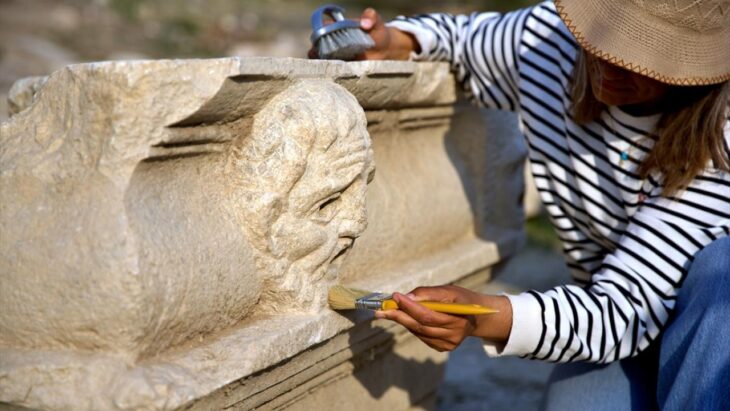
Archaeological excavations have been taking place on the Posaer Berg (Posa Hill) near Zeitz (Burgenland) every year since 2017. They have already provided numerous surprising insights into the history of construction and use as well as new insights into the historical significance of the medieval complex on the prominent mountain spur above the Elsteraue.
The focus of the ongoing investigations, which are being carried out by the State Office for the Preservation of Monuments and Archeology in Saxony-Anhalt and the newly founded “Association for the Promotion of Archeology and Historical Research in Zeitz e. V.” are carried out, is the area where the cloister of the monastery was once located. Despite the demolition of the buildings to extract stone material for the construction of the Zeitz Moritzburg and the subsequent leveling of the site in the 17th century, parts of the cloister were found here in an unexpectedly good state of preservation. A special find and a real architectural gem is a perfectly intact ornate keystone that comes from its vault.
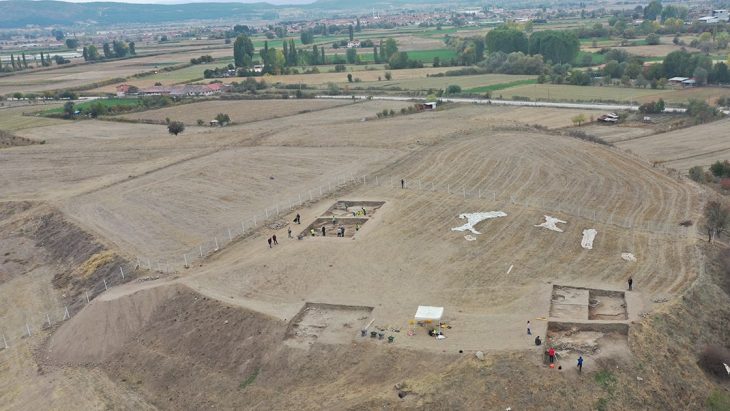
Since 2017, with the support of the ›Kultur- und Bildungsstätte Kloster Posa e. V.‹ and committed volunteers, annual archaeological excavations take place on the Posa hill under the direction of Holger Rode. The results of investigations in recent years indicate that there was a castle of considerable importance here as early as the 9th and 10th centuries, in which the first church building was possibly built as early as the 10th century. In 1114 a Benedictine monastery was founded on the prominent mountain spur above the Elsteraue, which almost completely disappeared by the 17th century. In 2017, architectural remains revealed the location of the monastery church.
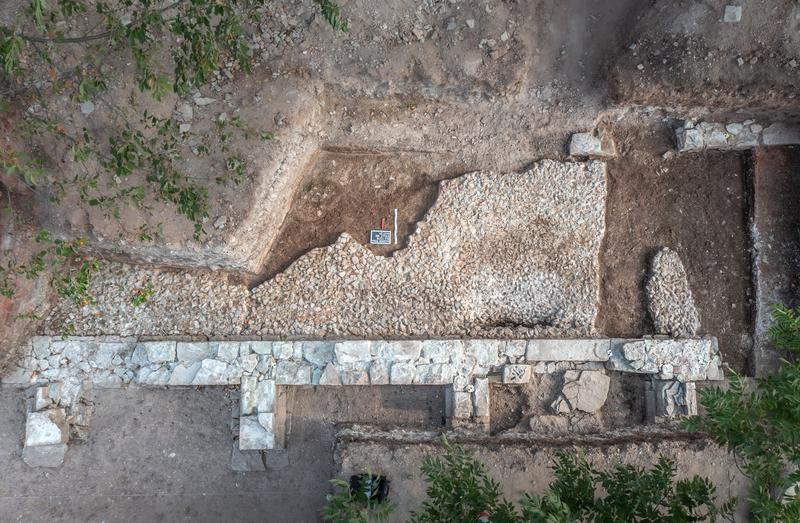
The focus of the current excavation, which has been ongoing since March 2023, is the area south of the church, where the cloister of the monastery was once located.

