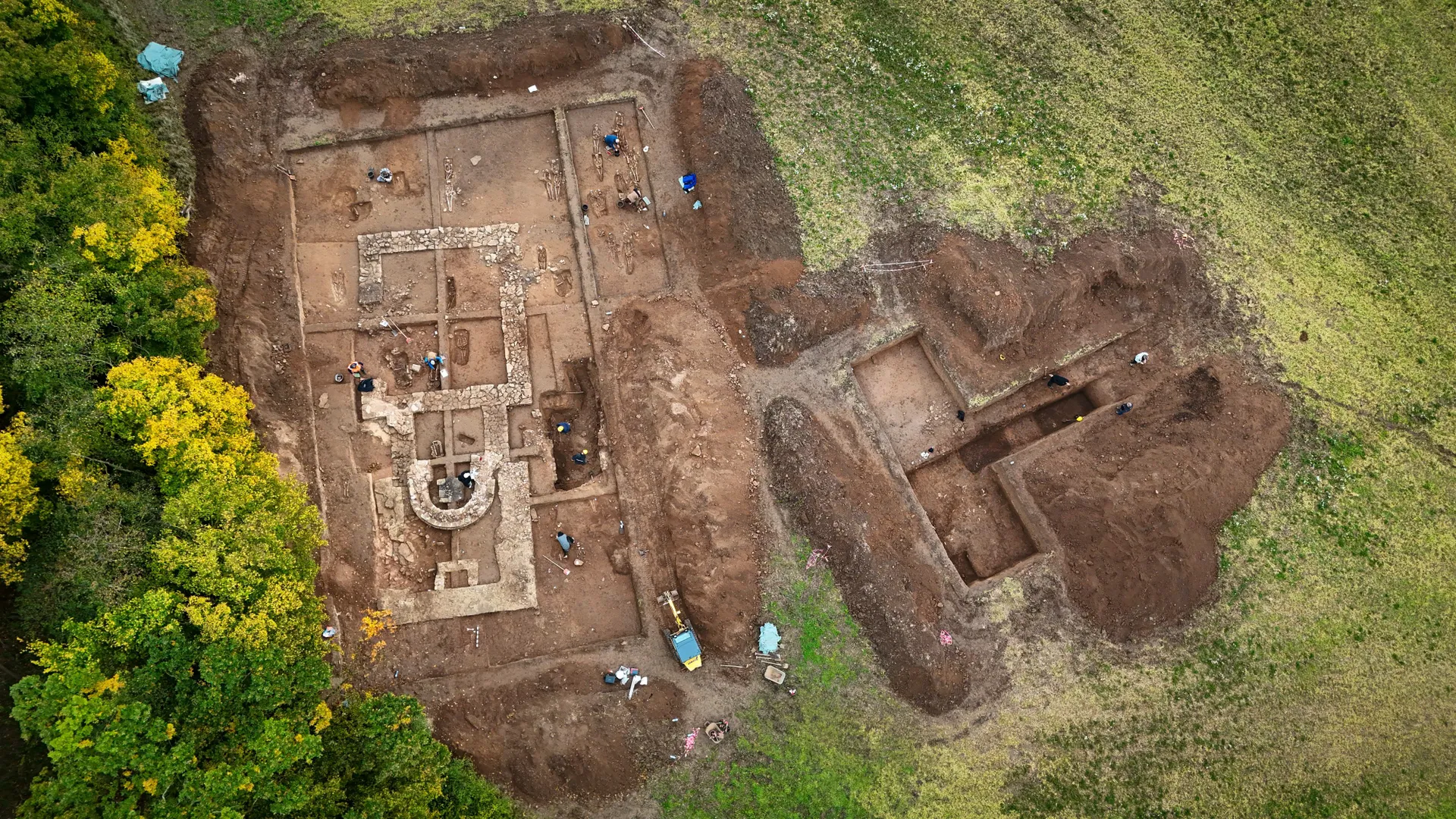
Archaeologists in Saxony-Anhalt in Germany have uncovered around 1,000 medieval artifacts and more than 50 graves, including those of children buried in places where rainwater once streamed down the walls of a church. Researchers believe this placement was intentional — a spiritual act rooted in the medieval belief in a “holy water effect” that could grant salvation to unbaptized infants.
