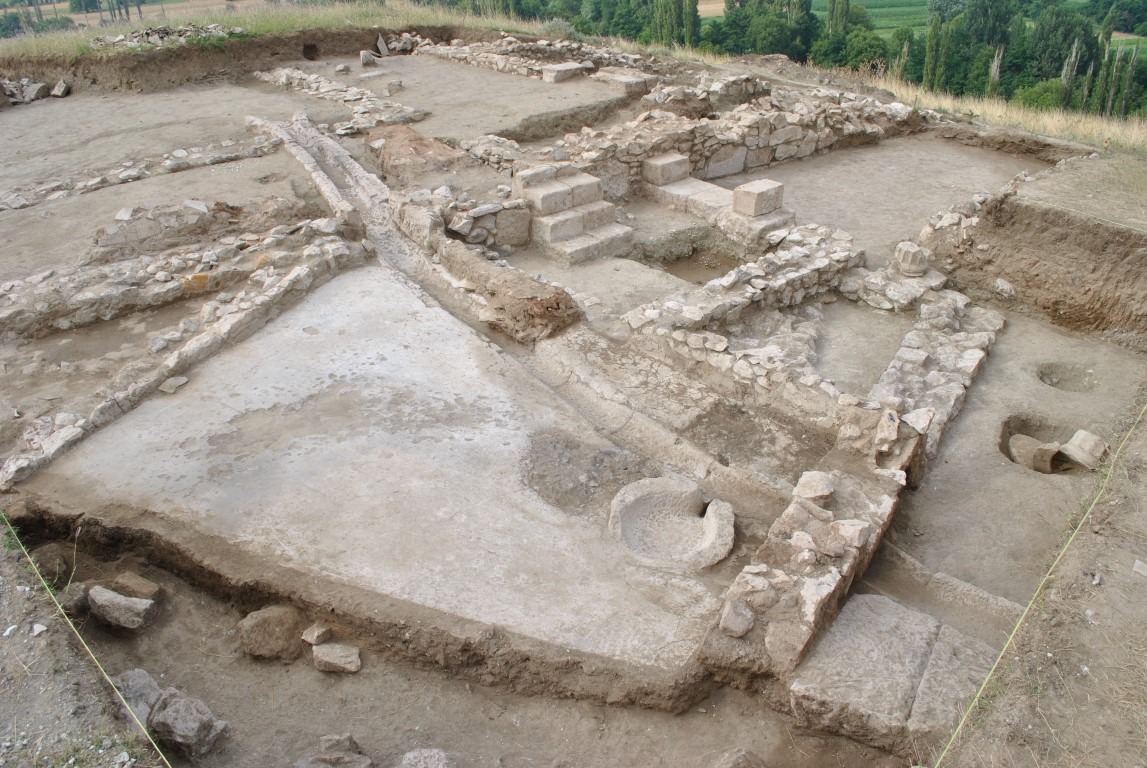
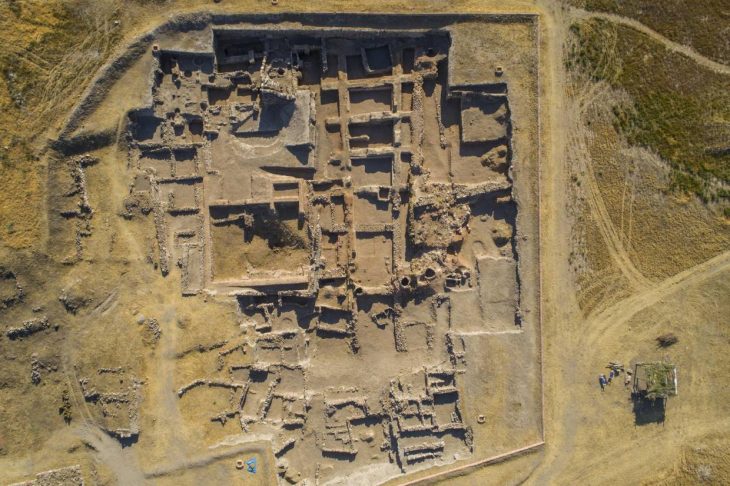
In a groundbreaking archaeological campaign, the NL Museum of Kumanovo has unearthed a remarkable Hellenistic-era residence near the village of Mlado Nagoričane. Directed by Dejan Gjorgjievski, the excavation at the Gradishte site has revealed what experts are calling one of the most significant discoveries in the central Balkans, shedding new light on the region’s cultural ties to the Hellenistic world during the late 4th century BCE.
