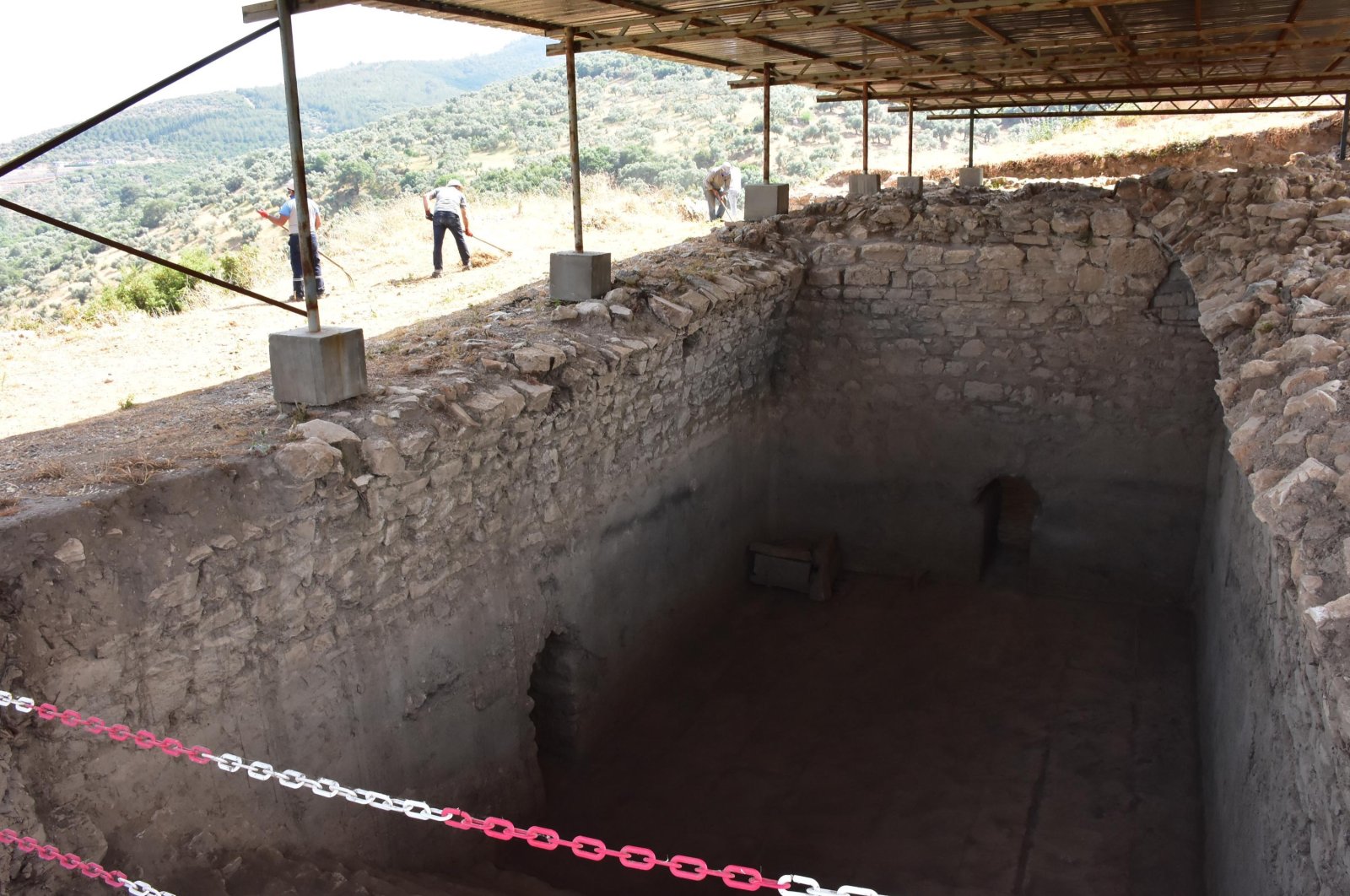
In the ancient city of Metropolis, in western Turkey, in the province of Izmir, something that played an important role in the lives of the people of the ancient city was unearthed: cisterns.
