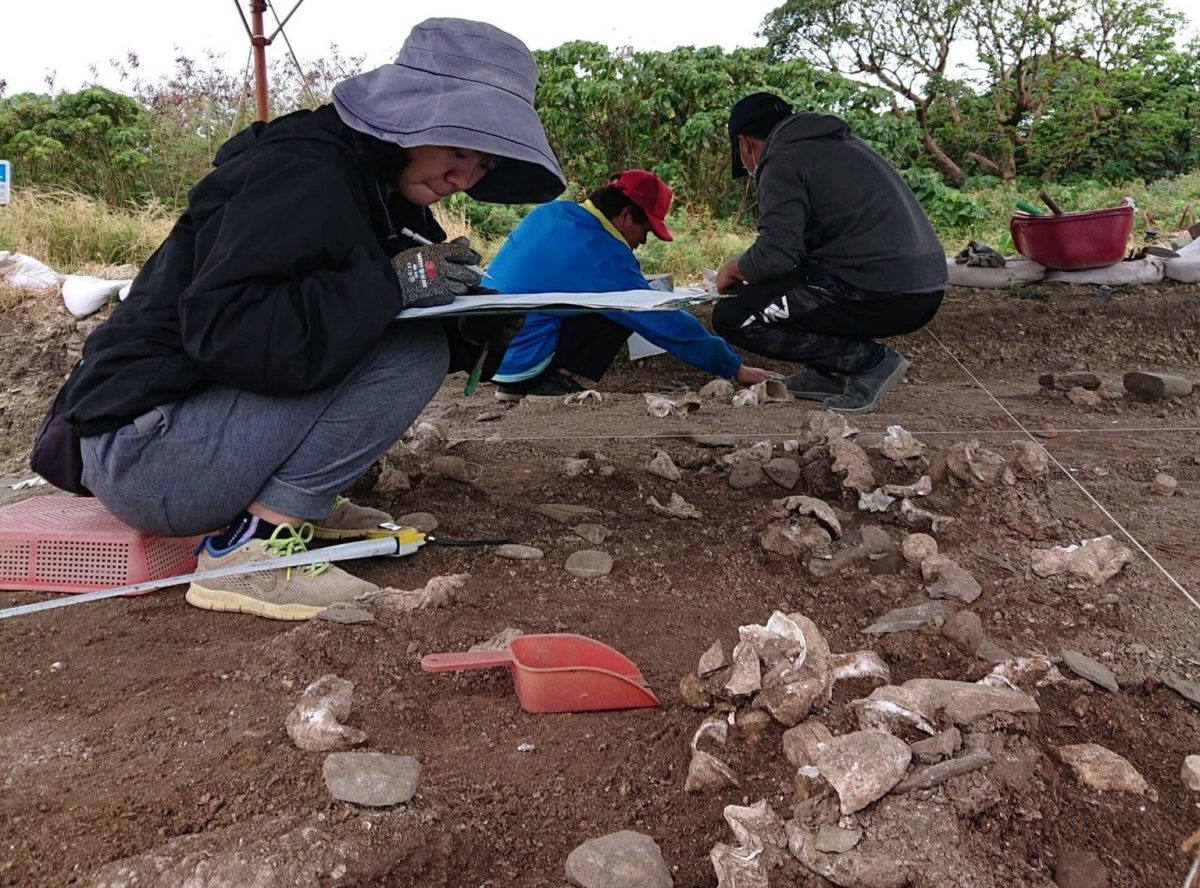
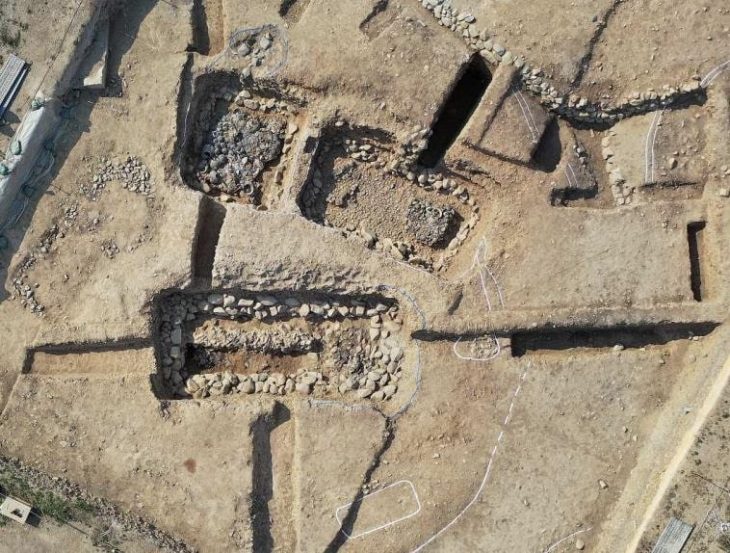
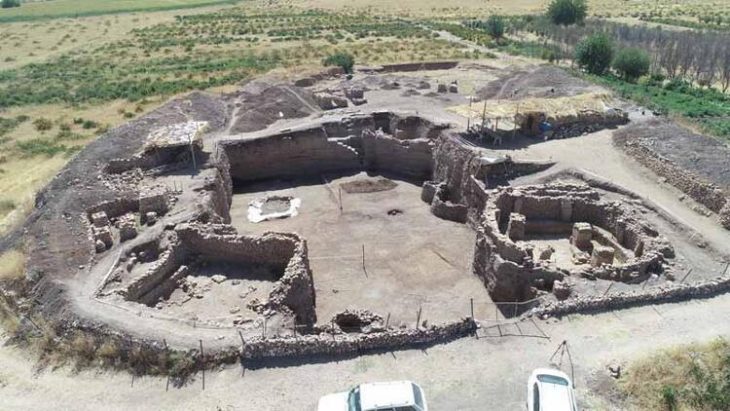
A 4,000-year-old cemetery and shell tool processing site has been discovered in Kenting National Park, Taiwan’s oldest and southernmost national park on the main island, covering the southernmost region of the island of Taiwan.