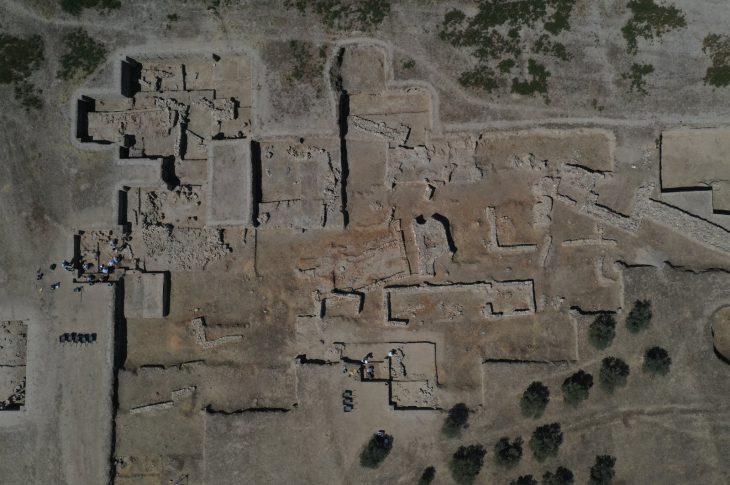
The structure — believed to have been the home of a local nobleman — rests atop the summit of the Gradishte hill, a location interpreted as the ancient acropolis. Its architectural layout closely mirrors that of elite Hellenistic houses commonly found in the Mediterranean, but rarely so far north. The building includes a central courtyard surrounded by a portico, interior walls decorated with painted plaster in masonry-style techniques, and a private bath equipped with a plastered floor and a water-supply system — features that suggest not only wealth but also deep cultural integration with the Greek world.

A Hellenistic Footprint in the Northern Balkans
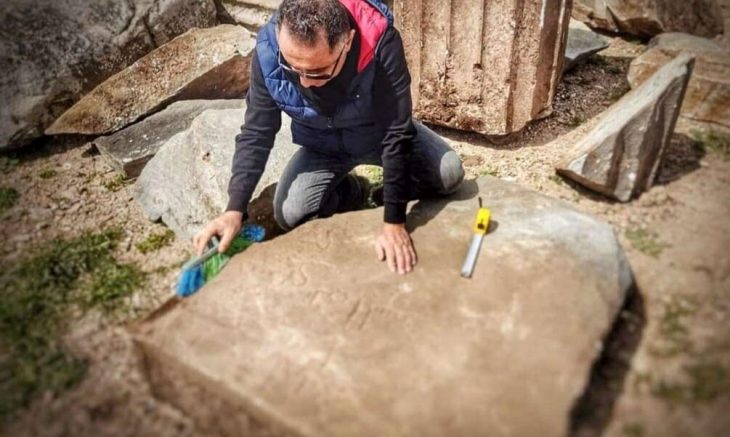
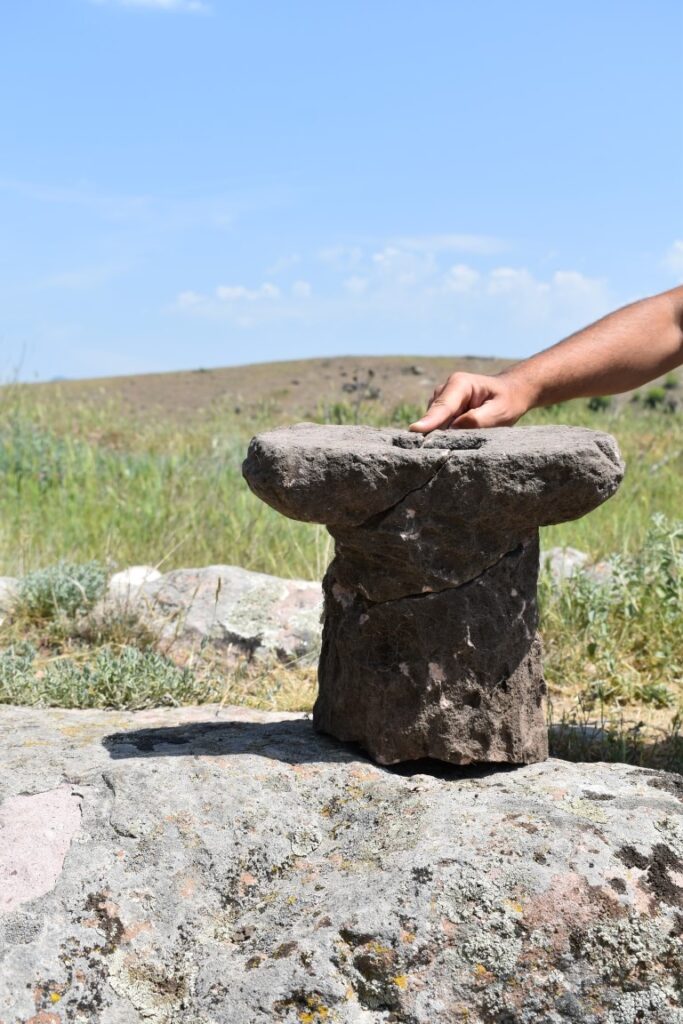
One of the most striking finds from this season’s excavation is the presence of fully preserved Ionic capitals and bases, coated with plaster. In his statement to Arkeonews, project