Archaeologists conducting archaeological excavations in the French city of Nimes have discovered the remains of two high-status Roman domus (houses).
Nimes became a Roman colony sometime before 28 BC, called the colony Nemausus, and became the main administrative center that ruled southern Gaul.
In its heyday, the city had approximately 50,000 to 60,000 residents, as well as various civil and leisure buildings, such as a civil cathedral, Guria, gymnasium, amphitheater, several temples, and even a circus.
Excavations were conducted by the National Institute for Preventive Archaeological Research (Inrap) in the area of the Roman forum district.
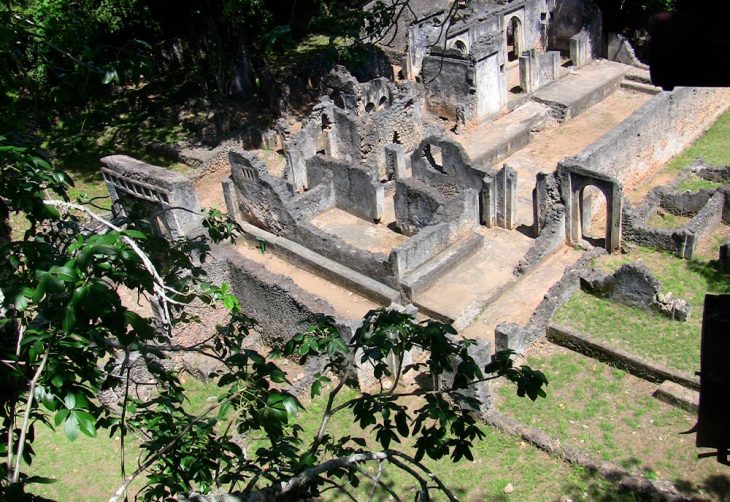
The team excavated two Roman Domus, which are typical high-level buildings occupied by the upper class of Roman society. Usually, the dome’s vestibule (entrance hall) leads to a large central hall: atrium with multiple compartments (bedrooms), dining room with three oblique squares, Tallinn (living room or study), and Culina (Roman kitchen).