The site is the first prehistoric shell tool processing site discovered in Taiwan and the oldest and largest site found on any Pacific island, the National Tsing Hua University announced in a statement.
The site was uncovered in 2017 during a renovation effort to turn Eluanbi Park’s deteriorating shopfronts into new green structures. Contractors discovered human bones, some in slate coffins, and shell tools barely beneath the soil’s surface. Construction work was halted as archaeologists from the Institute of Anthropology at National Tsing Hua University (NTHU) inspected the site.
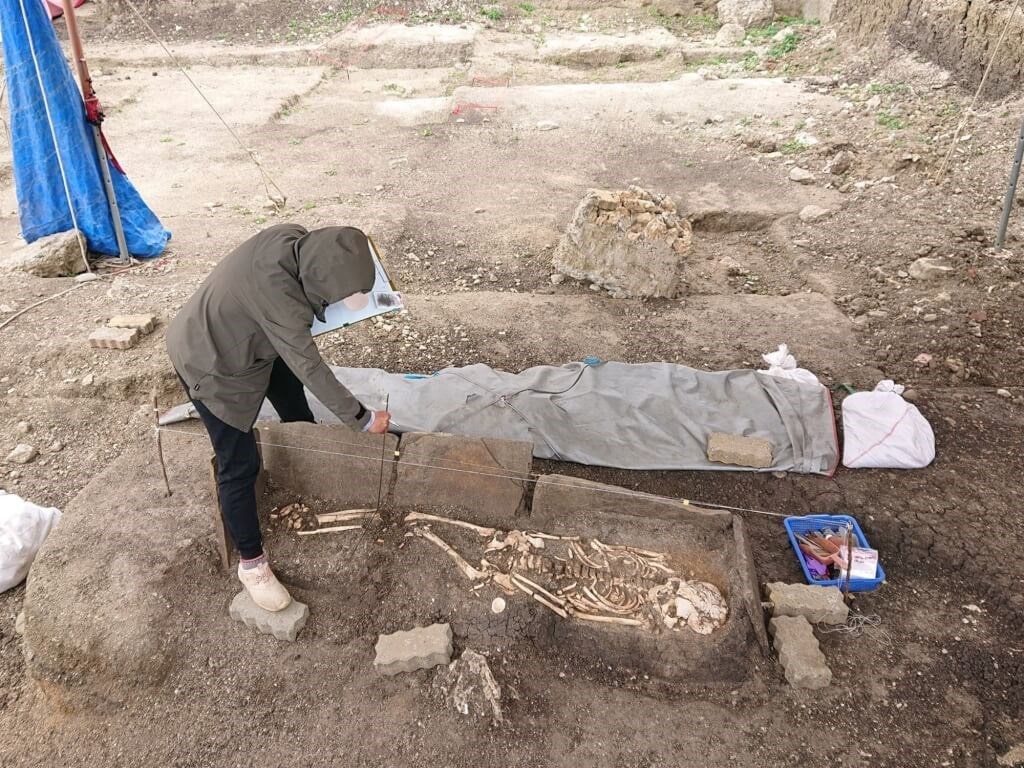

Associate Professor Chiu Hung-lin (邱鴻霖) and his team, commissioned for the research, uncovered numerous remains and artifacts between 2019 and 2021, including 51 skeletons, 10 of which were buried in slate coffins along with coral funerary objects.
