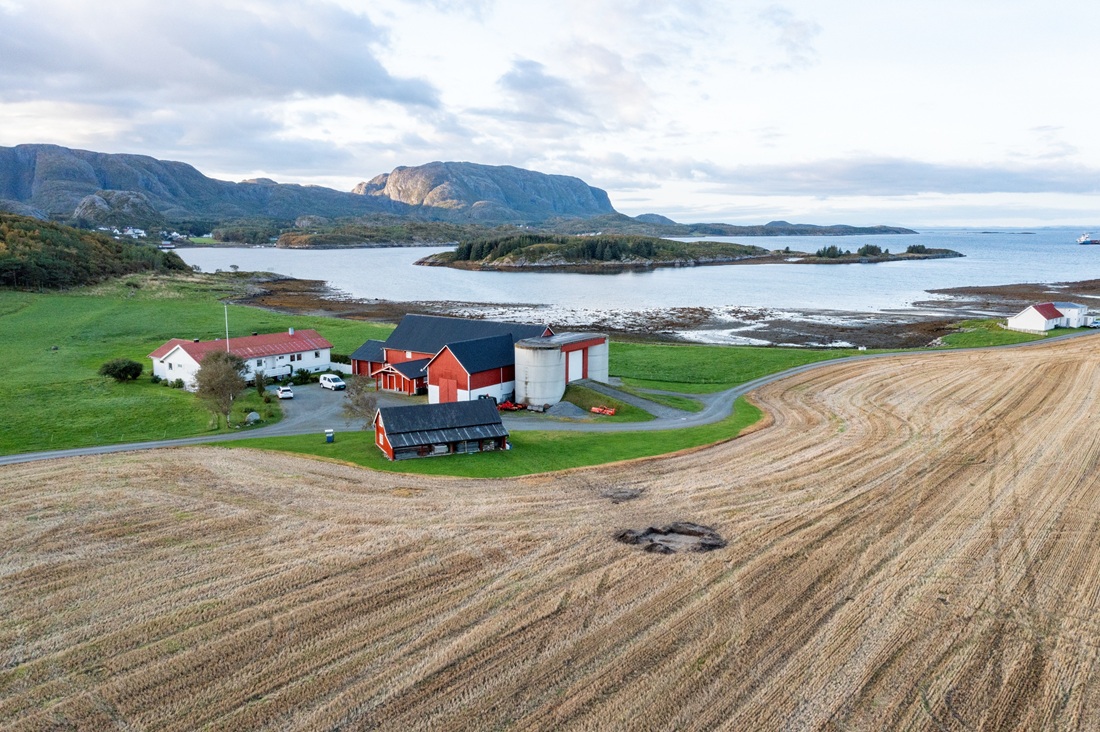
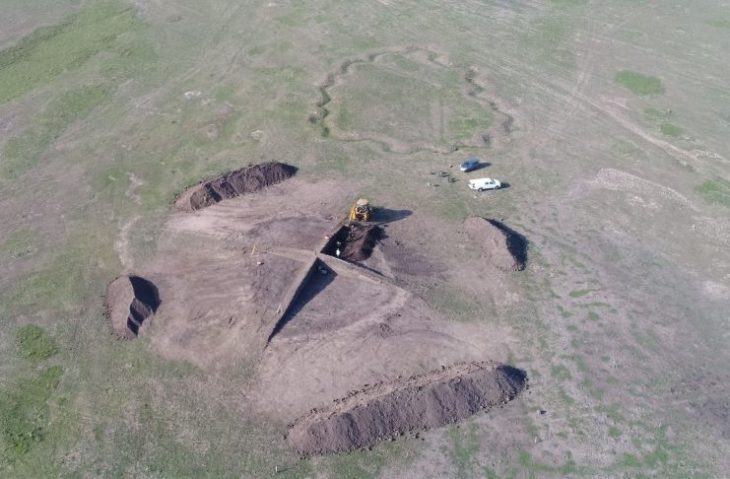
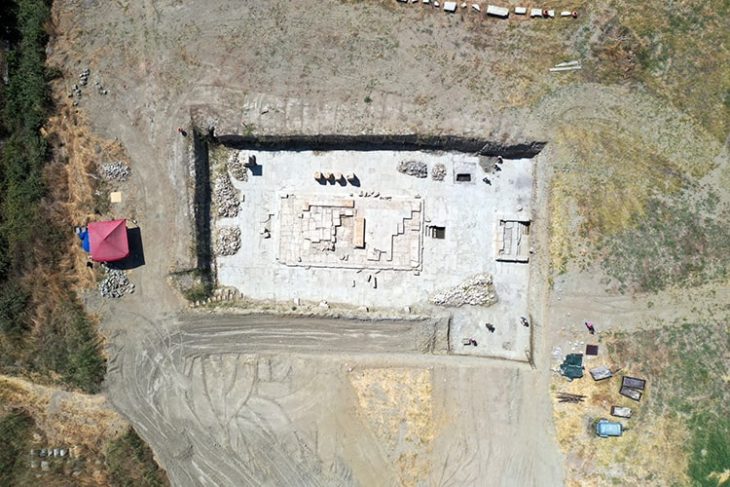
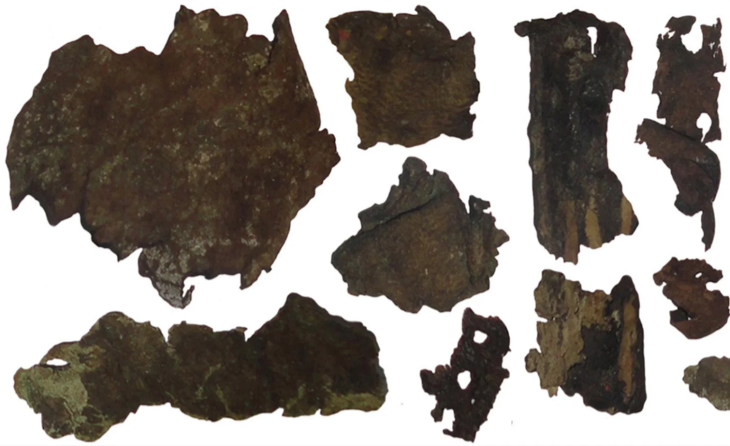
Archaeologists in central Norway have revealed a groundbreaking Viking-age find that has been kept secret for months. At Val in Bjugn, located in the coastal region of Trøndelag, a uniquely preserved grave dating back to the 9th century has come to light — and experts say it challenges long-held assumptions about burial customs in early Scandinavia.
The discovery, made by researchers from the NTNU University Museum in collaboration with Trøndelag County, includes an exceptionally well-preserved skeleton, a rarity in Norway where acidic soil typically destroys human remains. Project leader Raymond