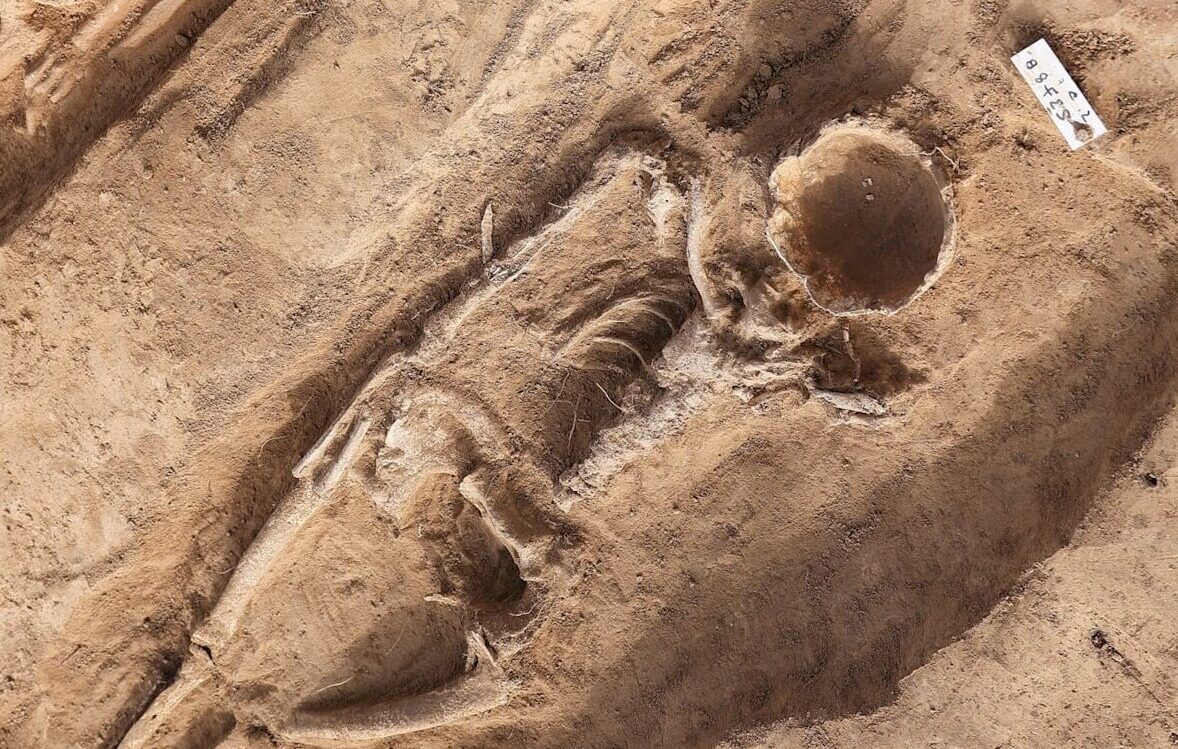
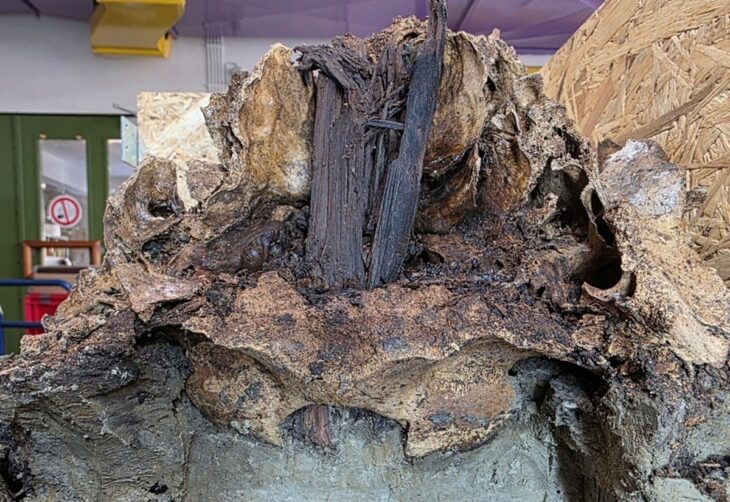
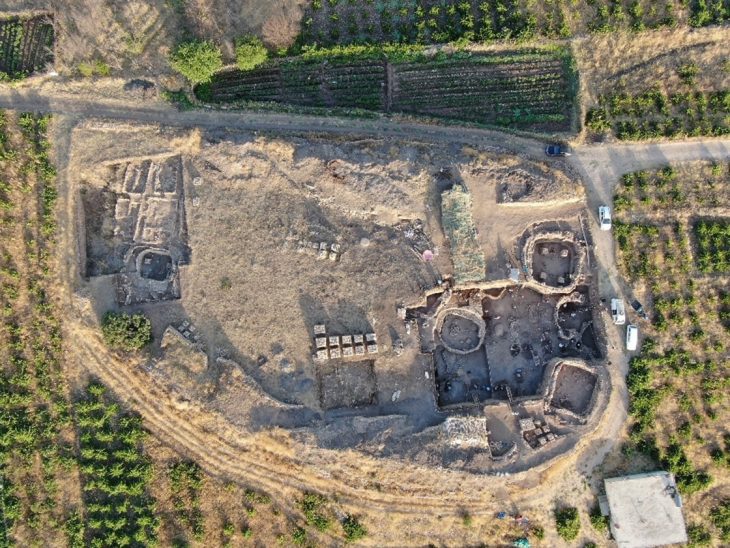
Archaeologists unearthed the 1,000-year-old remains of a woman with her face and head hollowed out buried next to her husband near the town of Eisleben in Germany’s Saxony-Anhalt state.
