The General Authority for Antiquities and Museums’ Dhamar branch has unveiled a remarkable archaeological find in Wadi Hijrat Munathidah, north of Dhamar city. The discovery illuminates the extraordinary technical skill of ancient Yemeni farmers in managing water resources for agriculture.
Underground Water Channel Unearthed
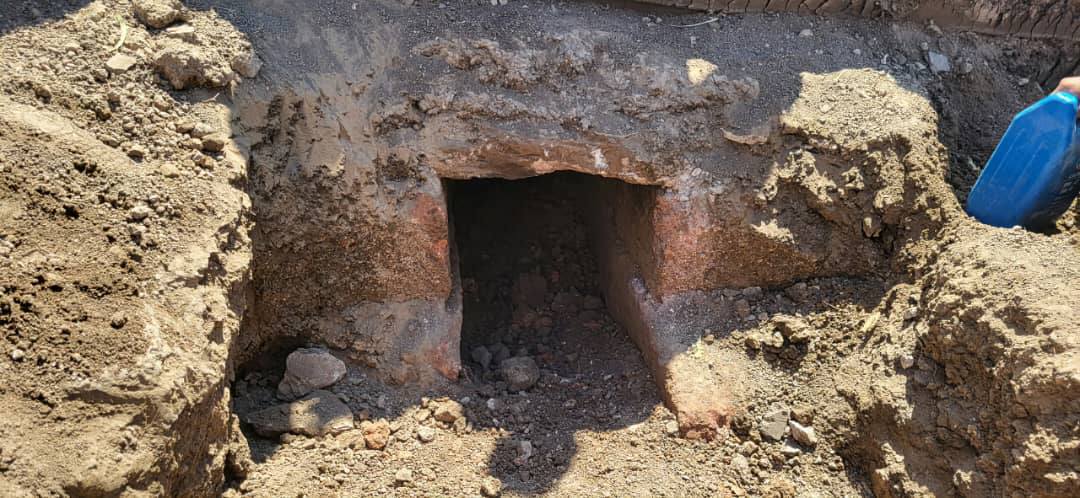
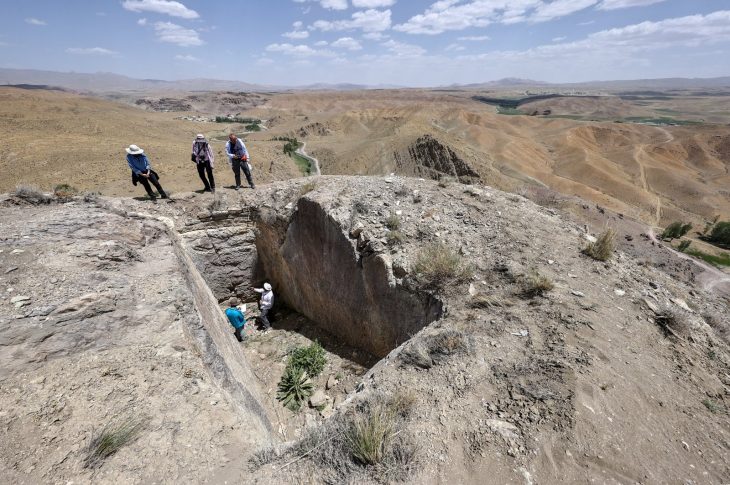
During works in the valley, archaeologists uncovered an underground water channel (tunnel) measuring approximately 1.5 to 2 meters deep and 0.5 meters wide, constructed from precisely cut stones and integrated into a wider valley irrigation network.
Dr. Fadl Al-Amisi, Director of the Authority’s Dhamar branch, commented that the tunnel served to transfer, store, regulate, and distribute water to support crop irrigation — a testament to the ancient Yemeni farmer’s ingenuity.
The tunnel runs from the southern to the northern side of the valley. Its walls are made of large, polished limestone blocks, and its roof is capped with flatter, harder stones locally known as “Al-Salal.” Over time, the tunnel’s interior had become covered by mud sediments.
