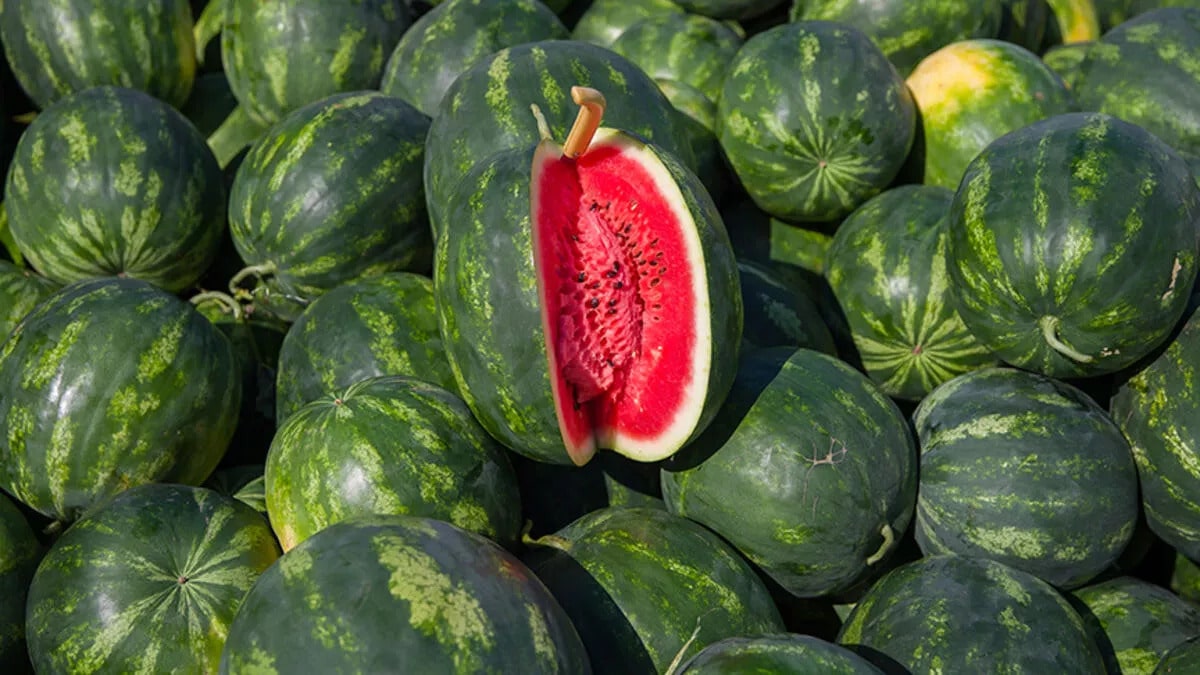
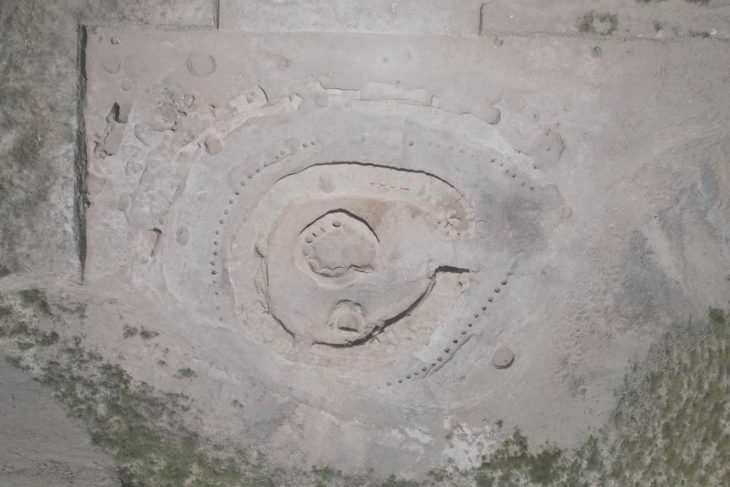
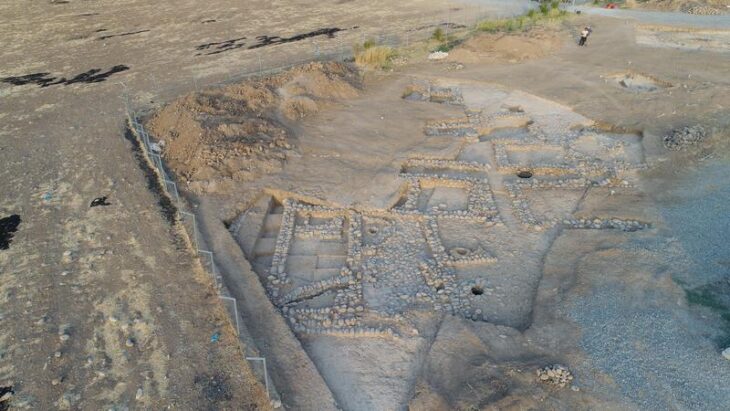
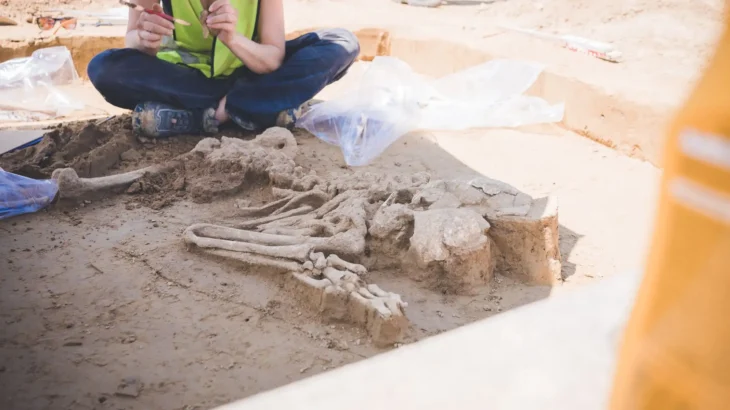
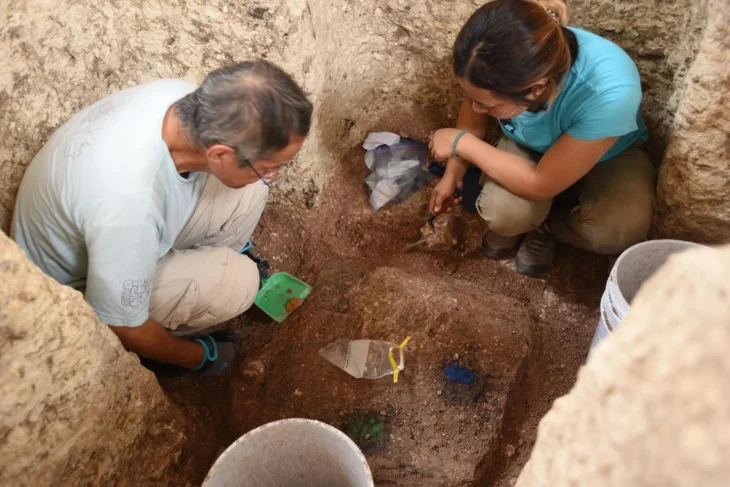
The earliest known seeds from a watermelon related were discovered during an archaeological dig in Libya, going back 6,000 years to the Neolithic period. An examination of these seeds performed by biologist Susanne S. Renner of Washington University in St. Louis offers some surprises about how our ancestors used a predecessor of today’s watermelon.
These results and two new genomes of ancient seeds are published in the journal Molecular Biology and Evolution.
Scientists generally agree that watermelons came from Africa, but exactly where and when watermelons with red, sweet flesh were first domesticated from their wild form is debatable. The most recent data point to watermelon getting its start in the Nile valley, which is consistent with archaeological evidence.