Archaeologists assume that the petite woman (around 1.55 meters tall) and her slightly taller husband lived in the 9th century. Their remains were excavated at the former royal palace of Helfta – a place where the emperors Otto the Great and Otto II resided.
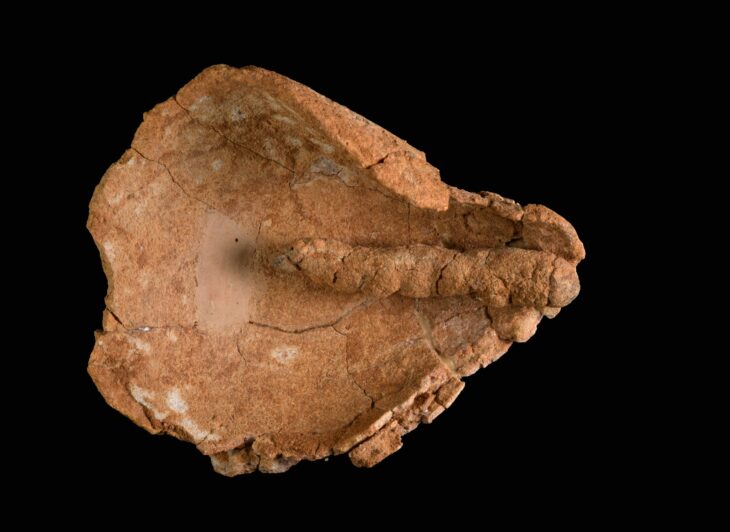
It is unclear how or when the couple died, but what was most unusual was that the wife was missing all of the bones in her face while her husband’s countenance was still intact.
It is not currently known if they died together or separately, or why the wife’s facial bones are missing.
Archaeologists are currently examining the remains at the lab to try and crack this 1,000-year-old cold case file.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Archaeologists believe that it was likely the husband was a dignitary of some kind.
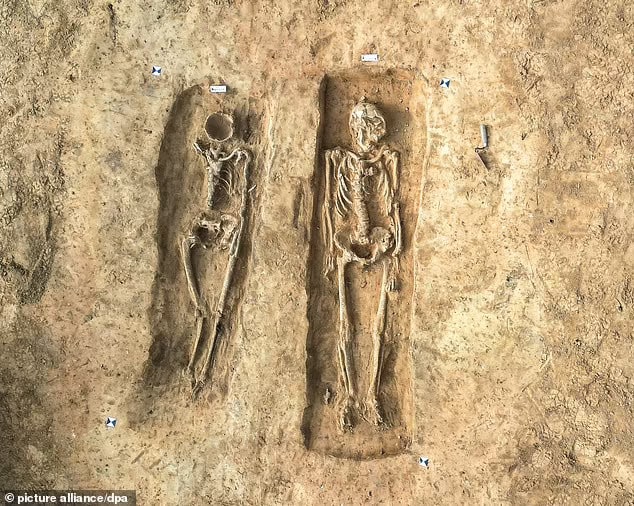

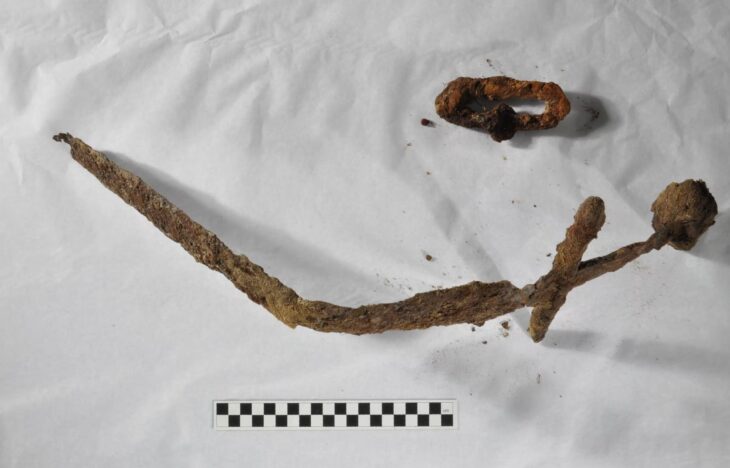
“Among other things, they found a knife, a belt set and the fittings for a so-called official staff, such as those carried by generals, on him,” archaeologist Felix Biermann from the Saxony-Anhalt State Office for Monument Preservation and Archeology told the German newspaper Bild, per the Daily Mail.
It is therefore likely that the dead man was the manager of a castle. According to the archaeologists, the woman may have consciously expressed her wish to be buried without the grave goods that were common at the time, such as jewelry. This suggests that she thought in a much more modern way than her husband.
“The fact that there was nothing with her is very unusual,” says Biermann. “Maybe she was already Christian, but the man was even more traditional. In Christianity, these kinds of additions were avoided.”
The couple’s bones are now being examined in a laboratory to determine how they died.
Cover Photo: Jan Woitas/dpa