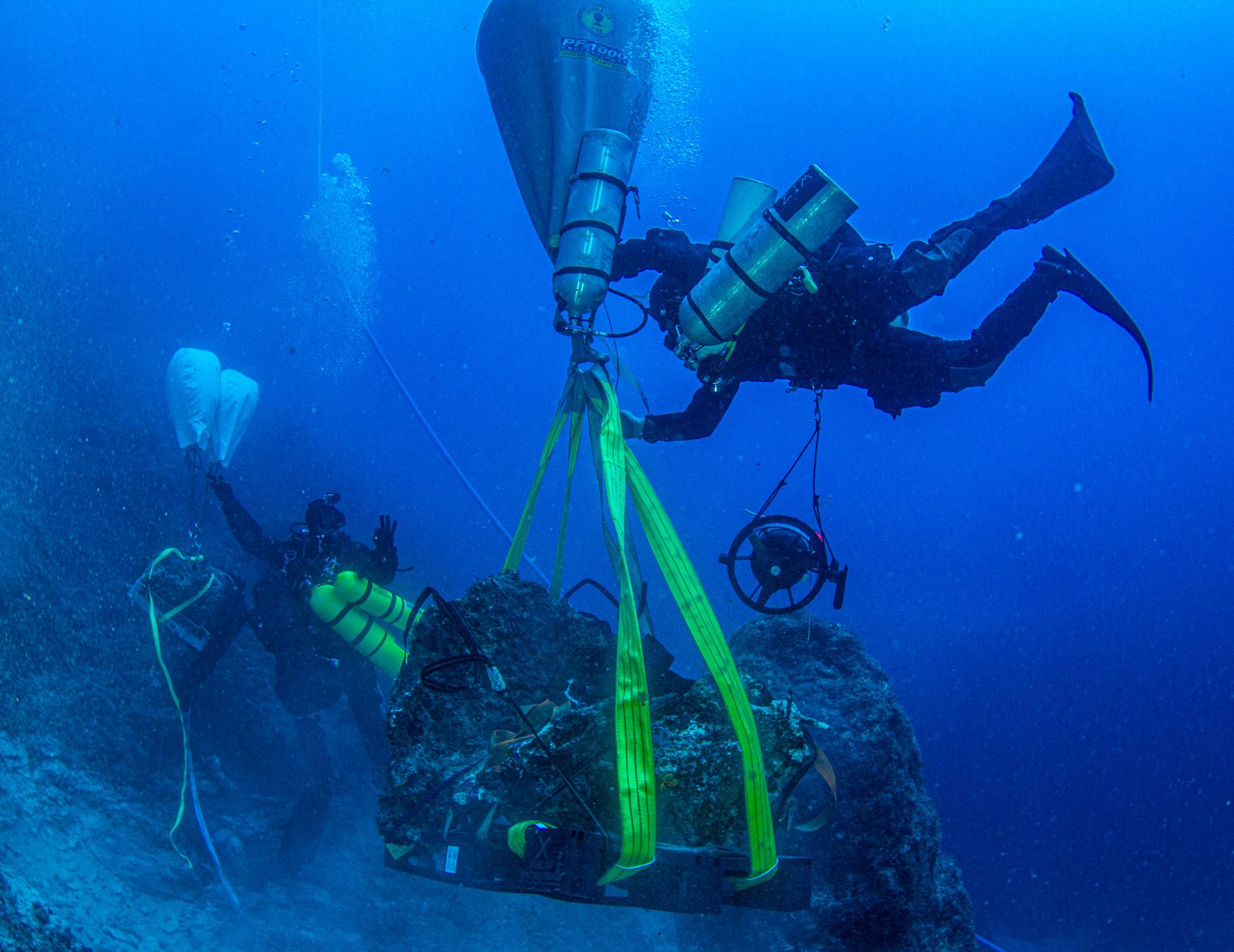
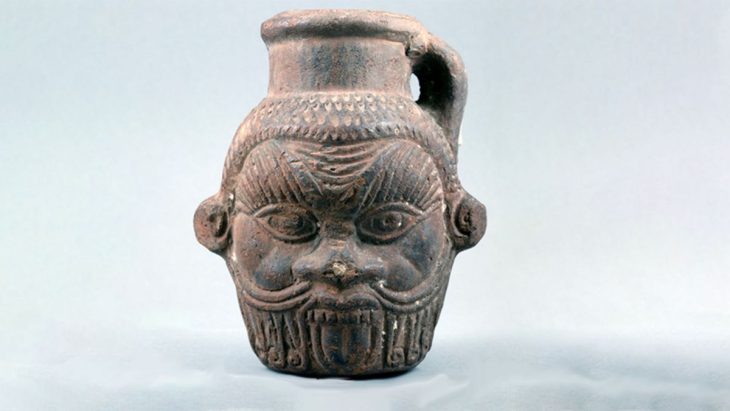
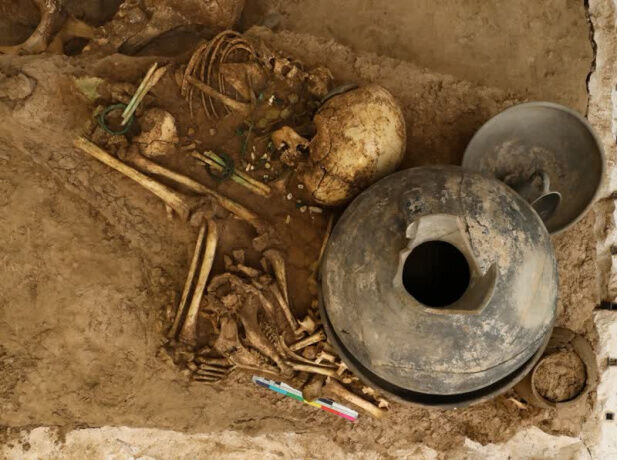
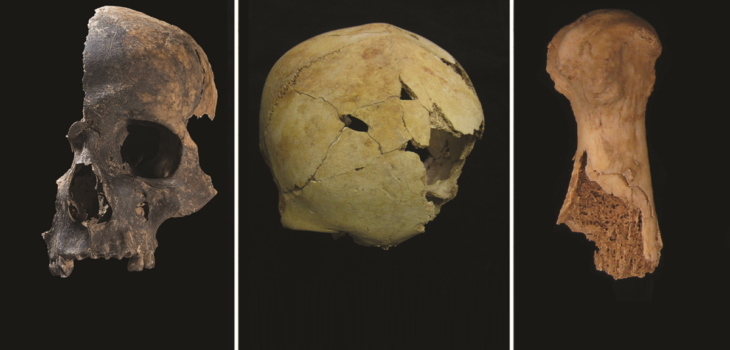
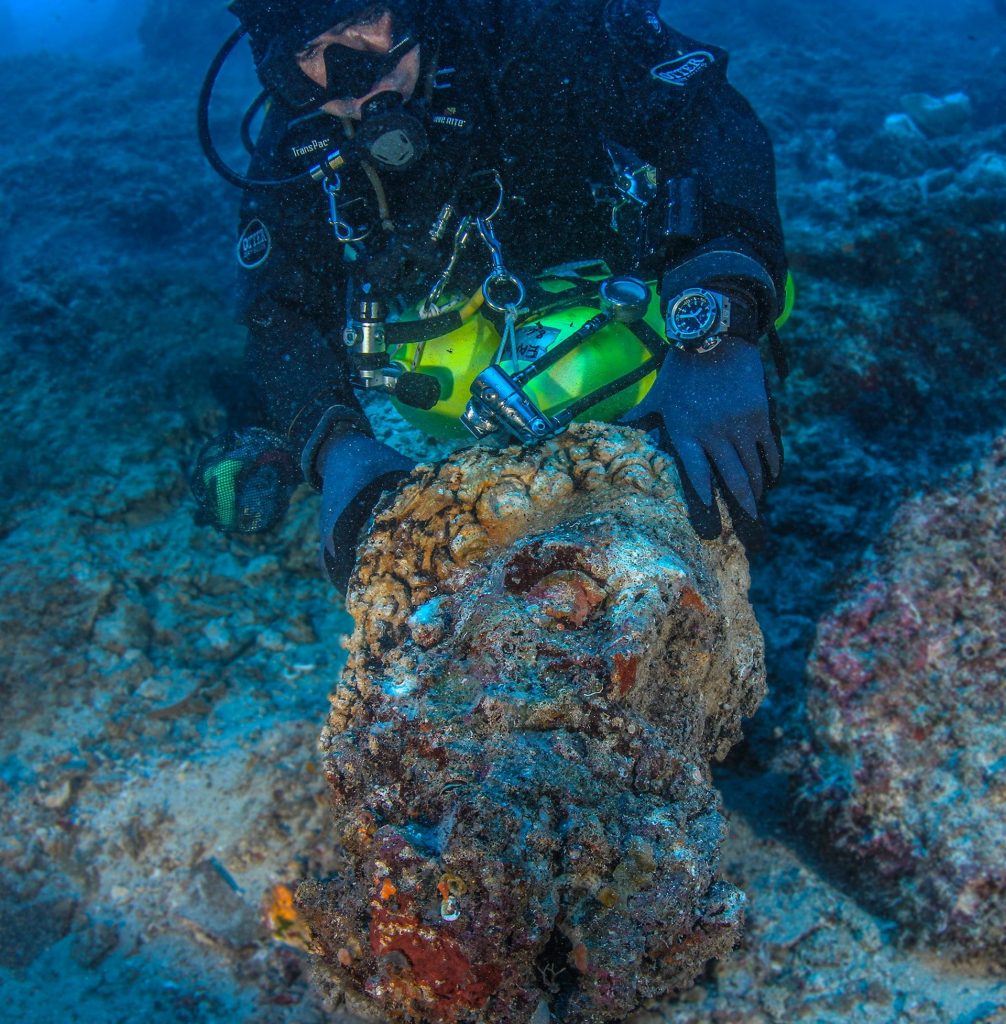
The second phase of underwater archaeological research (May 23 to June 15, 2022) on the Antikythera shipwreck resulted in the discovery of a statue head identified as Farnese-type Hercules and two human teeth embedded in a compact mass with copper traces.