Sauvage emphasized the significance of the find in comments shared with Gemini.no, describing the grave as “extraordinary on multiple levels.”
A Viking Woman Buried in Full Dress and Jewelry
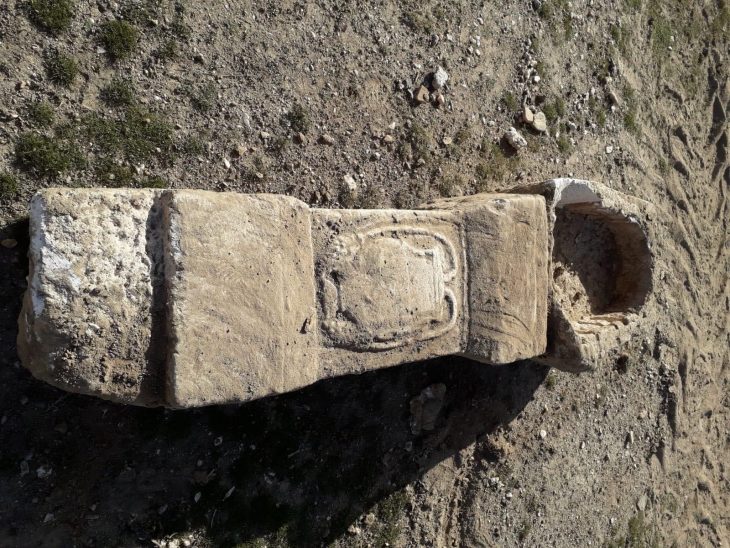
According to archaeologists, the grave likely belonged to a free, married woman who lived on a local farm during the early Viking Age. She was interred wearing a complete set of jewelry and a full traditional dress — a combination rarely found intact after more than a millennium underground.
Among the items documented are a beautifully crafted brooch and several personal adornments that paint a vivid picture of her social status. The burial layout suggests she may have been the husfrue, or lady of the farm, during her lifetime.