The investigations are being carried out by the State Office for Heritage Management and Archaeology Saxony-Anhalt (LDA) and the newly founded ‘Association for the Promotion of Archeology and Historical Research Zeitz e.V.’.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
First of all, the massive accumulation of rubble that had been leveled on the area after the demolition of the monastery from about 1657 was cleared. At that time, the monastery served as a quarry for the extraction of building material for the new construction of Moritzburg Castle in Zeitz. Large areas of the foundations of the monastery buildings were also broken down to the last stone.
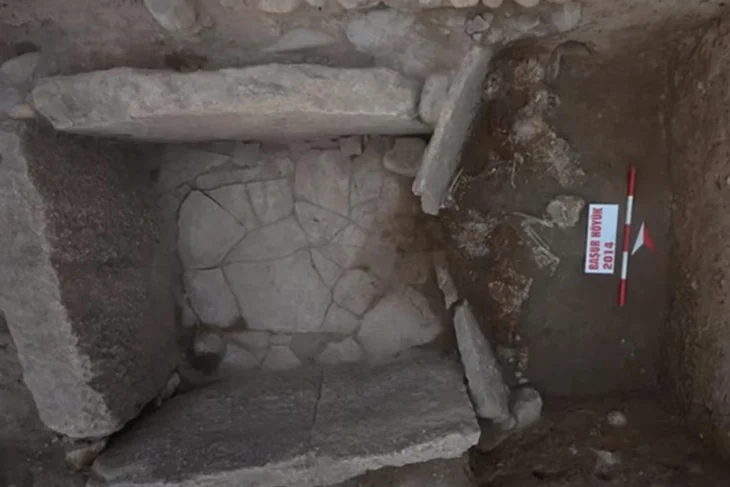
Beneath this leveled layer of debris, some parts of the south wing of the enclosure were found in an unexpectedly good state of preservation.
The north facade of the cloister is still about 70 centimeters high over a length of about 10 meters. The buttresses made of ashlar masonry towards the cross courtyard are particularly impressive. There are even remains of plaster on the inside of the cloister. The floors of the southern cloister wing are still almost complete. The upper one consisted mainly of very high-quality red brick chippings, which was probably supposed to have the appearance of red marble.
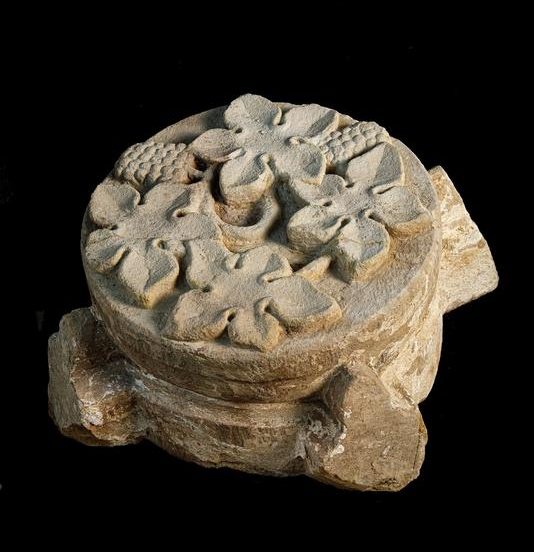

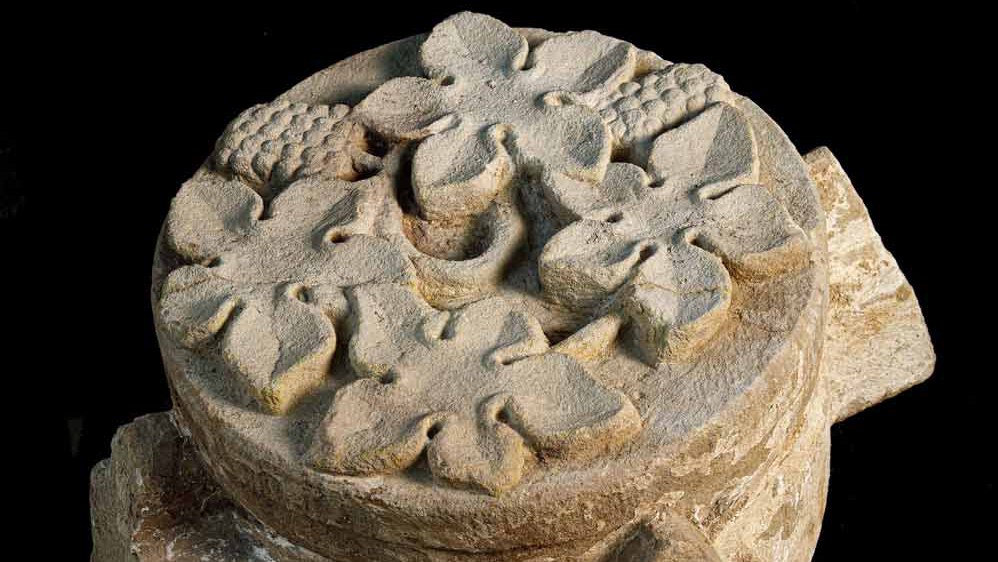
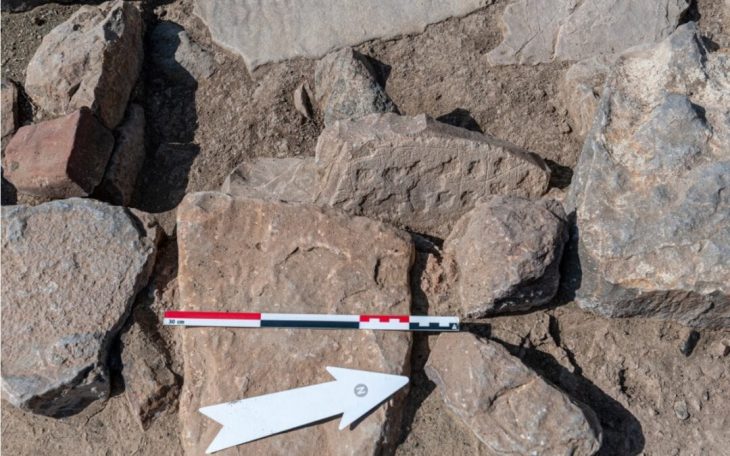
Flaws in the screed floor indicate the position of grave slabs, which were removed as valuable building material. Surprisingly, larger sandstones were also found in the up to 1.80 meter thick layers of rubble above the ruins, which had obviously been overlooked when the