Marble head of a male bearded figure, bigger than life-size, which at first sight can be identified with Herakles (Hercules) of the so-called Farnese type. It most probably belongs to the headless statue of the so-called “Herakles of Antikythera”, inv. no. 5742 of the National Archaeological Museum, which was retrieved by sponge divers in 1900.
Two human teeth recovered in a solid agglomeration of marine deposits, together with bits of copper, wood, and other components indicative of a nautical calamity, are likely to yield important information. The genome and other features related to the origin of the persons to whom the teeth belonged might be deduced using a genetic and isotopic examination of the teeth.
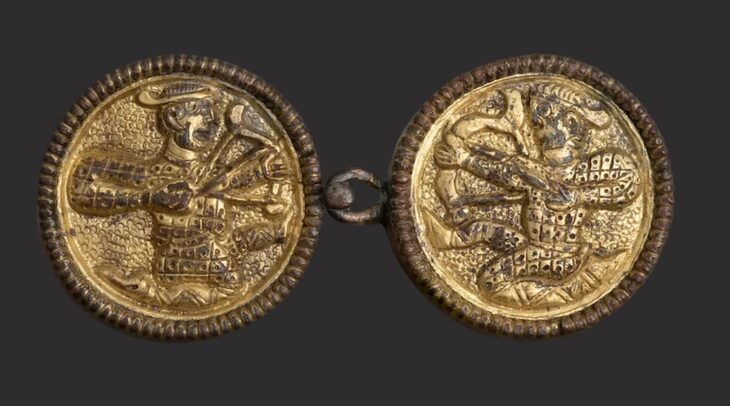
Several items from the ship’s equipment were also found, including bronze and iron nails, a lead collar from a large wooden anchor, and amorphous iron concretion masses coated in marine deposits. Their function will be determined using X-rays and other specialist laboratory tests.

