It is aimed to reach new information about the traditions of the Hittite civilization with 249 new hieroglyphs discovered in the Yerkapı Tunnel in Hattusa the capital of the Hittites.
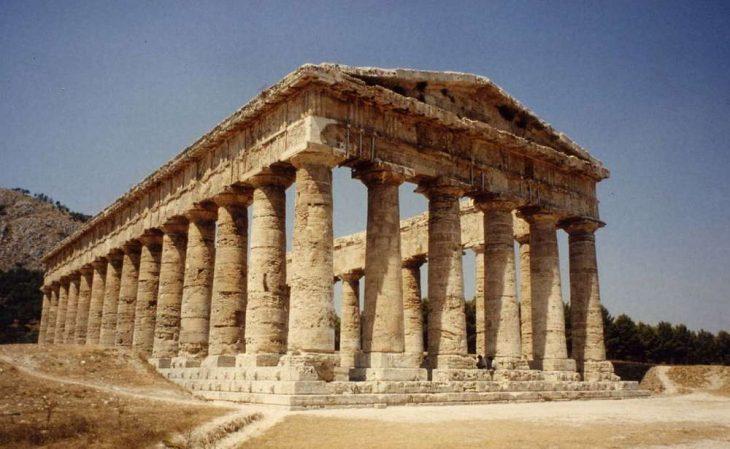
Hattusa, located in Türkiye’s (Turkey) Anatolian heartland province of Corum, was added to the UNESCO World Heritage Site list in 1986. The remnants of the Hittite Capital date back to the Bronze Age, around 2000 BC. The Hittites were a remarkable civilization. The kingdom stretched from the Aegean across Anatolia, northern Syria, and to the Euphrates river.
Archaeological excavations, which started in 1907 at the archaeological site of Hattusa in the Boğazkale district of Çorum, the capital of the Hittites, one of the first civilizations of Anatolia, continue under the direction of Professor Andreas Schachner from the German Archaeological Institute.
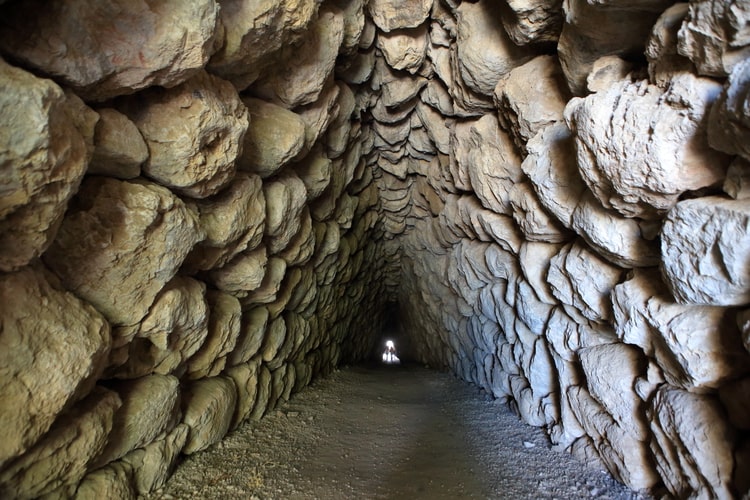
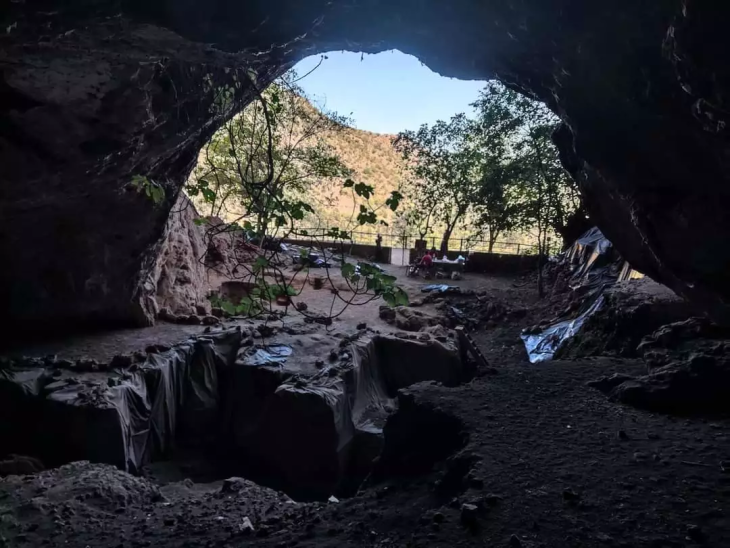
During the excavations carried out by archaeologists, Hittitologists, and scientists from different fields of expertise from different countries and universities, new symbols, estimated to have been drawn about 3,500 years ago, were found in the Yerkapı Tunnel, which was built using thousands of stones.