But what has truly astonished researchers is a pair of scallop shells placed near the woman’s mouth. Sauvage notes that such a practice is completely unheard of in pre-Christian Scandinavian graves. “We have never seen scallop shells used this way — not in Norway and not elsewhere in Scandinavia,” he told Gemini.no. Similar grave goods only begin appearing 300 to 400 years later, making this placement unusually early and completely unexpected.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Archaeologists are now trying to determine what symbolic or ritual significance the shells may have held. The find opens new gaps — and opportunities — in understanding the spiritual beliefs of early Viking societies.
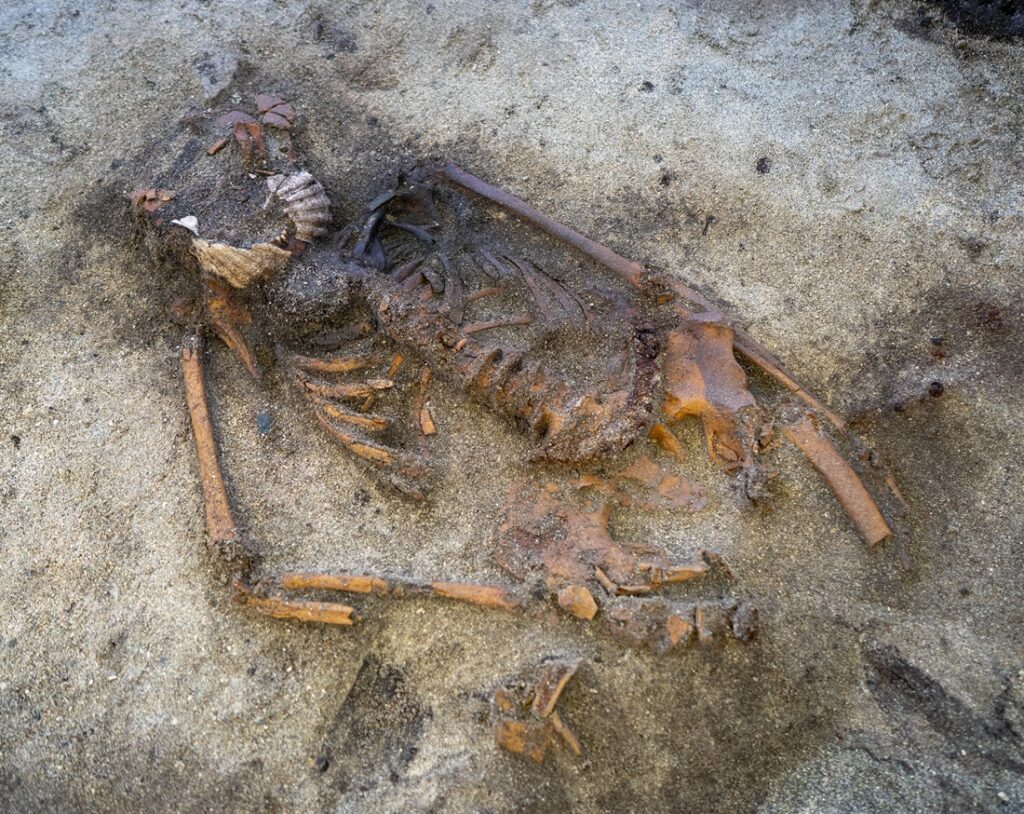

A Rare Skeleton in Remarkable Condition
The preserved skeleton itself is considered nothing short of remarkable. “Finding such a well-preserved skeleton in such an old grave is extremely rare,” said Hanna Geiran, Norway’s national antiquarian. She described the discovery as having “enormous cultural heritage value and research potential.”
Because of its importance, the Directorate for Cultural Heritage allocated special funding to ensure the excavation and preservation were carried out with maximum care. Geiran also praised both the landowner and the person who reported the discovery, noting that collaboration between locals and archaeologists is crucial for safeguarding Norway’s hidden past.
An Area Rich in Viking History
The new grave was discovered only a few months after another Viking burial was unearthed in the same region, suggesting that the Val area may have been home to a notable settlement or lineage. Archaeologists believe upcoming analyses could clarify connections between the two graves.
At NTNU’s laboratories, the remains and artifacts are now undergoing detailed examination. Field leader Hanne Bryn explained that researchers will assess whether the woman had any diseases or physical conditions that might shed light on her life or social position.