director Dejan Gjorgjievski explained, “These are currently the northernmost examples of such classical architectural elements known in the Hellenistic world.” Their preservation and stylistic execution point to skilled craftsmanship and a deliberate alignment with Mediterranean elite aesthetics.
The discovery aligns with broader regional patterns discussed in the academic study A Tale of Two ‘Hellenised’ Sites, co-authored by Gjorgjievski and Ivan Vranić. That study compares Gradishte with another site in the region, emphasizing how Hellenistic cultural practices — especially in architecture, luxury consumption, and symbolic spatial organization — penetrated deep into the interior Balkans during the late Classical and early Hellenistic periods.

Artifacts of Trade, Culture, and Daily Life
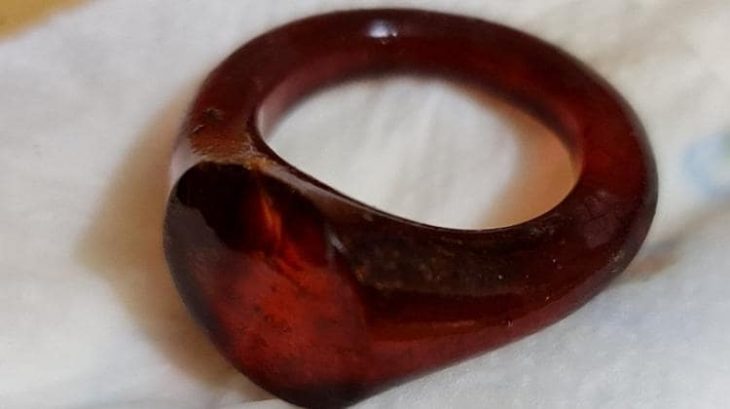
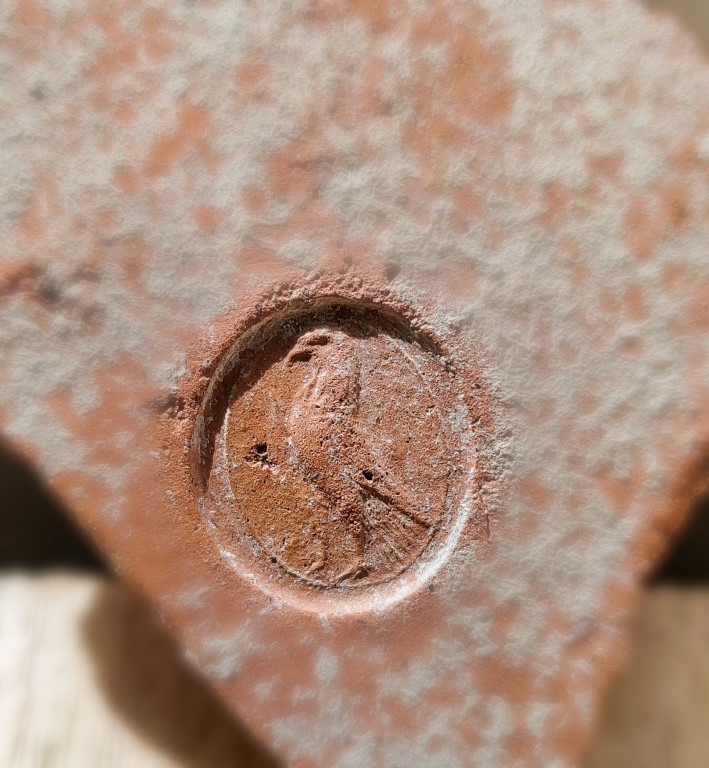