building material was salvaged or were perhaps simply too heavy. In addition to parts of the vaulted ribs of the cloister, some of which still have remnants of a red paint finish, a completely intact keystone of the former cloister vault represents a special find. Vine leaves and grapes are depicted on its face. They refer to the long history of local viticulture, which was successfully revived just a few years ago.
The finding of the keystone and some other stones now allows a comparatively exact dating of the southern wing of the cloister to the end of the first third of the 14th century. Comparable stones of this type are known from the cloister of the Zeitz Cathedral and the Naumburg Cathedral.
The 14th-century cloister at Posa replaced a Romanesque predecessor. The monastery church, rediscovered in 2017, also shows a modernization of the originally Romanesque building in the Gothic style during the 14th century.

Further archaeological investigations will focus on parts of the southern and eastern cloister wing and the cross courtyard. The aim is to learn more about the older church, believed to be beneath the Gothic and Romanesque walls and floors. The first traces of this presumed early sacred building have been uncovered in recent years. It was probably built in the 10th century and burned down at the end of the 11th century. Findings from the 9th century are also of great scientific interest. They are the oldest evidence of a settlement on Posa Hill and are closely related to the large ramparts that enclose the entire mountain.
The research excavation in Posa will continue throughout the year.
Landesamt für Denkmalpflege und Archäologie Sachsen-Anhalt
Cover Photo: Philipp Baumgarten