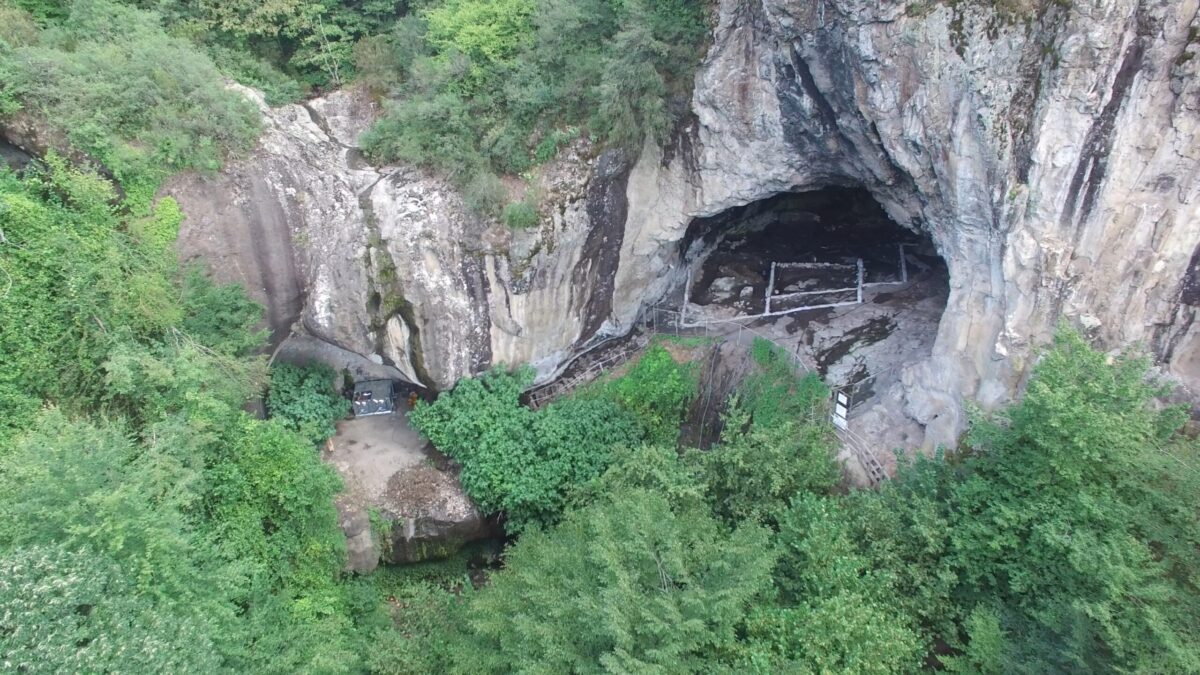
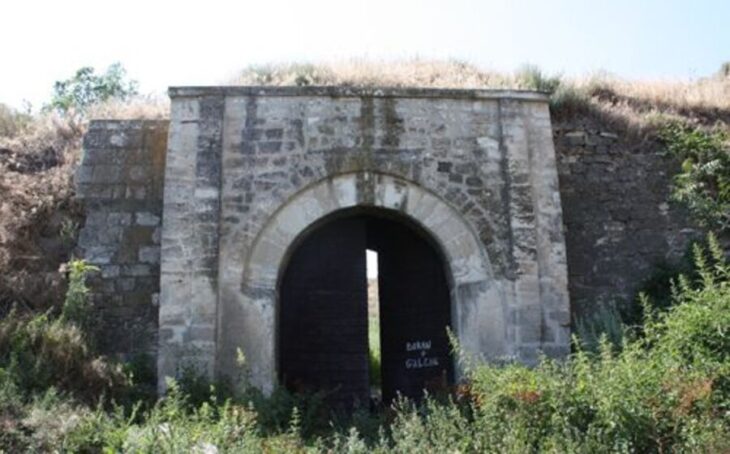
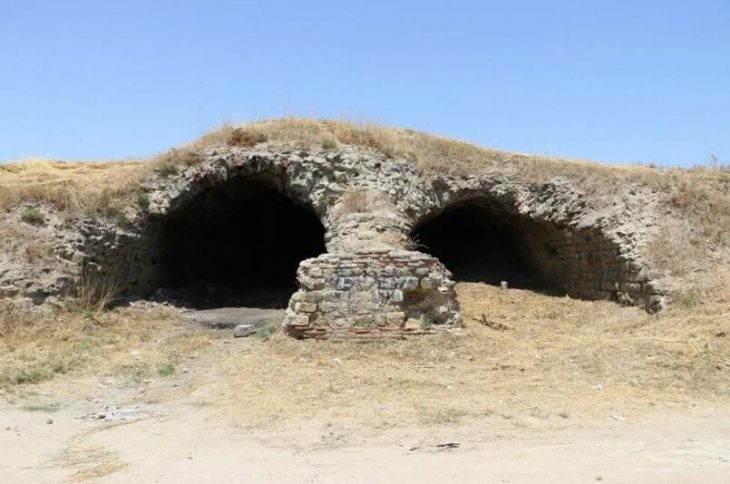
In the course of the excavations conducted by Zonguldak Bülent Ecevit University‘s Department of Archaeology, artifacts from the Late Bronze Age that are connected to the Kaska, a lost Anatolian community, were uncovered in İnönü Cave in Alacabük village in the Ereğli district of Zonguldak, northern Türkiye.