In the longer term, DNA testing will be carried out. These analyses may reveal whether the woman was related to previously discovered individuals from the region, potentially mapping out family ties from more than a millennium ago.
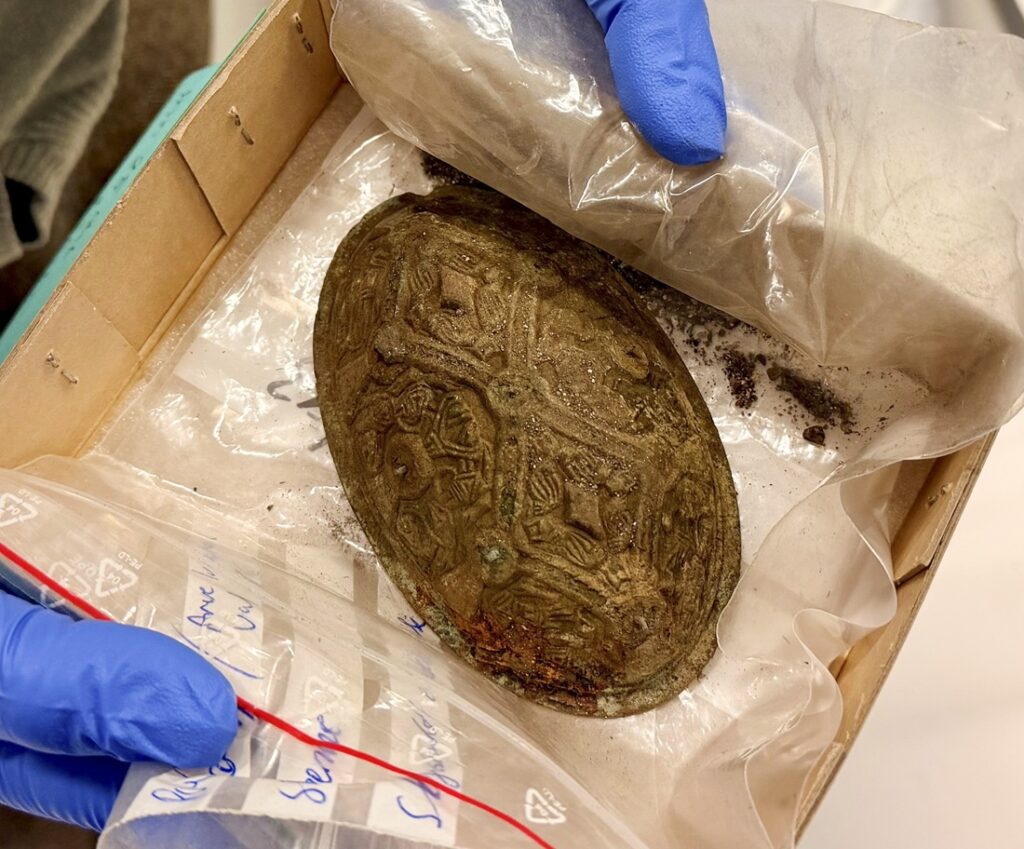

A Discovery That Could Rewrite Viking Burial Traditions
Experts agree that the grave’s unusual features — particularly the placement of scallop shells — could reshape academic understanding of early Viking religious practices. The find raises questions about ritual influences, possible travels undertaken by the deceased or her community, and burial symbolism during the transition from pagan to Christian customs.
The fact that the shells appear in this grave centuries earlier than in any documented Scandinavian burial is especially intriguing. Whether this suggests a local innovation, contact with other cultures, or an undocumented ritual tradition remains unknown.
Growing Public Fascination with the Viking Age
The Viking Age continues to capture global attention, and discoveries like this offer a rare, personal glimpse into the lives and beliefs of individuals who lived more than 1,200 years ago. As Geiran noted in her interview with Gemini.no, “This find will help us learn more about the burial culture of the Viking Age, which fascinates so many people.”
With meticulous laboratory analysis now underway, archaeologists hope that the Val grave will eventually provide answers to long-standing mysteries — and perhaps raise new ones. For now, the extraordinary burial stands as one of the most intriguing Viking discoveries in recent Norwegian history.
Cover Image Credit: From the farm in Bjugn where the Viking grave was discovered. Credit: Kristoffer Rantala, NTNU University Museum