Archaeologists in Bedfordshire, England, have made an intriguing discovery: a tableman gaming piece was discovered at a medieval site.
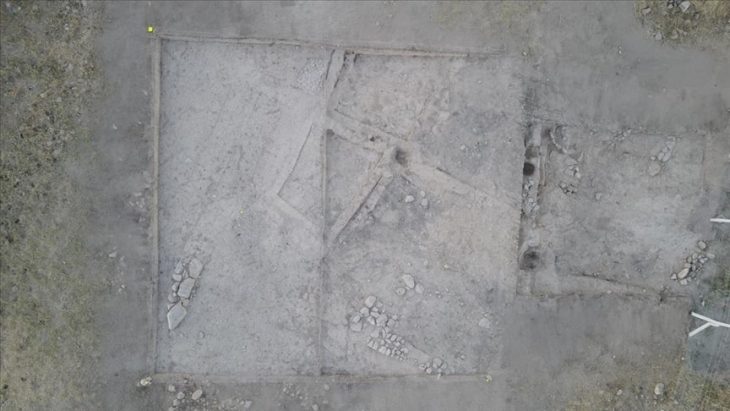
Cotswold Archaeology excavated in preparation for a Taylor Wimpey housing development at Bidwell West, near Houghton Regis and Dunstable.
In addition to the tableman, the archaeological team discovered a medieval timber-framed building and a series of medieval enclosure ditches.
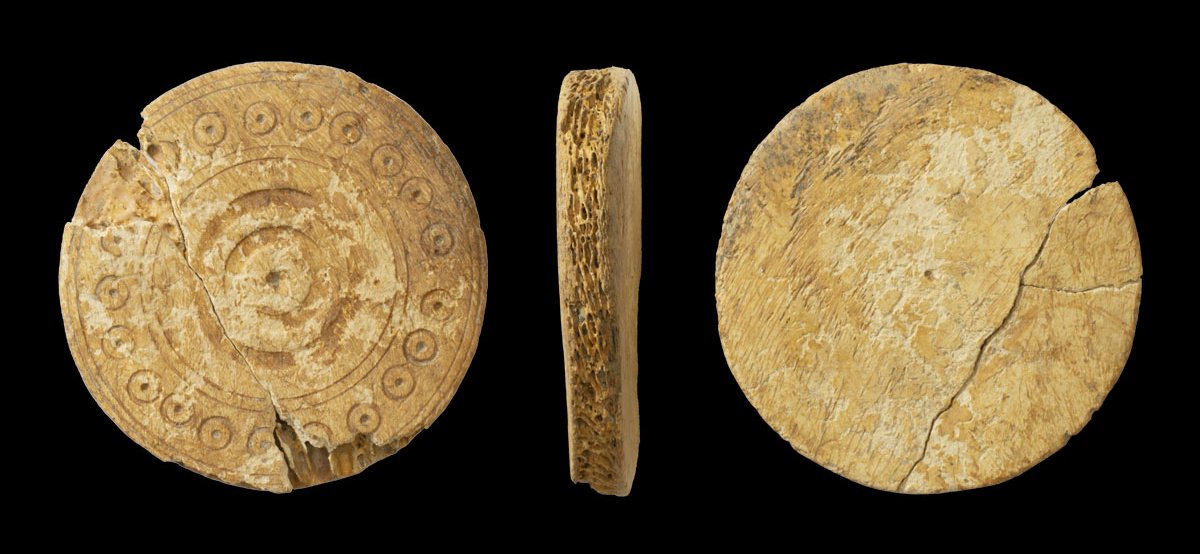
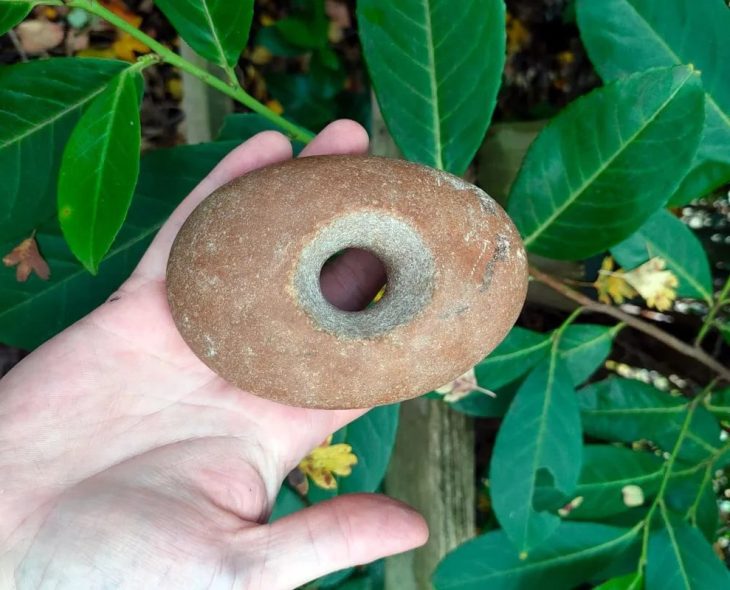
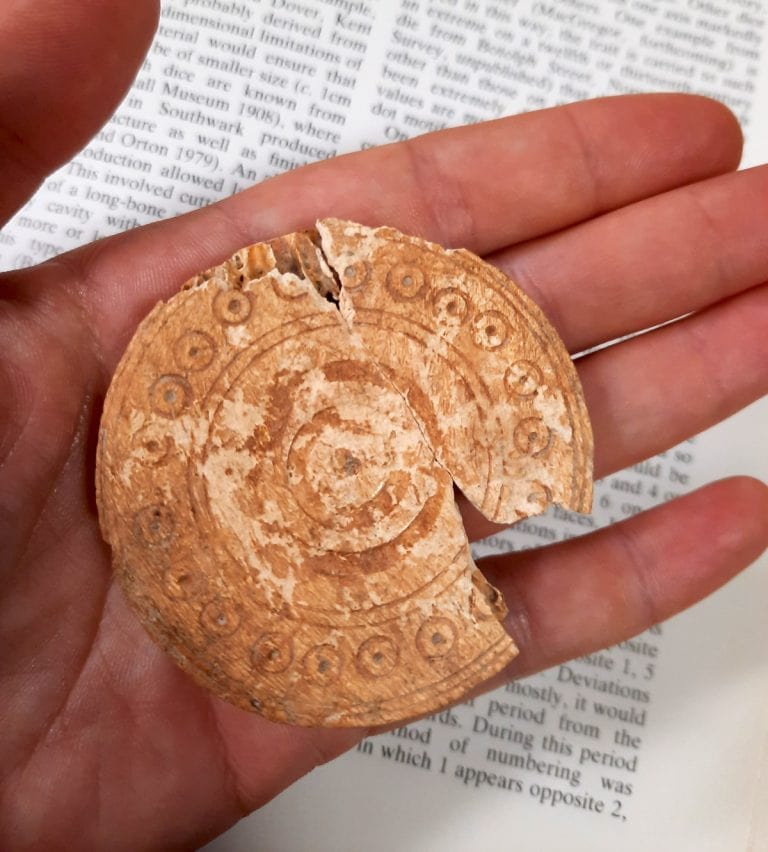
The gaming piece, which has a diameter of nearly 6cm, is made from a cattle mandible – a large, sturdy bone, which serves as the lower jawbone of a cow, according to a press release. Its face has been decorated with concentric circles and a ring-and-dot design, which is attractive although not unusual.
Tablemen were used to play a variety of board games in which two players rolled dice and moved their pieces across rows of markings. The term ‘tables’ is derived from the Latin tabula, which originally meant “board” or “plank” and was introduced to Britain during the Roman period.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!

One of the more popular table games among the Romans was Ludus duodecim scriptorium. It was a dice game with three cubic dice, and each player had 15 pieces to move. The game of tabula was most likely refined from Ludus duodecim scriptorium, and it grew in popularity during the medieval period. Tabula, like Backgammon, has two rows of twenty-four points.
The tableman found at Bidwell West has a diameter of nearly 6cm (2.36 in) and similar examples in both size and decoration style have been recovered at other sites, including an example from Winchester, Hampshire which was made in the medieval period (11th-13th centuries).
As Cotswolds Archeology also wrote in its description:: “It is not always possible to identify which game the gaming pieces recovered from archaeological excavations would have belonged to, because there is often no surviving board.
However, due to the association with the medieval site, the style of decoration, and the size, it is likely that the gaming piece was used to play tabula during the medieval period.
Cover Photo: Cotswold Archaeology