Medieval warhorses are often depicted as massive and powerful beasts, but in reality, many were no more than pony-sized by modern standards, a new study shows.
Horses during the period were often below 14.2 hands high, but the size was clearly not everything, as historical records indicate huge sums were spent on developing and maintaining networks for the breeding, training, and keeping of horses used in combat.
A team of archaeologists and historians searching for the truth about the Great Horse have found they were not always bred for size, but for success in a wide range of different functions – including tournaments and long-distance raiding campaigns.
Researchers analyzed the largest dataset of English horse bones dating between AD 300 and 1650, found at 171 separate archaeological sites.
The study, published in the International Journal of Osteoarchaeology, shows that breeding and training of warhorses was influenced by a combination of biological and cultural factors, as well as behavioral characteristics of the horses themselves such as temperament.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
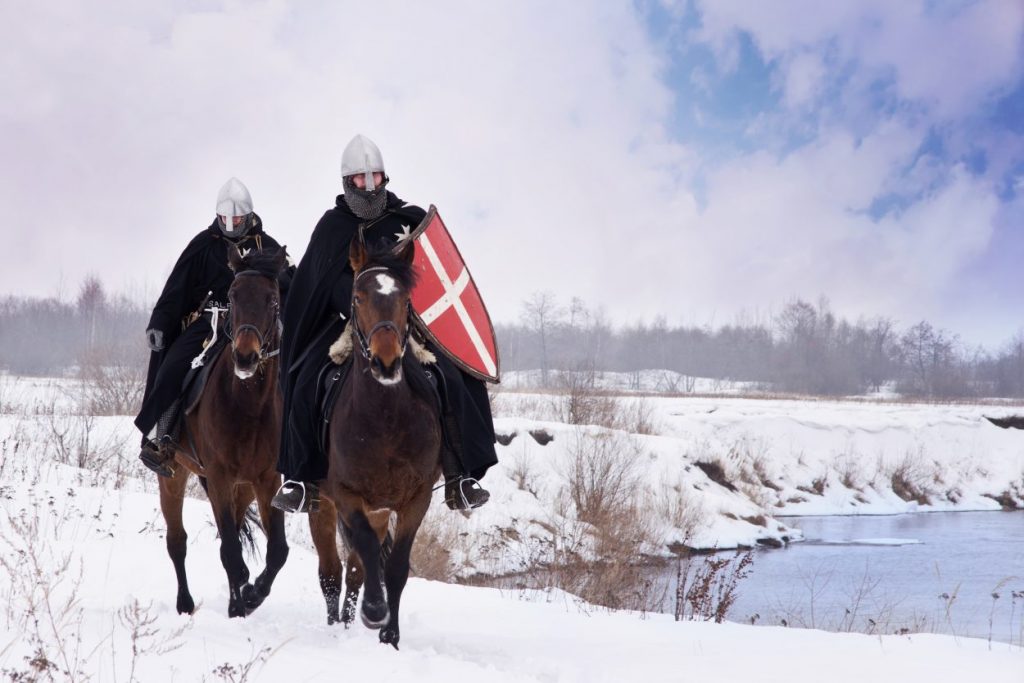

Depictions of medieval warhorses in films and popular media frequently portray massive mounts on the scale of Shire horses, some 17 to 18 hands high. However, the evidence suggests that horses of 16 and even 15 hands were very rare indeed, even at the height of the royal stud network during the 13th and 14th centuries and that animals of this size would have been seen as very large by medieval people.
Researcher Helene Benkert, from the University of Exeter, said: “Neither size nor limb bone robusticity alone, are enough to confidently identify warhorses in the archaeological record. Historic records don’t give the specific criteria which defined a warhorse; it is much more likely that throughout the medieval period, at different times, different conformations of horses were desirable in response to changing battlefield tactics and cultural preferences.”
The tallest Norman horse recorded was found at Trowbridge Castle, Wiltshire, estimated to be about 15hh, similar to the size of small modern light riding horses. The high medieval period (1200-1350 AD) sees the first emergence of horses of around 16hh, although it is not until the post-medieval period (1500-1650 AD) that the average height of horses becomes significantly larger, finally approaching the sizes of modern warmblood and draft horses.

Professor Alan Outram, from the University of Exeter, said: “High medieval destriers may have been relatively large for the time period, but were clearly still much smaller than we might expect for equivalent functions today. Selection and breeding practices in the Royal studs may have focused as much on temperament and the correct physical characteristics for warfare as they did on raw size.”
Professor Oliver Creighton, the Principal Investigator for the project, commented: “The warhorse is central to our understanding of medieval English society and culture as both a symbol of status closely associated with the development of aristocratic identity and as a weapon of war famed for its mobility and shock value, changing the face of battle.“