Al-Amisi estimates that the structure may date back to the Sabaean or Himyarite periods — eras during which Yemen was known for advanced water management and civilizational development.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
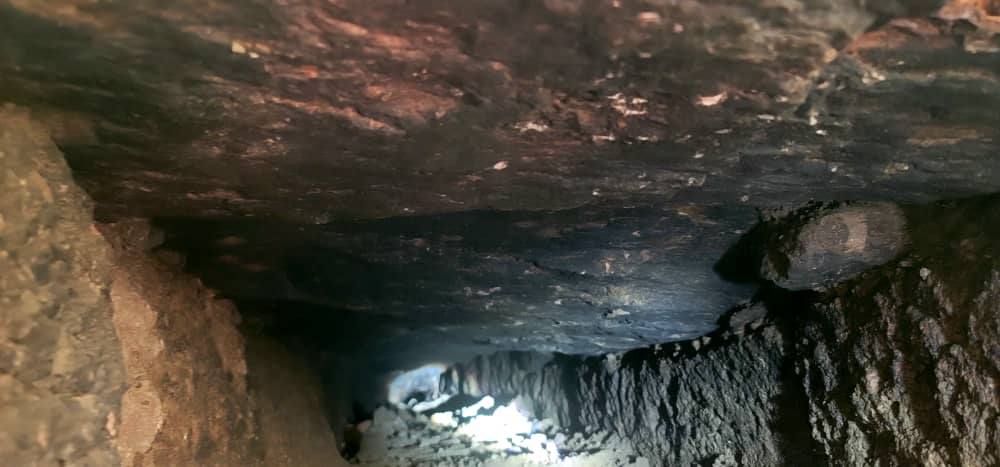

Location, Historical Context & Significance
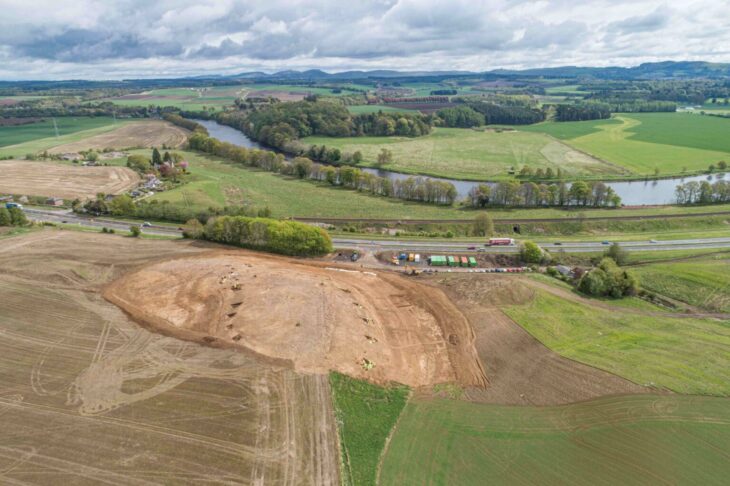
The channel lies on the eastern side of a watercourse in the middle of Hijrat Munathidah valley, one of the most fertile valleys in the Dhamar basin. Notably, it is near the ancient sites of Hijr Munathidah, Hijr Qureis, and Hijr Badash.
The find holds great historical and scientific importance, as Yemeni civilization has long been characterized as a “civilization of water and stone,” where water control was central to sustaining agriculture and life. The discovery may open paths to further research on how ancient inhabitants captured, stored, and drained water — techniques that underpinned the flourishing of civilization in arid environments.
Discovery Circumstances & Conservation Plans
Interestingly, the tunnel was discovered by chance, during the construction of a kareef — a traditional water-harvesting structure intended to capture rainwater and floods to recharge the groundwater basin. During construction, the workers encountered the stones of the ancient channel, leading to a halt in work and involvement of the Antiquities Authority.
Regrettably, about 10 meters of the channel had already been damaged before the discovery was recognized. In response, the Antiquities Authority and local leadership decided to stop further work, salvage exposed stones, and undertake scientifically guided restoration of the damaged section.
Dr. Al-Amisi emphasized the need for partial restoration, raising public awareness about preserving antiquities, and promoting field visits and study tours. He hopes to involve universities — notably faculties of agriculture, engineering, and antiquities — to examine the structure and learn directly from the ancient engineering.
