New Research Connects Ritual Cursing to the Book of Revelation
From jealous lovers to petty thieves, people in the ancient Roman Empire found a unique and chilling way to deal with their grievances: they wrote curses on thin lead tablets and hid them in places believed to be gateways to the underworld. Now, Professor Dr. Michael Hölscher of Ruhr University Bochum is uncovering how these ancient rituals not only shaped daily religious life but even left their mark on the Bible itself.
“Between 500 BCE and 500 CE, cursing was a part of everyday religious practice in the Roman world,” explains Hölscher, an expert in New Testament exegesis. “Because these curses were often written down, we can still read and study them today.”
Curses on Lead: Ancient Magic with a Message
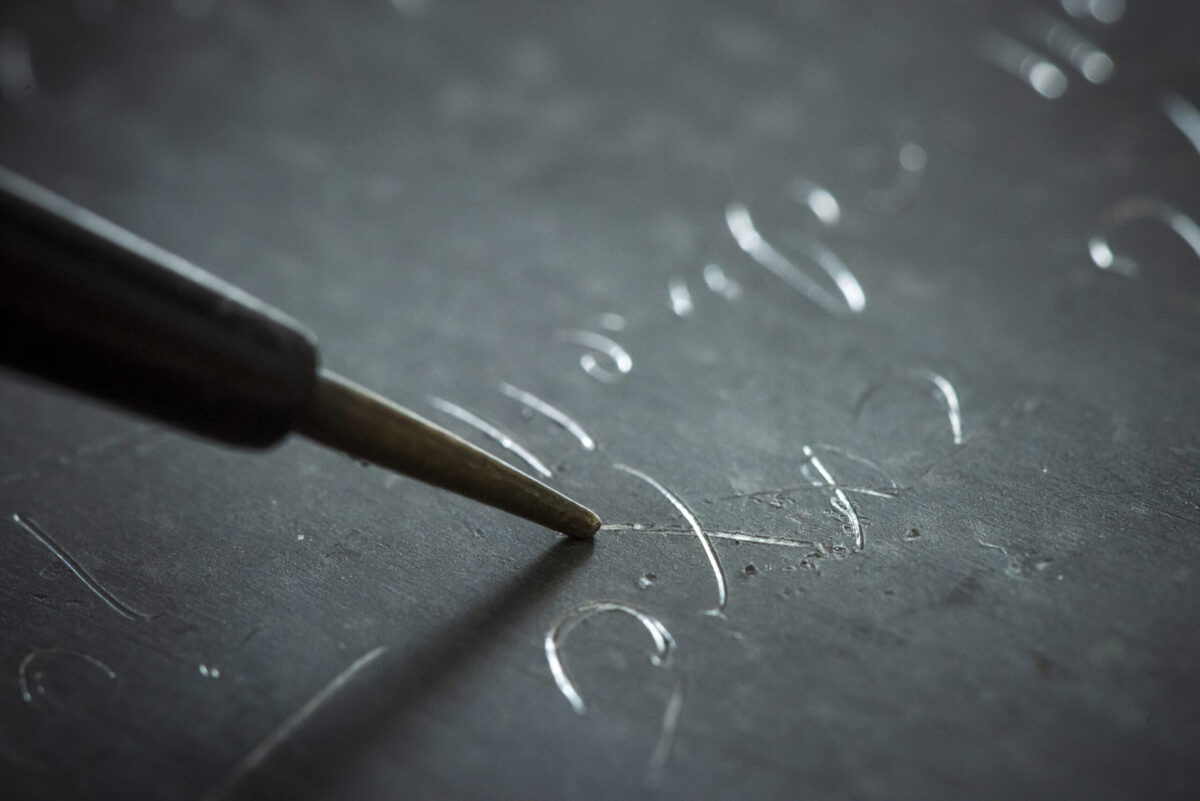
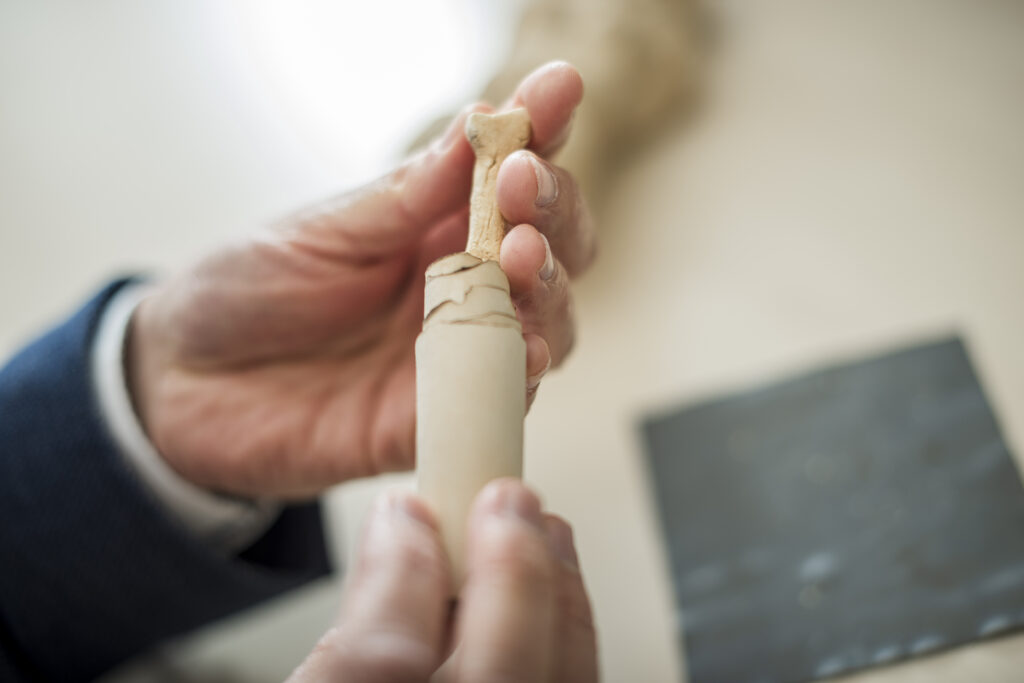
The so-called defixiones—thin lead tablets inscribed with malicious wishes—were often buried in graves, tossed into springs or the sea, or hidden near sacred sites. Some included symbolic items like pierced clay figurines or were wrapped around chicken bones to intensify the spell. The curses could be as vague as “whoever stole my bathing suit” or name specific enemies, often invoking gods or demons for support.
Importantly, the spell remained “active” as long as the tablet stayed hidden. If discovered and removed, the curse would lose its power.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
But these weren’t merely personal vendettas—according to Roman law, such practices were officially banned due to their perceived danger and magical nature. Yet the practice was widespread. Over 1,700 curse tablets have been found across the Roman world—from Rome to Trier, Asia Minor to Britain—often linked to the spread of Roman military culture.

The Forbidden Ritual that Echoes in the Bible
