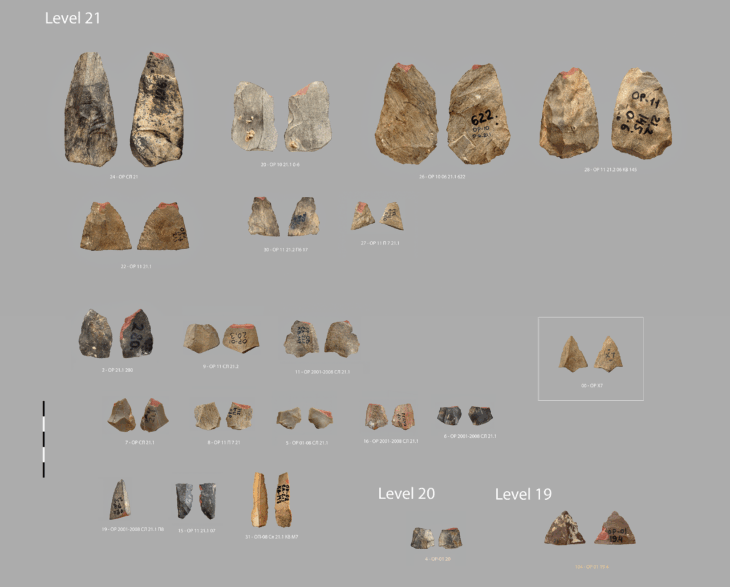
From August to October this year, the State Office for the Preservation of Monuments (LAD) in the Stuttgart Regional Council once again carried out archaeological research excavations near Altenburg (municipality of Jestetten). The late Celtic oppidum Altenburg-Rheinau was one of the most important large late Celtic settlements north of the Alps in the first century BC.
The finds provide insights into the everyday life of the Celts and reveal the importance of the settlement as a center for specialized crafts and trade with the Mediterranean region.
The oppidum of Altenburg-Rheinau occupies two peninsulas: the Schwaben peninsula, on the German side, and the Au peninsula, on the Swiss side, both enclosed by defensive walls.
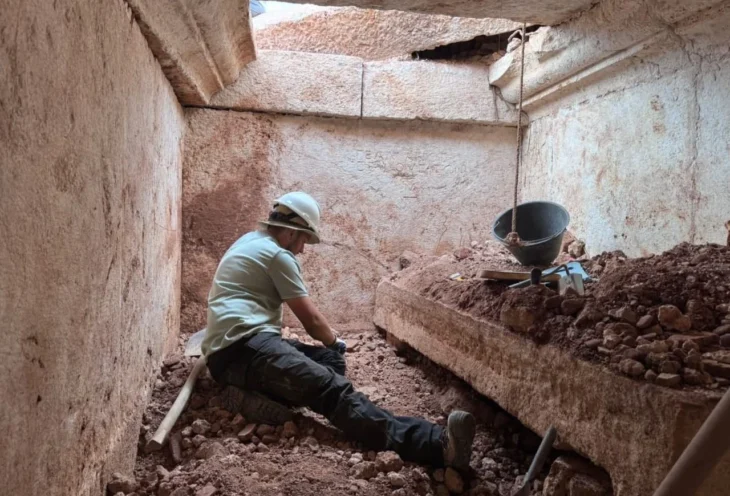
Excavations carried out by the University of Tübingen in the 1970s had already provided initial insights into the settlement structures on the 233-hectare ‘Schwaben’ peninsula, where the main rampart ‘Schanz’ demarcated the oppidum from the hinterland. The opposite peninsula ‘Au’ on the Swiss side was also protected by a rampart, with a settlement area of around 88 hectares. The LAD had already carried out archaeological investigations at various locations on the ‘Schwaben peninsula in 2022 and 2023. During the excavations that year, which took place close to the rampart, numerous backfilled pits were uncovered.