In addition to architectural remains, the excavation team recovered a wide range of imported and local artifacts. These include West Slope pottery, Thasian amphorae, and unguentaria, clearly dated to the 4th–3rd centuries BCE.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
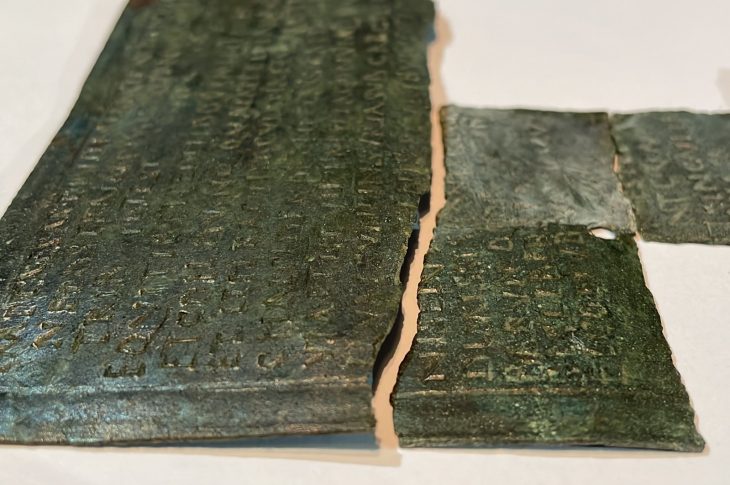
A particularly notable object is a locally made ceramic sherd inscribed with a Greek vulgar graffito (“Ψωλή κύ…”) — an example of what scholars term aporretic inscriptions. This inscription is now the northernmost known example of its kind, offering a rare glimpse into everyday speech and informal literacy in Hellenistic frontier zones.
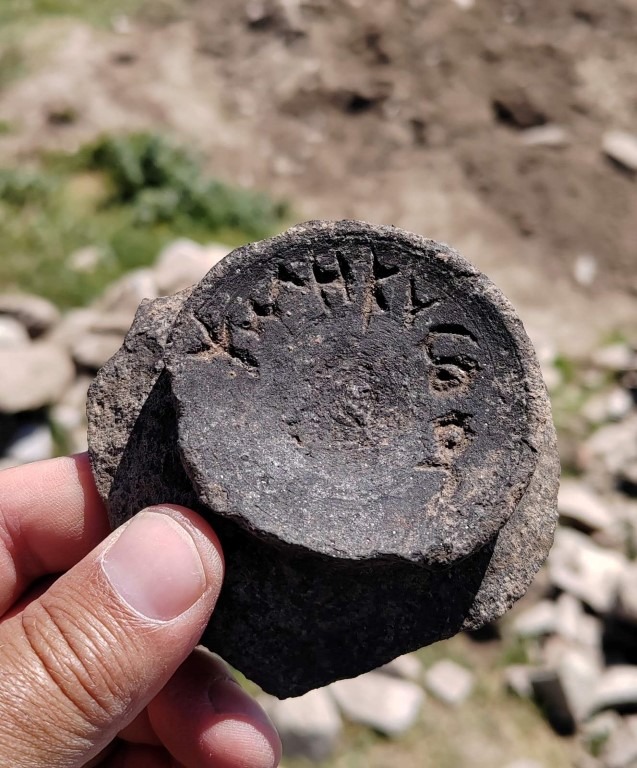

Unresolved Layers of History
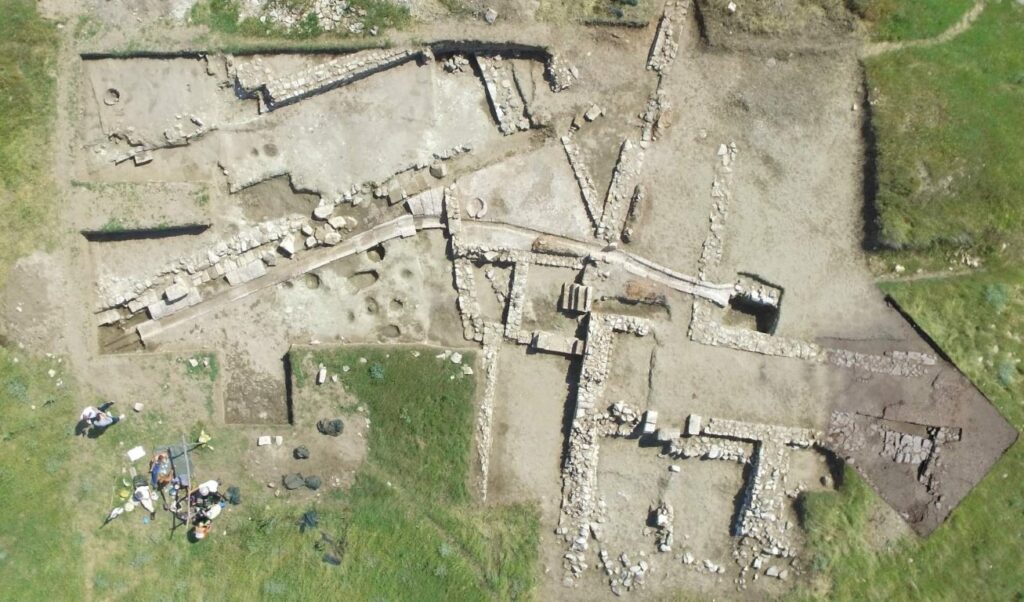
Beneath the grand residence, archaeologists encountered traces of massive stone walls, possibly from an earlier elite structure. However, due to stratigraphic ambiguity, these remains remain undated. Future excavation seasons aim to resolve this chronological uncertainty and determine whether Gradishte had multiple phases of elite occupation.
