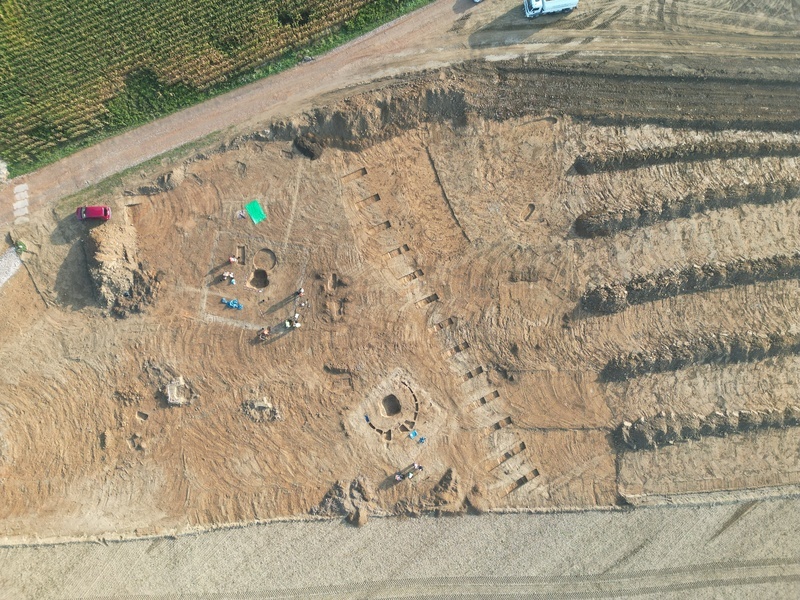
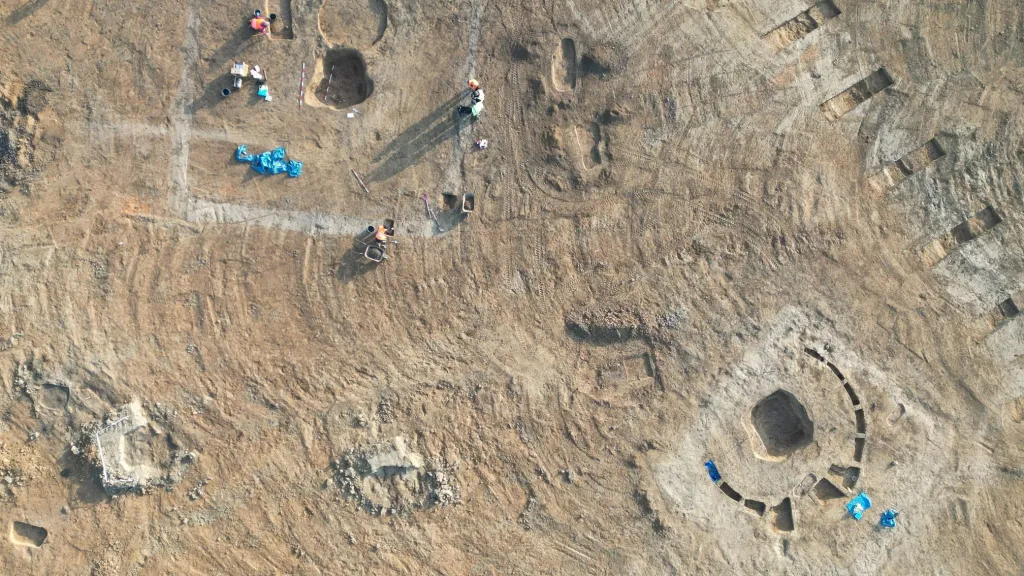
Archaeologists have uncovered the Nitra culture’s largest Bronze Age burial site near Olomouc in Central Moravia, during their rescue research on the future D35 motorway route between Krelov and Neredin.
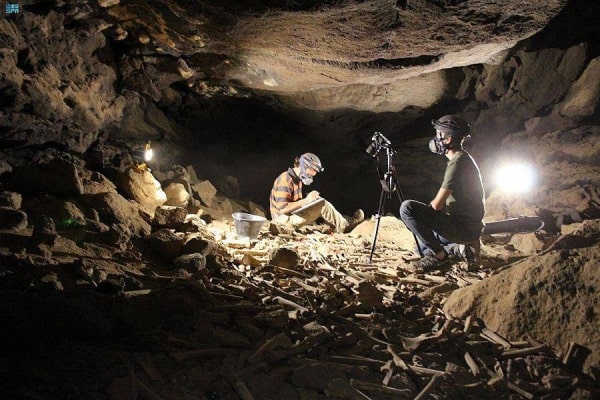
Representatives of the Olomouc Archaeological Centre told the Czech News Agency (CTK) that the biggest discovery of the research was the large burial site of the Nitra culture, which inhabited eastern Moravia and southwestern Slovakia during the Middle Bronze Age (2100-1800 BC). Archaeologists found 130 graves, making the site the largest from this culture.