The Kaska – also known as the Kaskans, Gagsa, and Kaskia – were an ancient Anatolian people who inhabited the remote valleys between the northern border of the Hittite kingdom and the Black Sea. They did not construct cities and lacked a written language. They are only known from Hittite accounts, which portray them as pig farmers and linen weavers.
The Hittites came into conflict many times with this ethnic group to the northeast of their empire. The Kaska leveraged their mountainous and densely forested territory along the southern Black Sea coast to outsmart one of the most formidable civilizations in the world. The holy Hittite cities of Nerik and Zalpa were overrun by the Kaska, who migrated down from their mountain homes around 1400 BC. Despite this fact, extraordinarily little is known about the Kaska.
Findings from the third layer of the cave, which dates to the Late Bronze Age, may provide the first archaeological proof of this mysterious group, according to Hamza Ekmen, an associate professor at Bülent Ecevit University and the excavation’s scientific adviser.

“We propose that the findings in this layer, linked to the period of 1650 to 1200 B.C., may be associated with the Kaskas, a lost community of ancient Anatolia,” Ekmen explained.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
The İnönü cave, believed to be the western Black Sea’s oldest settlement, has yielded evidence of continuous human habitation dating back 6,500 years to the Chalcolithic Age. Artifacts from five different settlement periods were found in the cave, including items related to the Hittites, a powerful civilisation of the Late Bronze Age.
“Ancient Hittite kings, from Hattusili I to Suppiluliuma II, documented the Kaskas as raiders who pillaged cities, temples, and settlements during periods of Hittite vulnerability. They even seized Nerik, a key religious city dedicated to the storm god,” Ekmen said.
Despite over a century of Hittitology research, concrete evidence of Kaska habitation has remained elusive. “The Kaskas have always been a central question for scholars studying Hittite archaeology. Although their existence is frequently referenced in cuneiform texts, no settlement linked to them has ever been conclusively identified — until now,” he added.
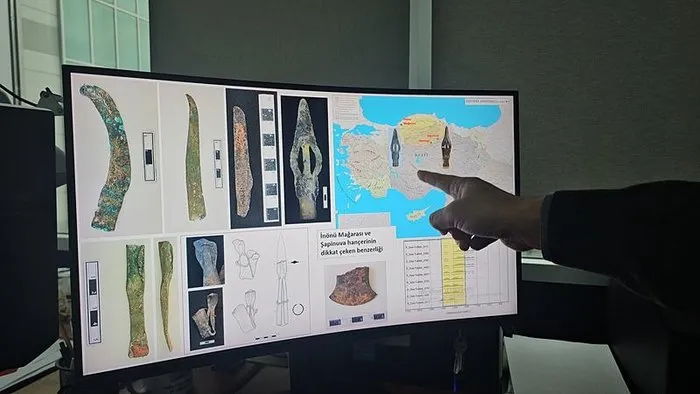
“The cave’s location and the lifestyle it suggests closely align with the geographical descriptions of Kaska territories in Hittite texts,” Ekmen noted. Artifacts from the Cave’s third layer bear striking similarities to Hittite-era objects but differ in context, suggesting a unique cultural identity.
In addition to a dagger that is identical to one discovered in the Hittite city of Şapinuva and seal stamps that resemble Hittite designs, the team discovered wooden platforms that were probably used as storage or living areas, as well as a variety of metal, clay, and bone artifacts.
“The combination of these artifacts offers compelling clues that Inönü Cave may be the first archaeological site linked to this enigmatic group. These discoveries provide a critical foundation for future research into their history,” he said.
Excavations in İnönü Cave, which has been taken under protection, continue. The studies are very important in terms of shedding light on the life of this mysterious people of Anatolia.
Cover Image Credit: DHA
