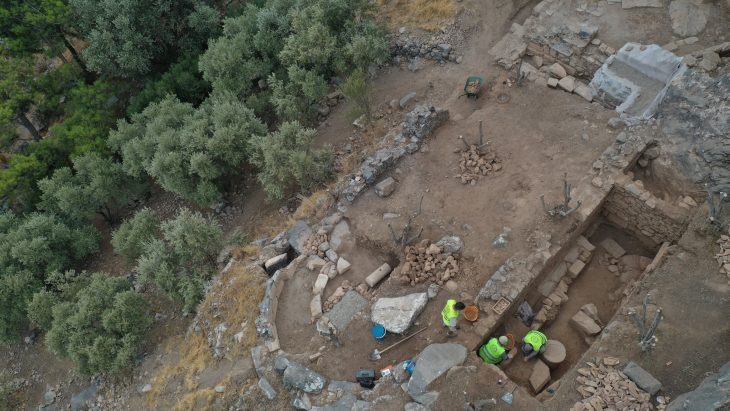
Elsewhere on the site, prior seasons revealed evidence of an internal fortification wall and a stylobate-like platform, as well as a rock-cut sanctuary — a ritual space reminiscent of the sanctuary at Rachi in Isthmia, Greece. These elements reinforce the interpretation of Gradishte as a well-fortified and ritually significant settlement embedded in Hellenistic cultural frameworks.
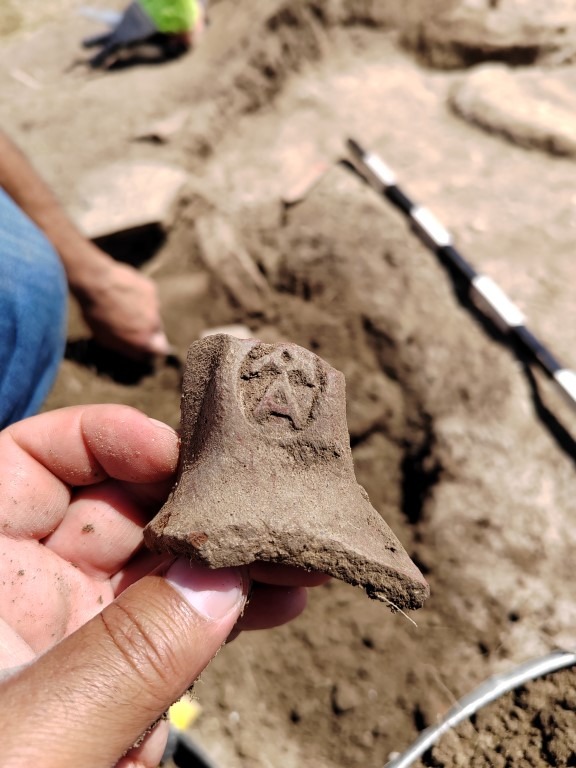

NL Museum of Kumanovo at the Forefront
The excavation was conducted under the leadership of Dejan Gjorgjievski and organized by the NL Museum of Kumanovo, a regional institution increasingly recognized for its contributions to Balkan archaeology. This latest discovery not only adds valuable data to academic discussions but also enhances cultural tourism prospects and heritage awareness in North Macedonia.