The Swiss School of Archeology in Greece is conducting the research under the direction of Dr. Angeliki G. Simosi, head of the Ephorate of Antiquities of Euboea, and Lorenz Baumer, Professor of Classical Archaeology at the University of Geneva; the field research is overseen by the Ephorate of Underwater Antiquities, and the project is supported by H.E. the President of the Hellenic Republic, Ms. Katerina Sakellaropoulou.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
The main objective of the program is to formulate a clearer and more acute understanding of the ship, its route, its cargo, and the wreckage conditions.
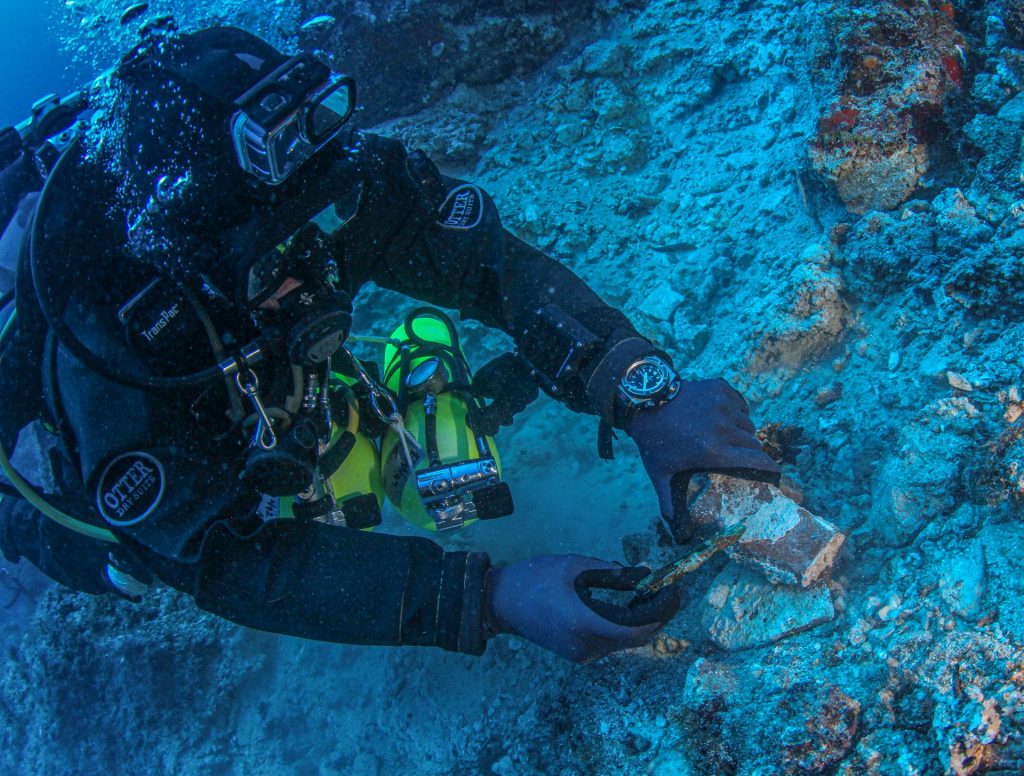
The 2022 field study included the movement of chosen large natural stones weighing up to 8.5 tons apiece that had partially obscured the shipwreck region during an investigational event; their removal allowed access to a hitherto unknown portion of the wreckage. The popular Swiss watchmaker’s Hublot Xplorations team planned and built a unique system consisting of sturdy rigging, underwater lifting bags, and pressurized air supply.
Antikythera Wreck
The Antikythera Wreck contains the wreckage of a Greek freight or commercial ship from the First Century BCE. It is situated at the crossroads of the Aegean and Mediterranean Seas on the east side of the Greek island of Antikythera, near Crete.