The Turkish word Yerkapı, which means “the gate in the ground,” perfectly describes this section of Hattusha fortifications. It is situated within an artificial embankment that serves as the southernmost point of the city walls. At its base, the embankment is 15 meters high, 250 meters long, and 80 meters wide.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
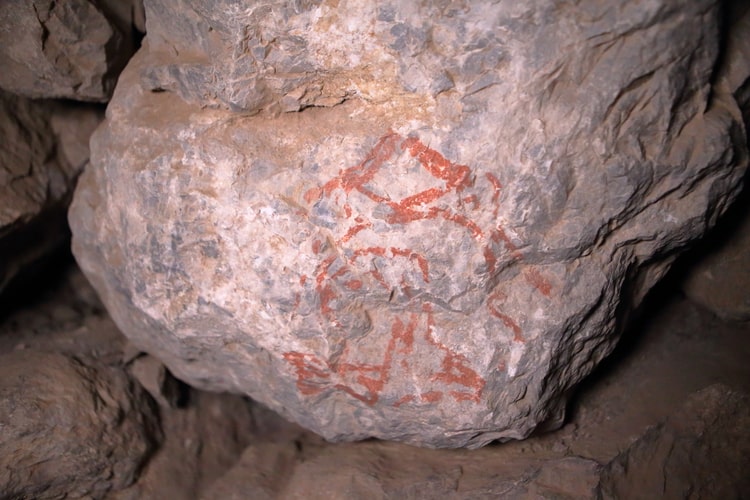

Associate Professor Bülent Genç, a member of the Mardin Artuklu University Archeology Department, who is one of the excavation team, noticed the symbols thought to have been drawn with madder on the stones in the middle of the Yerkapı Tunnel while he was visiting the site to take photos with the students on August 13.
Having identified 249 symbols in the tunnel, Genç shared his discovery with the excavation head, Schachner. Schachner also brought hieroglyphs to the scientific world by having the Yerkapi and symbols scanned in 3D.
Due to the Yerkapı tunnel’s nearly constant temperature throughout the year and that it is in a dark environment without sunlight and rain, it is estimated that the signs have survived to the present without deterioration for thousands of years.
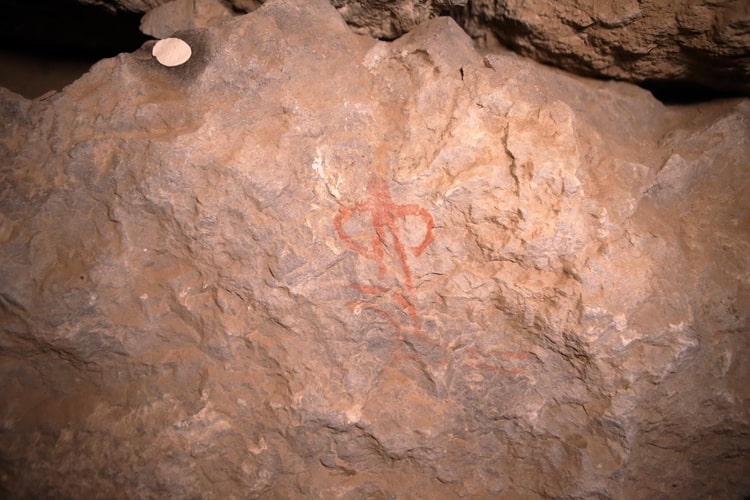

A study has been started on the meanings of the signs
Schachner said that scientists from different specialties continue to examine the 249 hieroglyphs, which are considered to be depictions of gods.