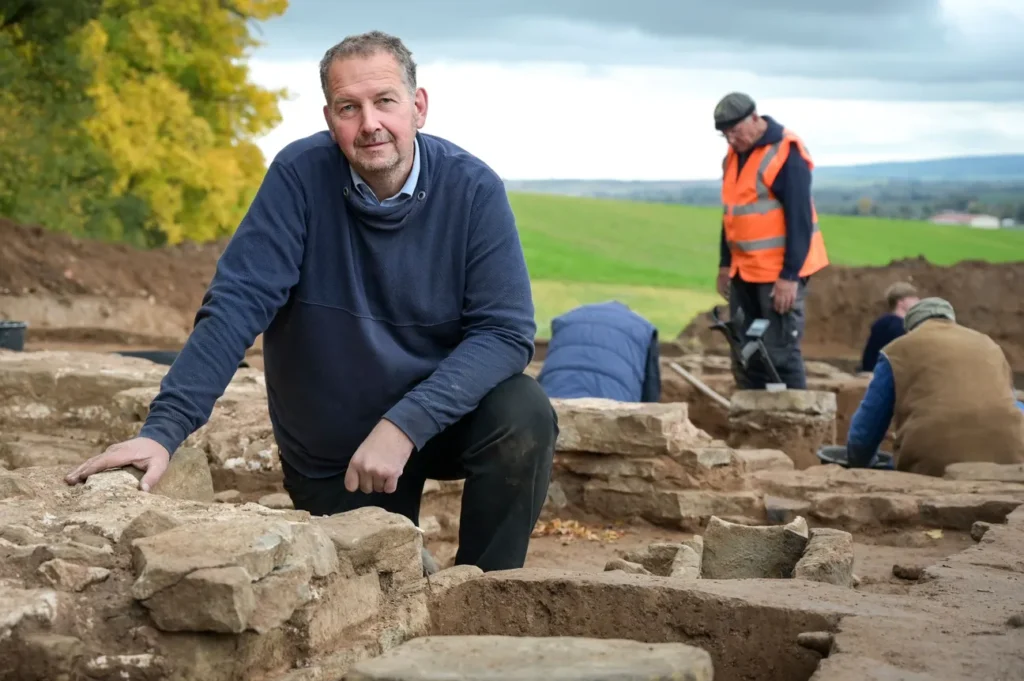
The discoveries were made at the site of the former Mallerbach Chapel, near the town of Allstedt in the Mansfeld-Südharz district. Led by Felix Biermann from the State Office for Heritage Management and Archaeology of Saxony-Anhalt, the excavation has revealed remarkable insights into a long-forgotten church, its community, and a deeply emotional side of medieval faith.
A Chapel with a Tumultuous Past
According to Biermann, the Mallerbach Chapel was built in the 12th century and underwent several transformations over the centuries — first serving as a village church, later as a roadside chapel, and eventually becoming a pilgrimage site.
But its story ended violently. On March 24, 1524, during the early waves of the Peasants’ War, the chapel was looted and burned by citizens from nearby Allstedt, likely influenced by the revolutionary sermons of theologian Thomas Müntzer. The attack on Mallerbach is now viewed as one of the earliest signs of the uprisings that swept through central Germany in the 16th century.
The recent excavation was part of the commemorative project “Gerechtigkeyt – Thomas Müntzer & 500 Years of the Peasants’ War”, which aims to reexamine this turbulent period through archaeological evidence.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
1,000 Finds: Coins, Pilgrim Badges, and Weapons
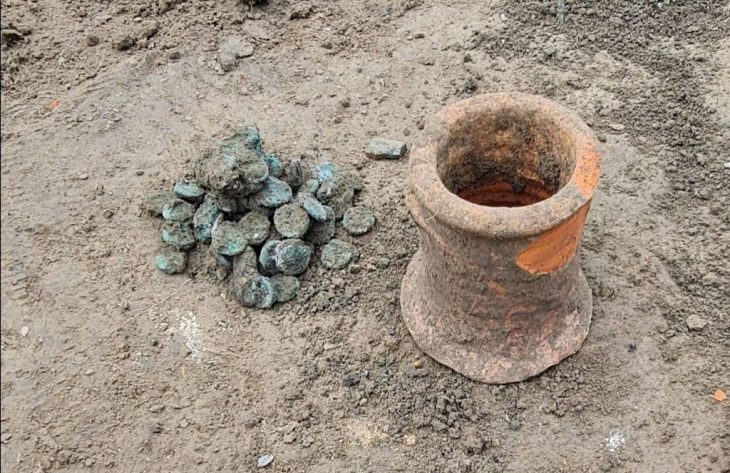
Among the roughly 1,000 objects unearthed were 25 silver coins dating from the 15th and early 16th centuries, pilgrim badges, belt buckles, knives, horseshoes, and a crossbow bolt. Archaeologists also recovered lead bullets, pottery shards, and the remains of building materials that hint at the chapel’s destruction by fire.