The ancient city of Metropolis, also known as the “City of Mother Goddess” has been a treasure mine for archaeologists since 1990, when excavations began. From the first settlements in the Late Neolithic Age through the Classical Age, from the Hellenistic Age through the Roman, Byzantine, and Ottoman periods, they have found signs of many civilizations.
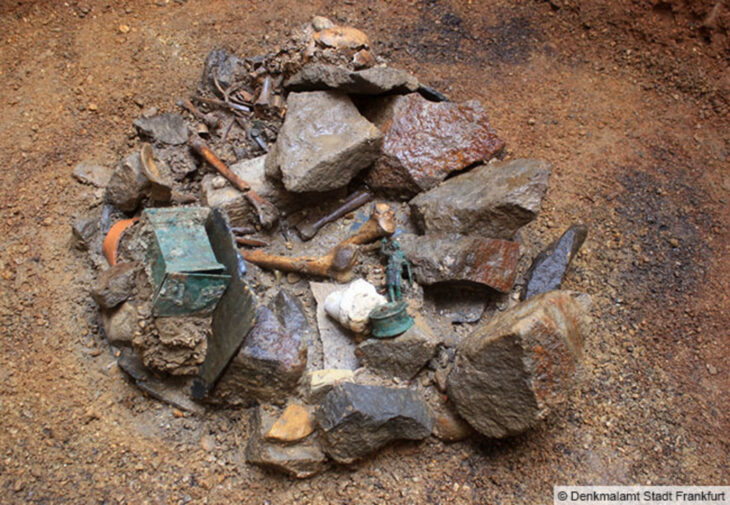
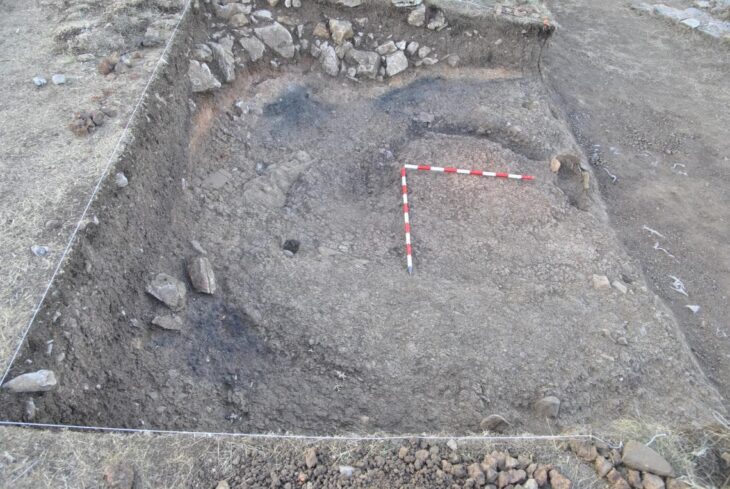
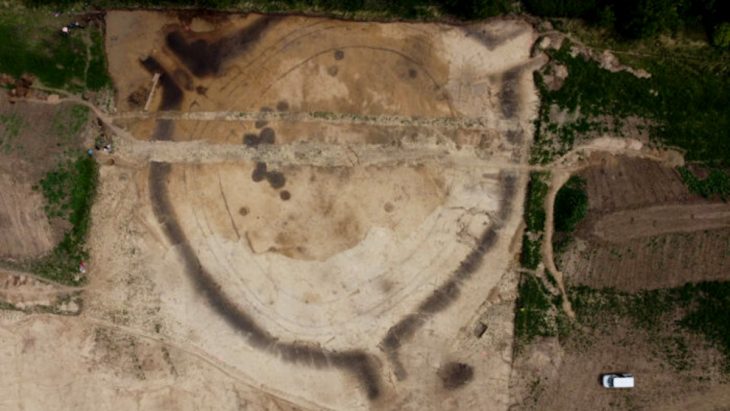
Four interconnected cisterns were discovered during last year’s excavations in the ancient city, which revealed many massive monuments. Two cisterns were discovered behind a 7-meter (23-foot) earth fill in this construction.