The wreck was discovered in the spring of 1900 by a group of Greek sponge divers on their way to Tunisia who took shelter from a storm near the island and decided to look for sponges while they waited for calmer conditions. One of the divers discovered the wreck at depths reported between 40 and 50 meters.
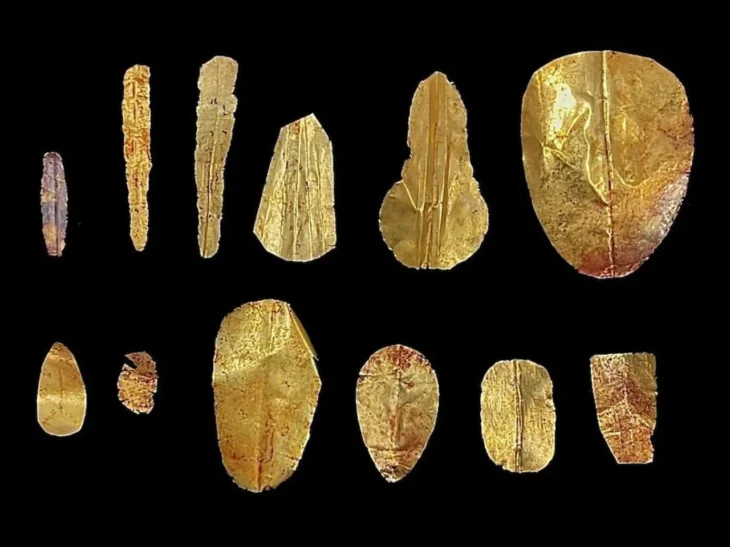
That excavation revealed a wealth of discoveries that today are housed in Greece’s National Archaeological Museum in Athens. These included three life-size marble horses, jewelry, coins, glassware, and hundreds of works of art, including a seven-foot-tall “colossus” statue of Herakles.
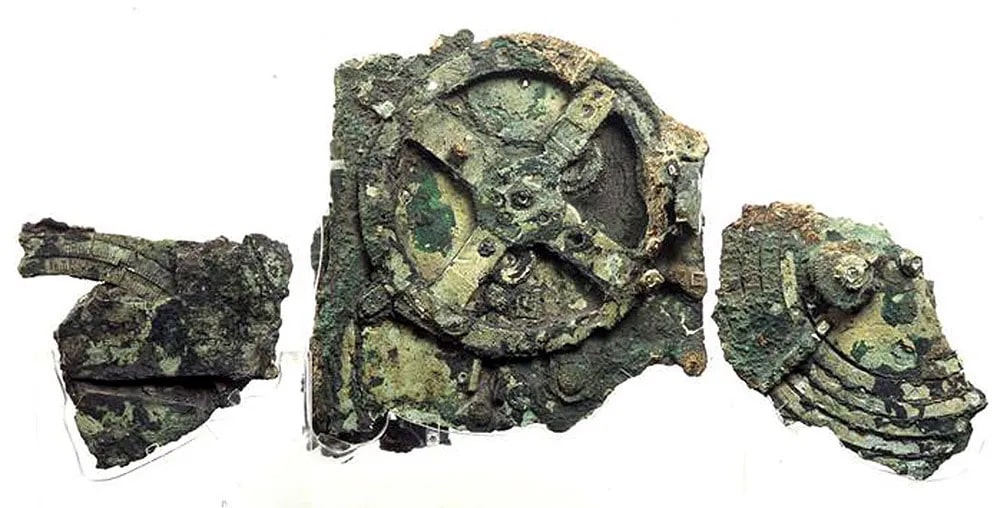

The most surprising discovery, however, was an unassuming lump of bronze recovered during the first excavation that was later found to be a complex set of interlocking gears capable of predicting the movement of the sun, moon, and several planets, as well as the timing of solar and lunar eclipses years into the future. The Antikythera Mechanism is believed to be an early computer used to plan important events including religious rituals, the early Olympic games, and agricultural activities.
Cover Photo: Marble base. Photo: Nikos Giannoulakis