In Gjorgjievski’s words, “Our findings at Gradishte contribute to a growing understanding that Hellenistic influence in the Balkans was not limited to coastal colonies or trade posts — it extended into local power structures and domestic life.”
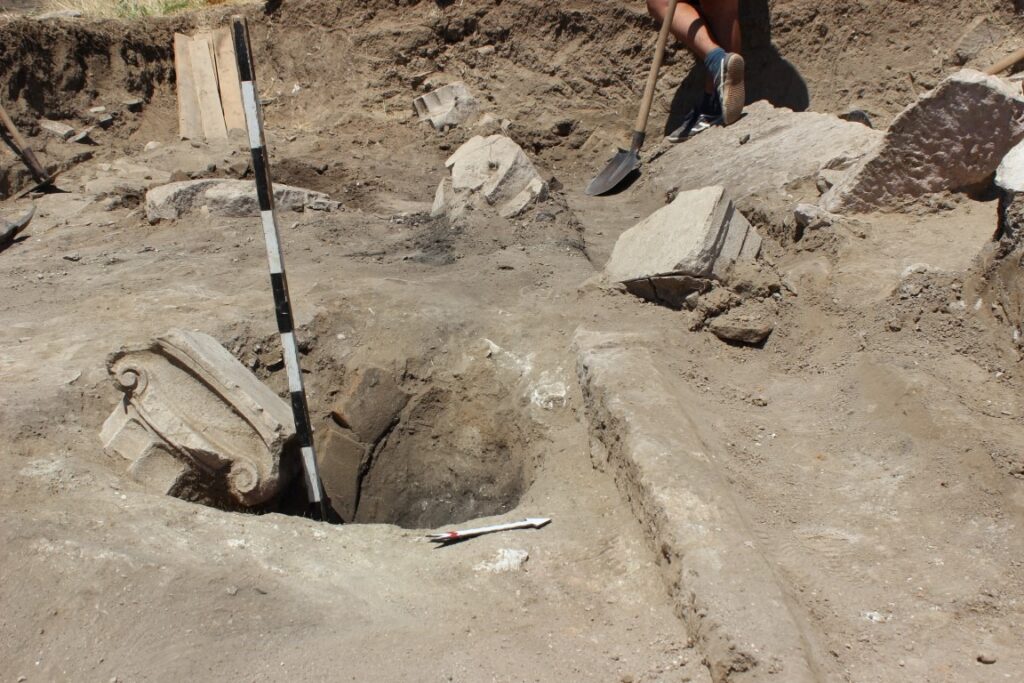

What’s Next for Gradishte?
Plans for future excavation seasons include extending the dig to lower layers, performing material analyses, and initiating conservation efforts. There is also interest in using digital tools to reconstruct the elite residence virtually, offering both scholars and the public a more vivid understanding of life in this high-status Hellenistic home.
As the Gradishte site continues to reveal its secrets, the work of the NL Museum of Kumanovo and researchers like Dejan Gjorgjievski ensures that North Macedonia plays a pivotal role in redefining the cultural boundaries of the ancient Hellenistic world.

Vranić, I., & Gjorgjievski, D. (2025). The story of two ‘Hellenized’ sites in southeastern Europe: Recent studies of Kale-Krševica and Gradište-Mlado Nagoričane (5th–3rd centuries BC). In J. Tzvetkova, V. Sarakinski, & F. Milivojević (Eds.), The unclassical Balkans: Ancient societies and cultures of the Balkan Peninsula beside the Graeco-Roman world (Special edition). Antiquité Vivante.
Cover Image Credit: Courtesy of Dejan Gjorgjievski