Schachner said that the archaeological excavations in Hattusa started from Yerkapı in 1907, and that everyone who has excavated, including himself, has passed through the tunnel dozens of times, but no one noticed the hieroglyphs.
Schachner also, stated that after the discovery, Hittitologist Associate Professor Metin Alparslan from Istanbul University started working to determine what meanings the symbols might have.
This elaborate structure, whose Hittite name we do not know yet, was not used for defense purposes but was most likely a part of cult ceremonies associated with the temples in the north of the city.
Schachner pointed out that with the newly found hieroglyphs, they will have the opportunity to better understand what the tunnel was used for. While some of the markings are too worn to be read, most are well preserved and clearly legible.
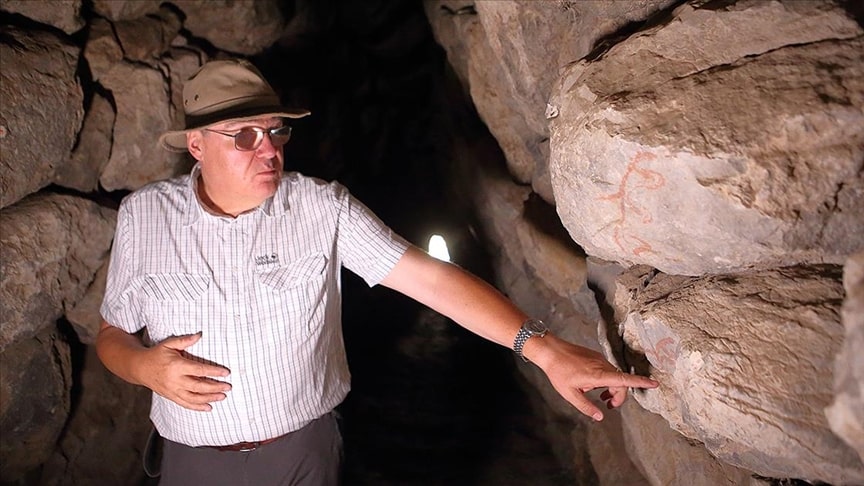

Pointing out that the hieroglyphs in the tunnel are similar, Schachner said, “When we share the symbols with the scientific world, our colleagues working on the Hittites will have an opinion and maybe one or maybe several ideas will emerge accordingly. We have identified a total of 249 Anatolian hieroglyphs here, but they are not all different from each other. We can divide them into 8 groups in total. They add innovation to us socially. Since they are written with paint, we need to interpret them more in the style of graffiti. We think it was done quickly and so that it could be understood quickly,” said.
Stating that most of the hieroglyphs found in Anatolia are seen in monumental inscriptions or seals that have their own meanings, Schachner underlined that the discovery of the symbols in the tunnel led to the idea that hieroglyphics were used much more widely in the Hittite period.
Expressing that they are excited to discover something new from an archaeological point of view, Schachner said:
“We know the Hittites mostly from the cuneiform texts, but we see that the Hittites and Hittite culture also have a different and unique Anatolian writing system. The interesting thing is that after the Hittite state collapsed, the cuneiform writing disappeared, but Anatolian hieroglyphs continue to be used. In the southern part of Central Anatolia, especially in Southeast Anatolia, we see that such inscriptions were used for another 400 years during the Iron Age, that is, following the Hittites.”