‘Characteristic features were several large, cylindrical pits with clearly distinguishable backfill layers that were up to two and a half metres deep,’ reports project manager Dr. Günther Wieland, Head of the Metal Age Department at the LAD.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
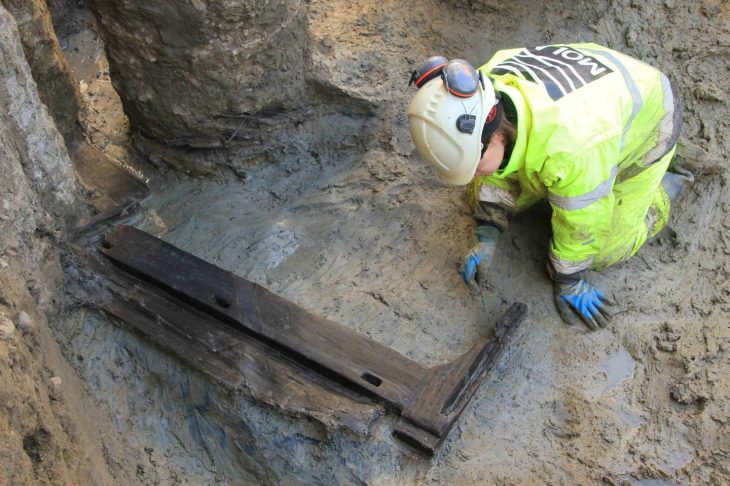
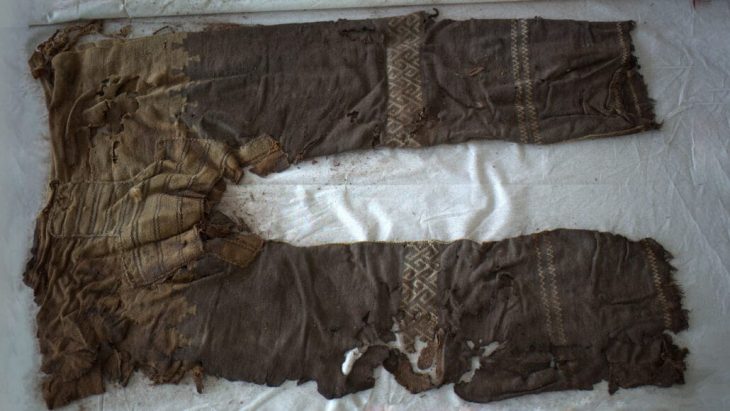
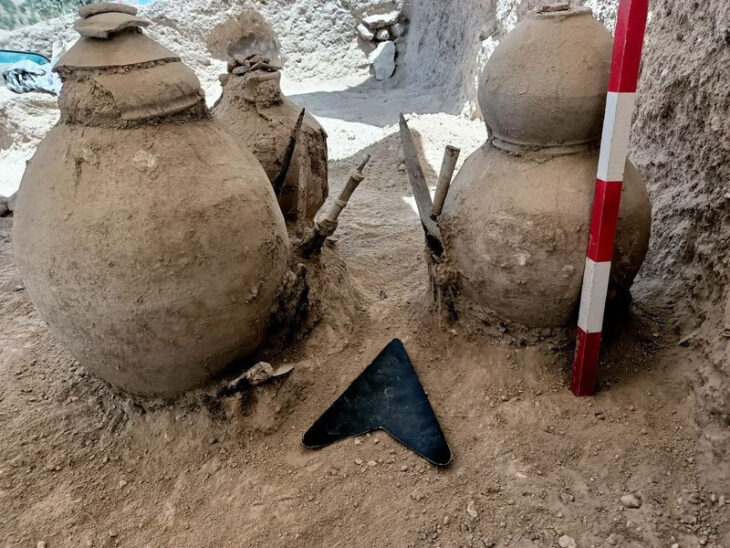
Traces of wall linings made of organic material suggest that these were originally storage pits for storing food. Large pits with a rectangular-oval floor plan were probably earth cellars that were accessible via an earth staircase or ramp. However, hardly any findings of associated house constructions have been found so far. Only the floor plan of a square post structure was uncovered, which, according to Wieland, was probably not a residential building but a storage building.