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
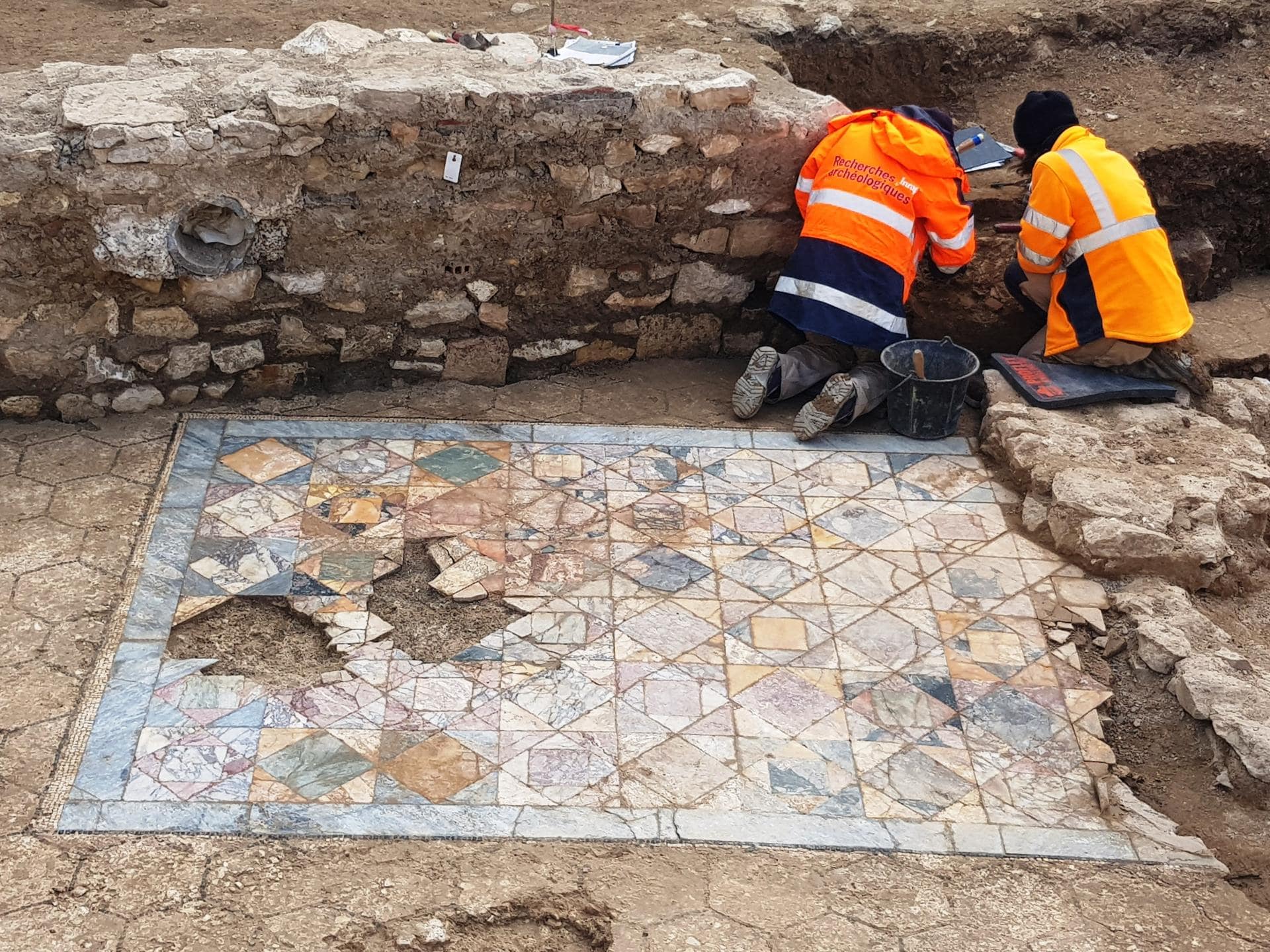

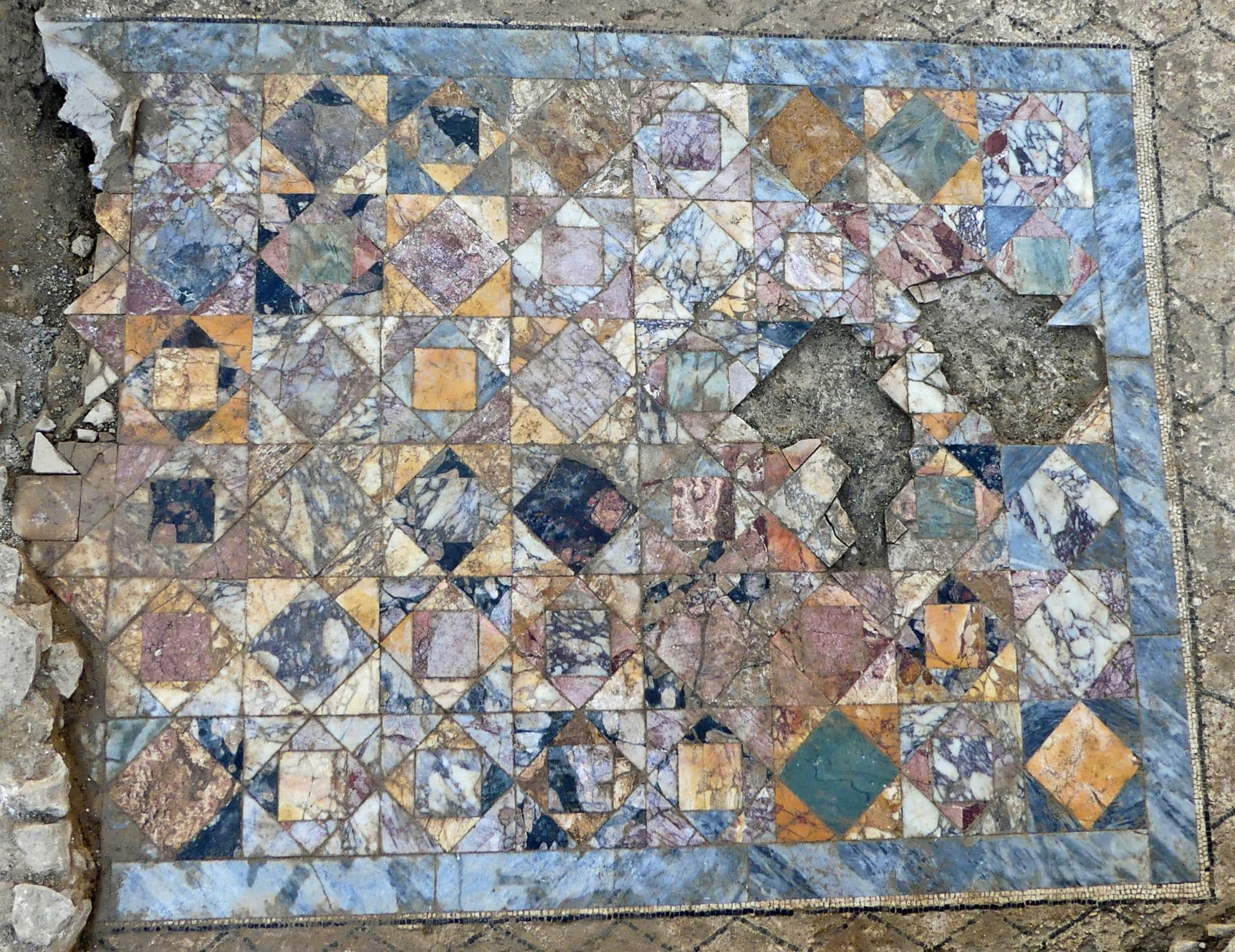
One of the excavated domus ornaments has a decorative checkerboard-shaped marble floor called sectile opus, an artistic technique in which the material is cut into small pieces, polished, and then further trimmed according to the selected pattern. Unlike tessellated mosaics, where the placement of very small pieces of uniform size forms an image, opus sectile pieces are much larger and can be molded to define large parts of the design.
Other discoveries include hypocaust heated rooms (a central heating system in which hot air circulates under the floor and through a series of pipes in the walls), courtyards with garden pots, and a marble washbasin with a semicircular apse.
You can visit the Inrap page for detailed information.