Among the findings were several finished and unfinished shell tools, as well as relics that indicated it was a site for making those tools, which provided proof that the early inhabitants of Eluanbi used “unique” shell-crafting techniques, Chiu Hung-lin said.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
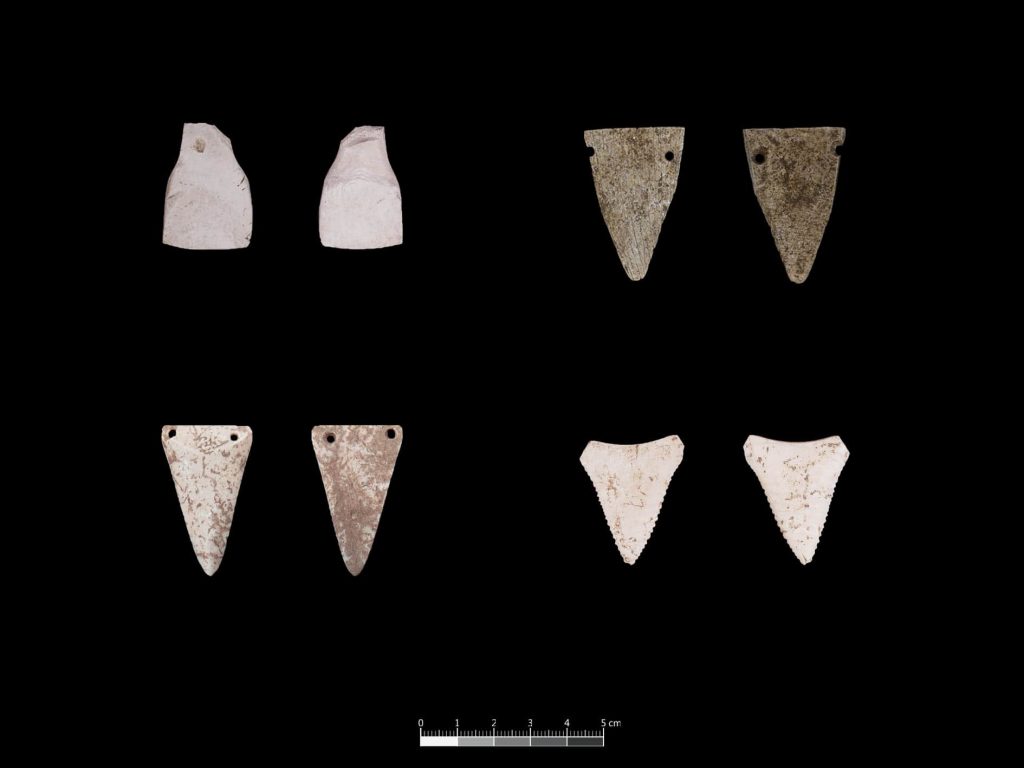

The discovery also provided insights into the people’s burial practices at the time, he added, adding that anthropologists may make new discoveries by researching the human remains discovered at the site.
The skeletal remains and shell tools date back about 4,000 years, which means it is the oldest shell tool site found on any island in the Pacific region, Chiu said, adding that it was also the largest.
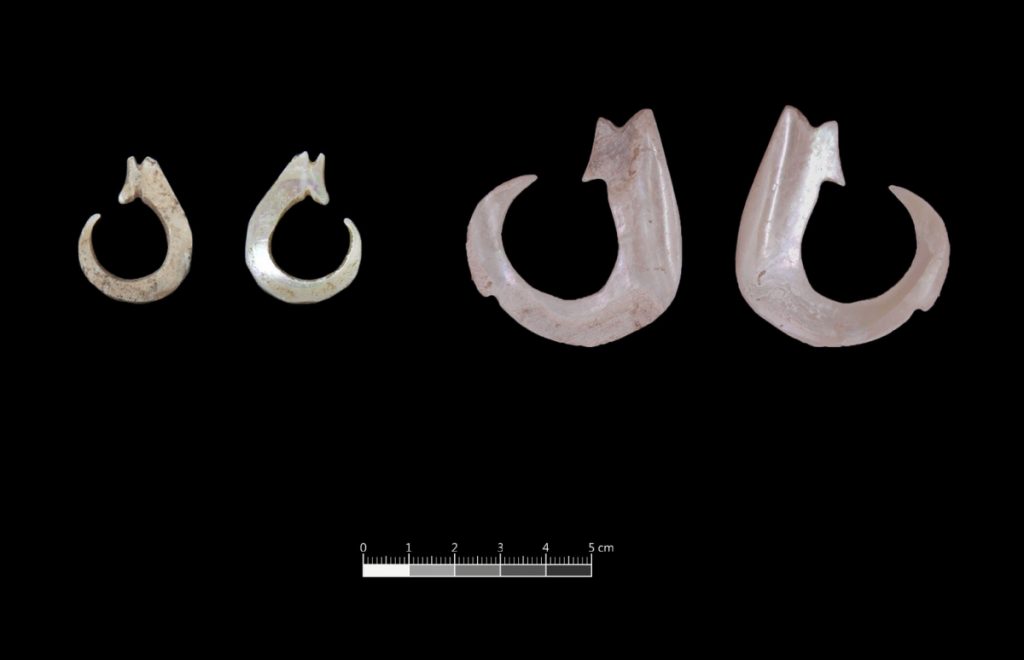
Prehistoric fishermen have a special ceramic processing technology. The design and function of the processed shell findings vary greatly. There are practical tools like a shell adze used for cutting, as well as ornaments like shell and shark tooth pendants. The presence of intermediary steps — semi-finished goods, blanks — as well as processing waste indicates a large manufacturing activity.
