The Old Bronze Age in Moravia is represented by two cultural groups, the Únětice culture and the Nitra group.
Nitra Culture belongs to the oldest cultures of the Bronze Age in Moravia and its representatives are characterized by the gradual introduction of bronze production, an alloy of already used copper with tin, which resulted in a metal of better strength and hardness.
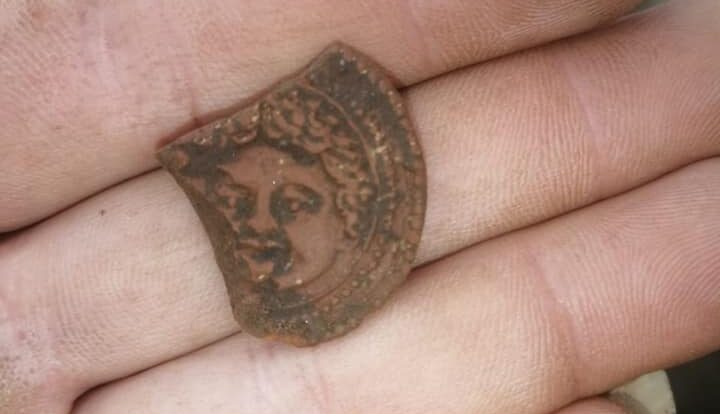
The graves contained skeletal remains and burial gifts, such as copper ornaments, bone beads, stone arrows, copper rings and bone awls, said archaeologist Vendula Vranova, the head of the research team.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!

Men and women were buried in different positions and were accompanied by different objects. Men, for example, were given boar tusks and hunting tools, while women had jewelry and antler beads in their graves, she added.
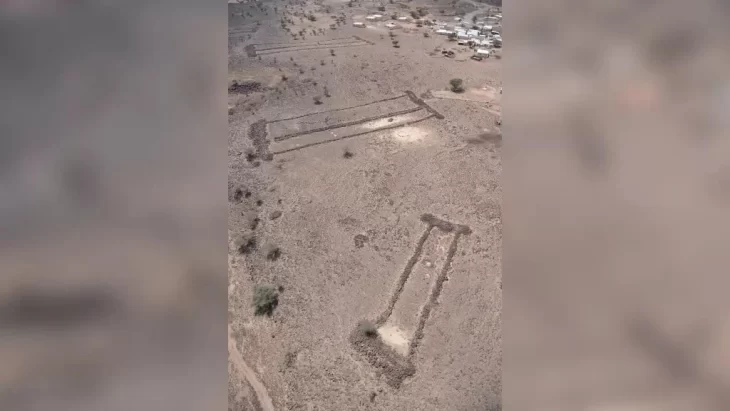
Additionally, a burial site of the Corded Ware culture (2600 BC) was discovered by archaeologists. It contained 17 skeletal graves, four of which appeared to be those of men who were interred with axes, flint tools, and ceramic vessels. Furthermore, the graves were surrounded by circular grooves that were most likely remnants of wooden structures that divided the surrounding area from the burial site’s sacred space.
The graves of the Nitra and Corded Ware cultures were intriguing, according to the experts, despite the wealth of discoveries, because they had not tampered with one another.
The archaeologists at the site in Krelov identified four different burial periods. “The area was used for burial purposes for more than 3,000 years, from the end of the Late Stone Age until the 9th century, when the Slavic population lived here on the territory of the Great Moravia state,” added Nikola Orlitova, spokeswoman for the center.