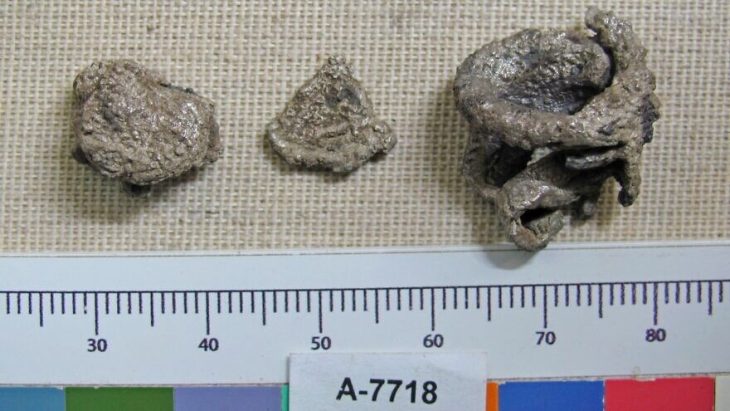
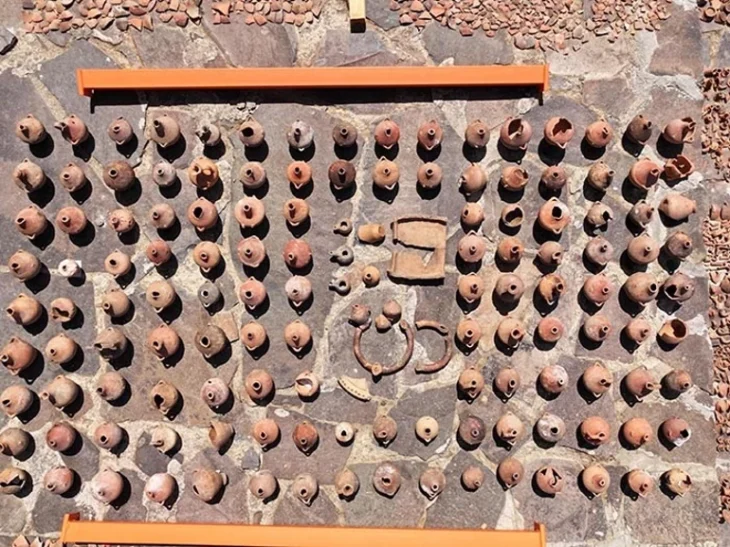
The excavations in 2022, 2023 and this year also yielded extensive finds. ‘In addition to local coarse and fine pottery, fragments of imported wine amphorae from Italy are particularly noteworthy,’ continues Wieland, “Wine from the Mediterranean was a coveted luxury good among the Celtic upper class and the basis for a lucrative trade”. Numerous Celtic coins that have been found can also be seen in this context: ‘The coinage economy was a key factor in flourishing trade,’ says Wieland. An insight into the everyday culture of the late Celtic period is provided by some ornately decorated costume components made of bronze and iron, such as numerous fibulae (garment clasps) and belt components. Their chronological classification makes it clear that the oppidum of Altenburg-Rheinau must have still existed in the 1st century BC, when most Celtic settlements in south-west Germany had already been abandoned.
Wieland describes a bone stylus found in 2023 as particularly interesting, a writing stylus used to write on wax tablets according to Mediterranean custom: “This is rare evidence of the use of writing in the oppidum, which, along with the coin economy, was an essential prerequisite for trade with the Mediterranean region.”

This object not only demonstrates the use of writing at the settlement but also underscores the administrative and economic sophistication necessary to sustain extensive trade exchanges.
The large quantities of well-preserved animal bones found also provide insights into the oppidum’s economic system, settlement organization, and long-distance relationships. These included mainly cattle bones, which indicate organized livestock farming and specialized meat production.
The excavation received extensive support on-site from volunteers and the municipality of Jestetten. In October, numerous visitors took the opportunity to learn more on-site and gain insight into the ongoing excavations.
Further research excavations are planned in Altenburg for 2025.
State Office for the Preservation of Monuments (LAD)
Cover Image Credit: Francois Ohl / LAD