What sets Hölscher’s research apart is his examination of how this clandestine ritual cursing influenced early Christian texts, particularly the Book of Revelation. Believed to be written in Asia Minor under Roman rule, Revelation used heavily symbolic and coded language to offer hope to early Christian minorities living under oppression.
Several passages in Revelation closely mirror ancient curse rituals. For instance, in Chapter 13, a beast from the sea is described with blasphemous names on its heads—just like names etched onto a curse tablet. Hölscher interprets the beast as a stand-in for the Roman emperor, with the curse motif symbolizing divine condemnation.
Similarly, Chapter 18 describes the fall of Babylon—interpreted as a metaphor for Rome—with a great angel casting a stone into the sea, paralleling the act of sinking a curse tablet to banish an enemy. In doing so, Revelation turns the Romans’ own forbidden rituals against them, framing the God of the Christians as more powerful than any Roman deity.
More Than Magic: A Question of Language and Power
While cursing may seem primitive or vengeful, Hölscher emphasizes its theological and linguistic significance. “The Bible doesn’t only bless—it also curses,” he notes. Even Jesus curses the fig tree in the Gospels. These acts raise deeper ethical questions: Is it ever right to curse? How should we use our words? The ultimate message, according to Hölscher: language should be used more for blessing than for harm.

For a more in-depth look at how ancient cursing rituals relate to the Book of Revelation, you can read the full article in Rubin, the science magazine of Ruhr University Bochum, featured in its special issue on ‘Mystery’.
Cover Image Credit: The name of the person to be cursed was usually enough. However, the tablets often contained both standardized and personalized inscriptions. Credit: Damian Gorczany