Steel tools were believed to have only become widespread in Europe during the Roman Empire, but a recent study shows that steel tools were already in use in Europe around 2,900 years ago, during the Final Bronze Age.
The study, conducted by researchers from the University of Freiburg, sheds new light on the early history of steel production in Europe. A study by an international and interdisciplinary team headed by Freiburg archaeologist Dr. Ralph Araque Gonzalez from the Faculty of Humanities has proven that steel tools were already in use in Europe around 2900 years ago.
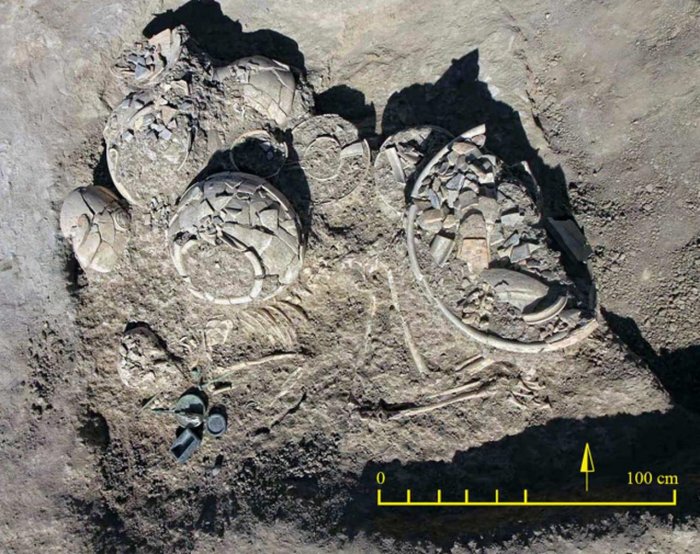
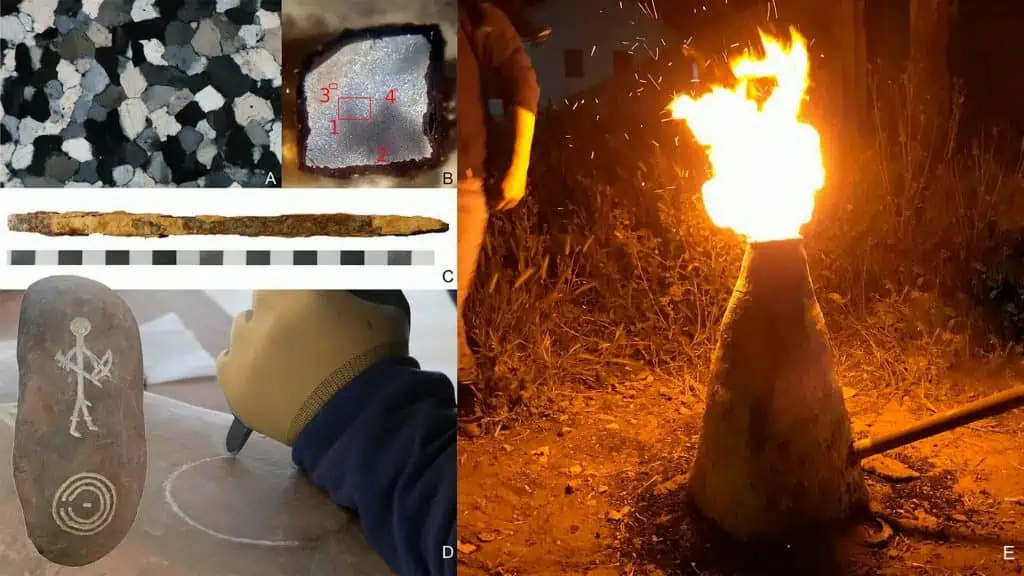
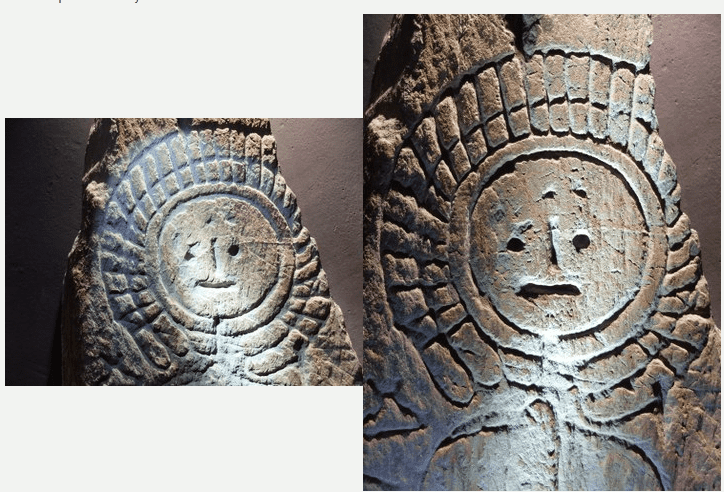
Using geochemical analyses, the researchers were able to prove that stone stelae on the Iberian peninsula that date back to the Final Bronze Age feature complex engravings that could only have been done using tempered steel.
Ancient Iberian stelae, upright monuments typically inscribed with information in the form of text, images, or a combination of the two, were found to be made of silicated quartz sandstone after the researchers conducted geochemical analyses.

“Just like quartzite, this is an extremely hard rock that cannot be worked with bronze or stone tools, but only with tempered steel,” said Araque Gonzalez.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
The researchers examined an iron chisel from the Final Bronze Age that was also discovered in Rocha do Vigio, Portugal, to confirm their suspicion that these monuments were etched with steel tools. To work with the tough silicated quartz sandstone, they learned that the chisel was made of heterogeneous but remarkably carbon-rich steel.
The result was also confirmed experimentally by undertaking trials with chisels made of various materials: only the chisel made of tempered steel was suitably capable of engraving the stone.

Until recently it was assumed that it was not possible to produce suitable quality steel in the Early Iron Age and certainly not in the Final Bronze Age, and that it only came to be widespread in Europe under the Roman Empire. “The chisel from Rocha do Vigio and the context where it was found show that iron metallurgy including the production and tempering of steel were probably indigenous developments of decentralized small communities in Iberia, and not due to the influence of later colonization processes.
This also has consequences for the archaeological assessment of iron metallurgy and quartzite sculptures in other regions of the world,” explains Araque Gonzalez.
The study ‘Stone-working and the earliest steel in Iberia: Scientific analyses and experimental replications of final bronze age stelae and tools’ has been published in the Journal of Archaeological Science.