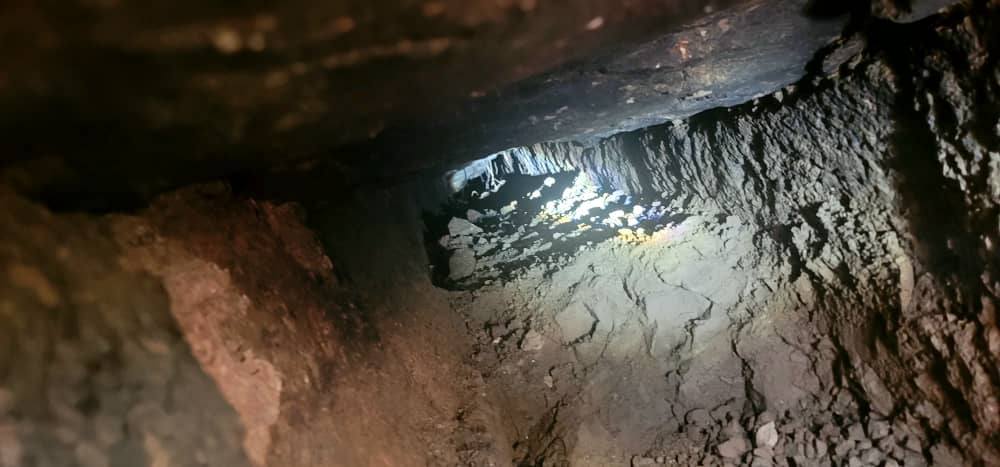

Comparable Discoveries & Broader Water Heritage in Yemen
Yemen is not without precedent in such finds. In March 2010, a similar network of channels was uncovered in the Al-Zabal area (Maifa’at Anas district), stretching about 200 meters. These tunnels were manually carved through rock, varying in width from 40 to 70 cm and in height up to 9 meters, roofed by flat rectangular stones.
That network collected water from springs and seasonal floods, channeling them through the valley system. It lies near other ancient sites that attest to continuous occupation from the Neolithic to Islamic periods.
Dhamar governorate is known for other historic water structures, such as the tunnels of Binoun and Bani Hadeejah in Al-Hada’a district, which similarly transfer water between valleys through remarkable engineering techniques.
Beyond Dhamar, Yemen’s long history of water infrastructure is well documented: ancient dams, agricultural terraces, cisterns, tunnels, and catchments formed a vital irrigation system across valleys and highlands. Many of these worked to harness rainfall rather than perennial rivers, reflecting clever adaptations to a challenging climate.
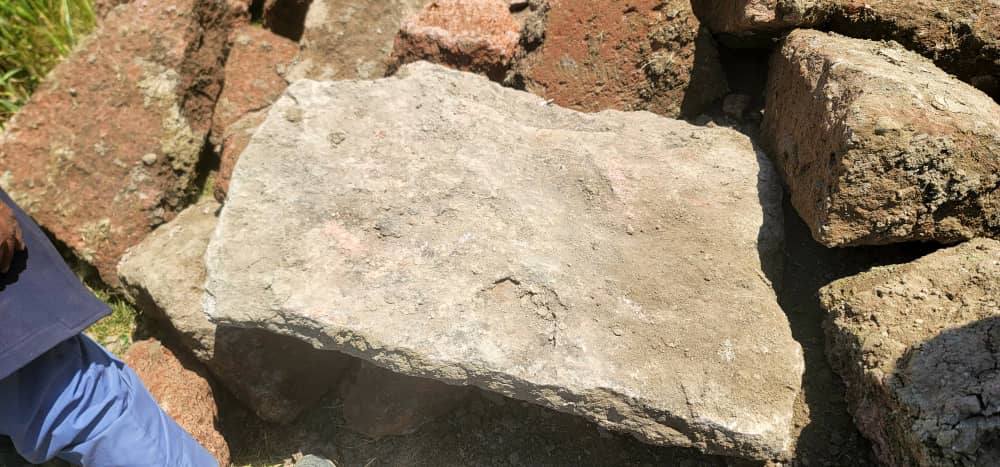

Why This Discovery Matters
This discovery is more than an archaeological curiosity; it highlights the remarkable sophistication of ancient Yemeni irrigation engineering, demonstrating how advanced water management systems played a central role in sustaining agriculture and civilization in the region.
The unearthed tunnel and its surrounding structures illustrate the innovative methods used to capture and channel seasonal rain and floodwater, reflecting early practices of water harvesting and environmental sustainability in arid conditions. Moreover, the find provides tangible evidence of civilizational continuity, deepening our understanding of Sabaean and Himyarite water technologies and their enduring legacy in the management of natural resources.
Beyond its historical value, the site also serves as a living classroom for heritage conservation and education, offering students, researchers, and local communities a direct opportunity to explore and learn from the engineering brilliance of Yemen’s ancient past.
Cover Image Credit: Dhamar via Facebook