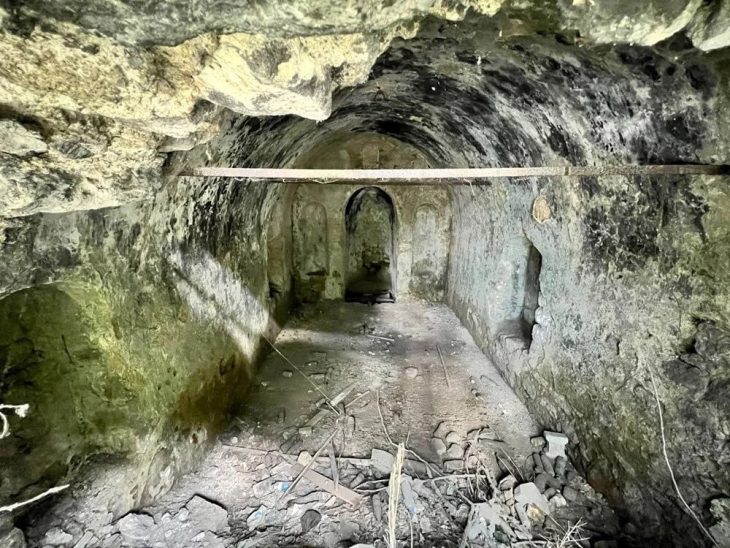
However, the very old seeds discovered at Uan Muhuggiag, a rock shelter in what is now the Sahara Desert in Libya, seemed at odds with this explanation. There was no way to be certain of their identity prior to this investigation.
“The oldest seeds of watermelons cannot be securely identified as either belonging to a sweet-pulped domesticated form, or instead to one of the bitter-pulped wild forms,” said Renner, an honorary professor of biology in Arts & Sciences. “The seeds of the seven species of Citrullus are basically undistinguishable.”
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
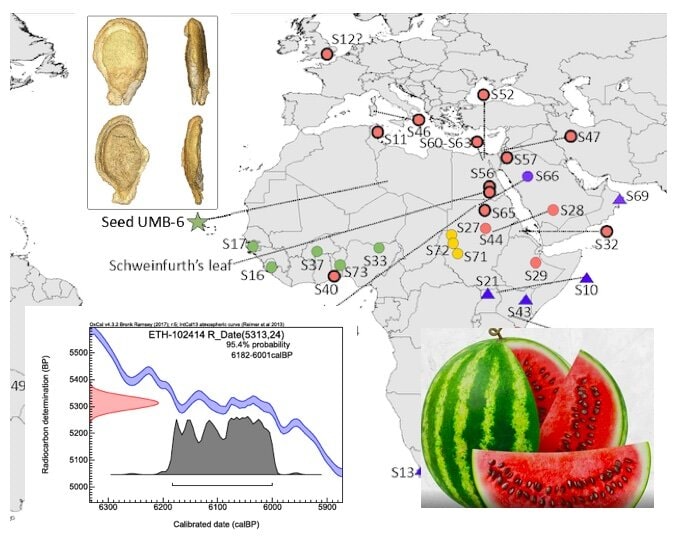
“Now, having a chromosome-level genome, we can be sure that Neolithic Libyans were using a bitter-fleshed watermelon,” she said. “We suspect they used the fruits to get at the (numerous!) seeds, which even today are eaten air-dried or roasted or also boiled in soups or stews.”
Co-senior author Guillaume Chomicki, a National Environmental Research Council fellow at the University of Sheffield in the United Kingdom, collected dozens of samples of watermelon and watermelon relatives from herbarium specimens in the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew, as part of the quest to trace the path of watermelon’s domestication.
He and Renner also obtained much older samples: the 6,000-year-old Libyan seeds and another set of 3,300-year-old Sudanese seeds.
“These seeds were a riddle because they were thought to be the oldest true watermelon seeds,” Chomicki said. “Yet they were from Libya, which was never thought to be the cradle of watermelon domestication.”
The scientists generated genome sequences from the seeds from Libya and Sudan and from the herbarium collections, and analyzed these data together with resequenced genomes from important germplasm collections. They discovered that the oldest seeds came from a plant known as an egusi melon, a watermelon relative that is currently restricted to western Africa.
“Both plant ‘fossils’ were C-14 dated and, as far as we know, are among the oldest plant genomes ever obtained,” Renner said.
“An unexpected new insight is that Citrullus appears to have initially been collected or cultivated for its seeds, not its sweet flesh, consistent with seed damage patterns induced by human teeth in the oldest Libyan material,” Chomicki said. “This study documents the use of the seeds (rather than the fruit) of a watermelon relative more than 6,000 years ago, prior to the domestication of the watermelon.”
“Watermelons — the wild species, as well as the domesticated form — have very numerous seeds that are tasty and oil-rich,” Renner said. “Different from the pulp, the seeds never contain the extremely bitter cucurbitacin chemical. Snacking on those easily available nutritious seeds may have been a good thing.”