The construction, which is assumed to have been utilized to fulfill the city’s water demands during the Late Roman Period, will help to uncover vital information, discoveries, and historical items from the time.
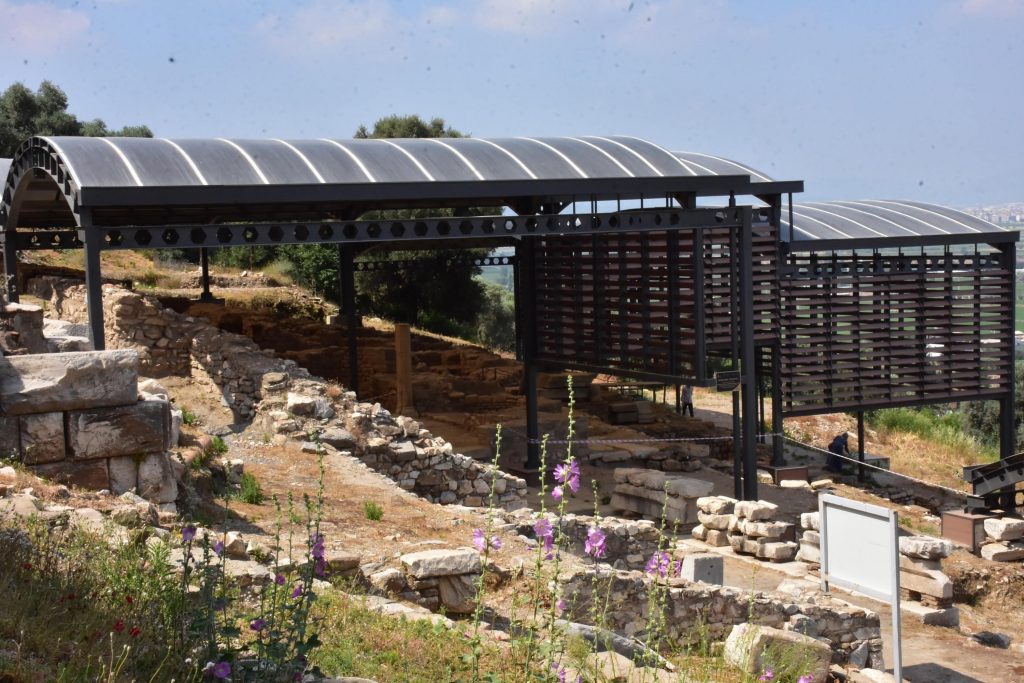

Professor Serdar Aybek of Manisa Celal Bayar University’s archeology department, who is the head of the excavation team, explained the importance of the cisterns for the ancient city. “(The city) has a deep-rooted history dating back to prehistoric times. The region has had fertile lands since prehistoric times. It has the fertility brought by the Küçük Menderes River. It is a region that has always been settled.”
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
“The city we are standing on now has been inhabited since the Hellenistic period. It was developed as a planned city. With the growth of the population in the Roman period, new buildings were built. The cistern structure we are in now was built to meet the water needs in the Roman period. It gives us important information about the period in terms of water engineering,” Aybek told Demirören News Agency (DHA).
“It is a structure built in the Roman period. It is located at the highest level of the city, which we call the Acropolis. Therefore, they are able to transfer the water collected in the acropolis to places on the lower slopes of the city more easily.”
“The cisterns have a capacity of about 600 tons of water,” he said. “We aim to reveal the remaining two parts with our (archaeological) work this year and bring this well-preserved and unique structure to cultural tourism.”