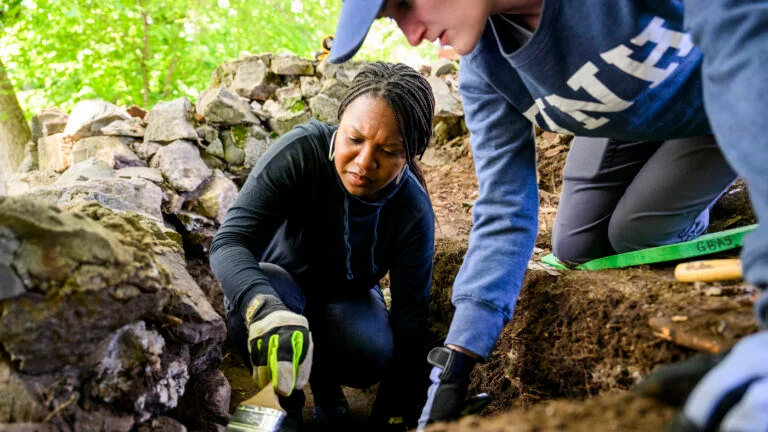

Historical accounts show that Pompey hosted free and enslaved Blacks on Black Election Day, one of the most important days in the colonial era for Black people in New England. On this day, Pompey was elected “king” annually. Whoever was elected king could later be called on to handle matters in the Black community.
The event was documented as lively and joyful with dancing and singing based on their West African traditions. It was held on the same day that white men voted for their leaders. The highlight of the day was voting for and crowning a king, who could later be called on to handle important matters in the Black community. Similar celebrations took place throughout New England and the rest of the Americas, including states like New Hampshire, Rhode Island, and Connecticut.
The archaeological team, which included community historian Diane Fiske from UNH’s Great Bay Archaeological Survey and archaeologist Alyssa Moreau, spent months combing through deeds, public records, and genealogical records in order to determine the location. In order to pinpoint the location and identify particular landmarks, they cross-referenced historical newspapers and probate records with modern LIDAR-derived topographic maps.
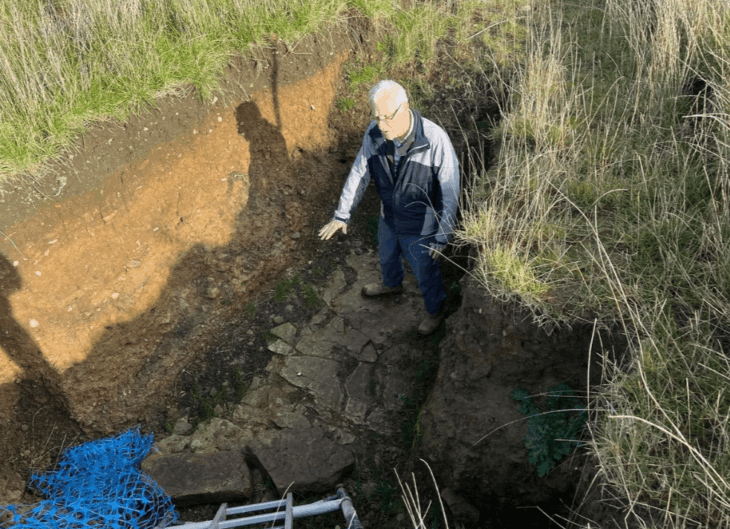
In a trench that was four feet deep, the team uncovered a foundation that was constructed of river rocks as described in the documentation. They had to dig through layers of several different eras of newer foundations covering the 1700s structure to reveal it. Below the trash, concrete and mortar, the team discovered a layer of smaller, smooth stones from the nearby tidal river that had been chiseled and layered so they fit together. All point to something that someone with limited resources would have done at the time to build a home.
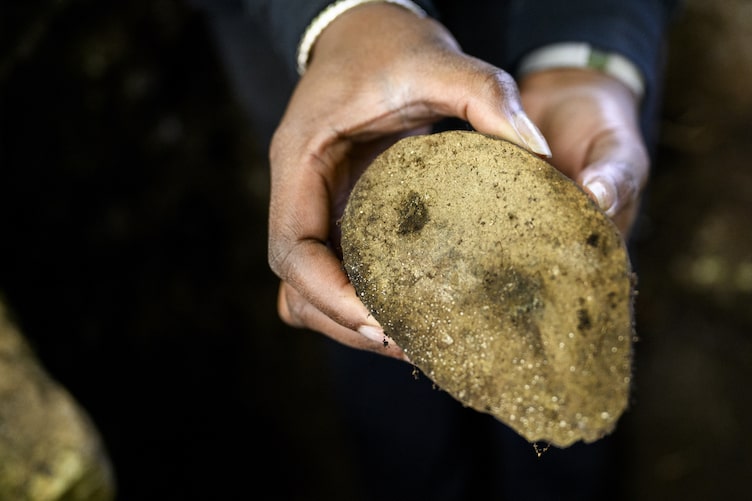

“The big find was the handmade pebble foundation without quarry rock,” said Meghan Howey, professor of anthropology and director of the University of New Hampshire’s Center for the Humanities “That showed determination and ingenuity. And then the compelling match of the historical descriptions, the bend in the river, marshy meadow, oak trees. While not everything in history is written down, or even written down correctly, when it comes to what people leave behind, they don’t edit their trash.”
“I’ve always been fascinated by those fleeting private and intimate moments outside of the watchful eye of an enslaver when Black people could be themselves and enjoy each other and be in community,” said Kabria Baumgartner. “It’s rare for me to get a chance to be on the site of a discovery and thanks to Meghan and her team’s archeological work we get a better sense of King Pompey’s world. It was just as described, serene and peaceful.”
Researchers are hopeful to eventually work with the National Park Service to establish a historical marker about King Pompey and do more outreach and exhibits that share the story and the figures of Black Election Day.
Cover Photo: Left to right, Kabria Baumgartner, Northeastern University historian, and Meghan Howey, University of New Hampshire archaeologist, at the dig site of what archaeologists believe is the home of King Pompey. Photo: Matthew Modoono/Northeastern University.