Each find contributes to a broader picture of life around the Mallerbach Chapel — from everyday devotion to the violent moments that brought its end.

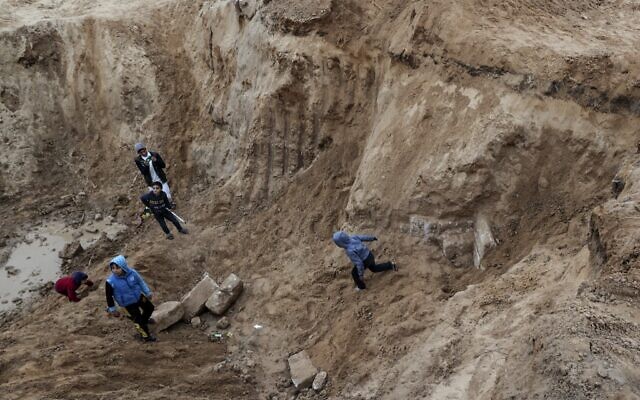
Children Buried Beneath the Rain: The “Holy Water Effect”
Perhaps the most striking discovery lies not in the artifacts but in the graves surrounding the chapel. Researchers uncovered over 50 burials, including around 25 children’s graves concentrated along the church’s eastern wall.
What makes these burials extraordinary is their placement. The graves were found exactly where rainwater had once flowed down from the roof, soaking into the soil below. Archaeologists believe this was no coincidence.
“These children were likely unbaptized, and the faithful may have hoped that the rainwater, touched by the church’s sacred walls, carried a kind of sanctifying power — a holy water effect,” explains project leader Felix Biermann.
In medieval Christian belief, baptism was essential for salvation. Unbaptized infants were thought to remain outside heaven’s grace, a doctrine that caused deep anguish for grieving parents. The placement of these tiny graves suggests that families sought to symbolically baptize their children posthumously through contact with this “sacred” rainwater — a touching intersection of faith, desperation, and hope.
A Glimpse into Medieval Grief and Faith
The emotional weight of these findings is compounded by the discovery of two child burials belonging to a noble family, one of which contained a small yellow clay pot painted in red — a piece of Pingsdorf ware from the 12th century, named after a pottery site in the Rhineland.
Objects like this, left with the dead, are rare glimpses into how families expressed love, protection, and belief in eternal life. Combined with the “holy water effect” burials, they offer a hauntingly intimate view of how medieval people confronted death — especially the death of children — within the framework of their faith.
Traces of a Lost Village
The excavations also revealed remains of the abandoned medieval village of Mallerbach, including the cellar of a house where a church watchman may have lived until the chapel’s destruction in 1524. Written records suggest that the village once hosted annual fairs, indicating a once-thriving settlement that faded by the 14th century, leaving the chapel as its final monument.
From Devotion to Discovery
For the team of archaeologists, the site tells a story that bridges faith, fear, and history. “Every find, every grave, brings us closer to understanding how ordinary people lived and what they believed,” Biermann notes. “The Mallerbach Chapel was not just a building — it was a spiritual focal point for a whole community.”
The artifacts and skeletal remains are now being analyzed in laboratories in Halle (Saale). A public exhibition featuring the finds from Mallerbach is planned for summer 2025 at the State Museum of Prehistory in Halle, where visitors will be able to explore the delicate interplay between faith and mortality that shaped medieval life.
State Office for Heritage Management and Archaeology of Saxony-Anhalt
Cover Image Credit: Heiko Rebsch / dpa