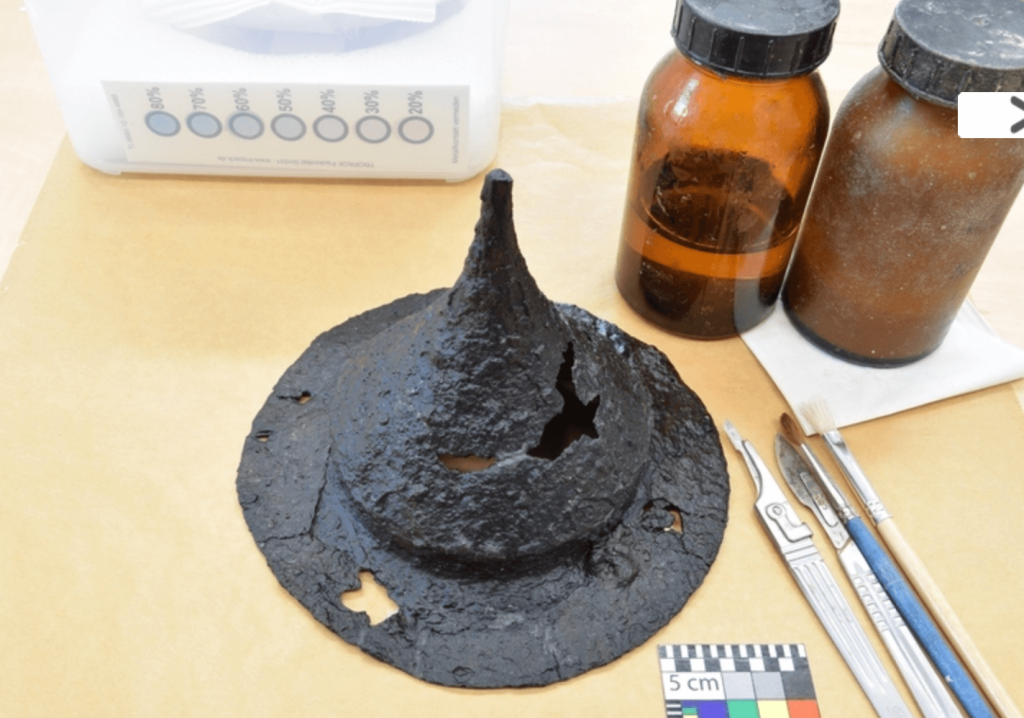

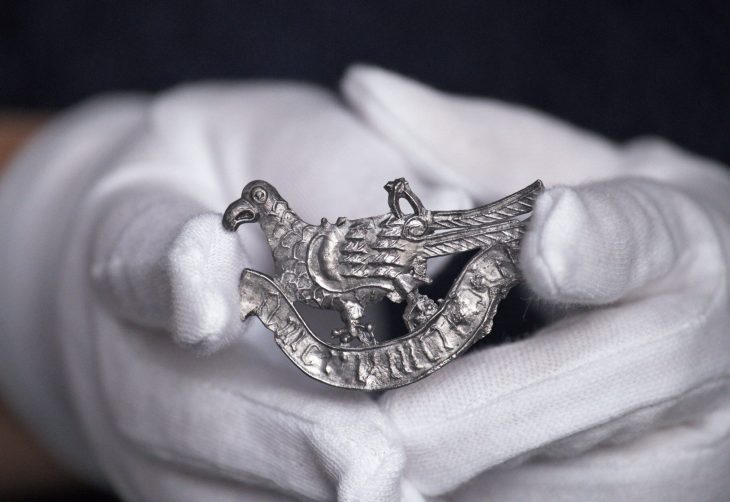
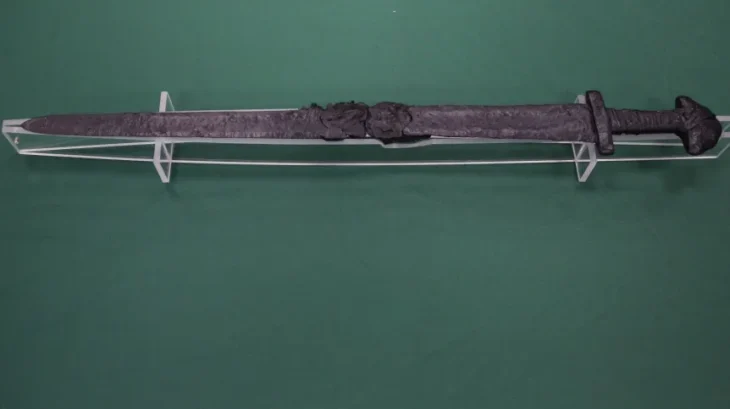
Researchers also uncovered seven cremation graves at the burial site, where they found typical metal jewelry associated with the Celts. The grave of a Germanic warrior with a shield and an iron spear from the third century is also noteworthy, as it is the first of its kind in Central Moravia.
From August 2023 to April 2024, an archaeological rescue excavation was conducted along the D35 route in the area between Krelov and Slavonin. The skeletal remains and artifacts that were discovered will now be examined. As a result, experts will have more information about residents’ physical characteristics, health, nutrition, and genetic relationships.
Cover Image Credit: Olomouc Archaeological Centre