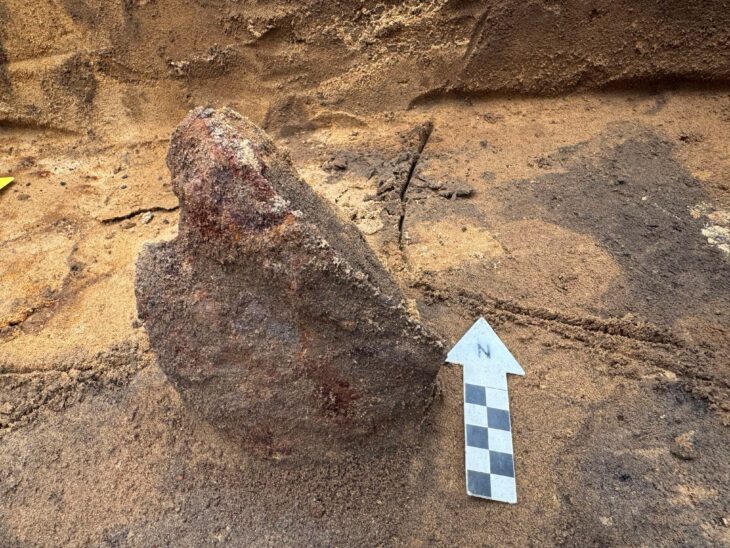
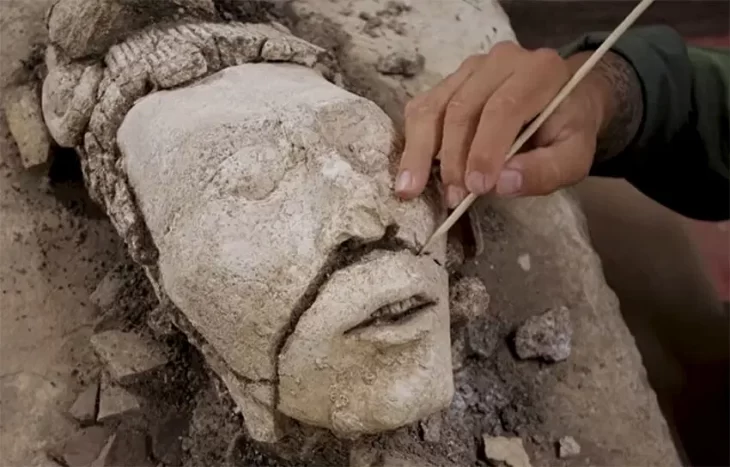
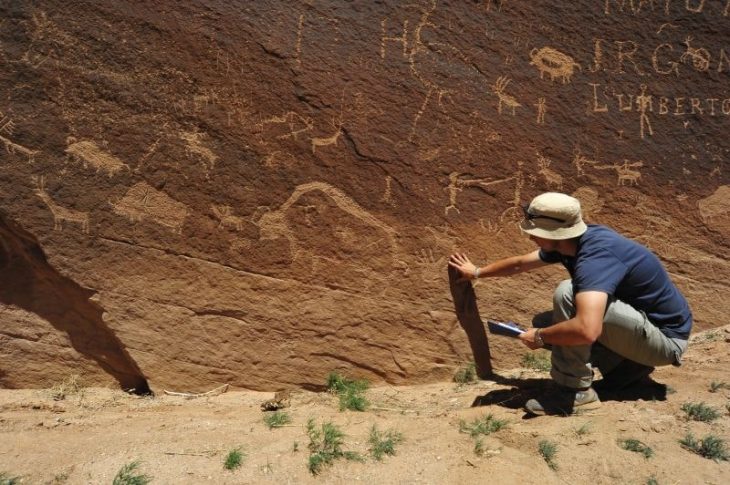
Saudi Arabia’s Heritage Commission announced the discovery of a rare bilingual inscription in the village of Alqan in the Tabuk region, reported the Saudi Press Agency (SPA) on Wednesday.
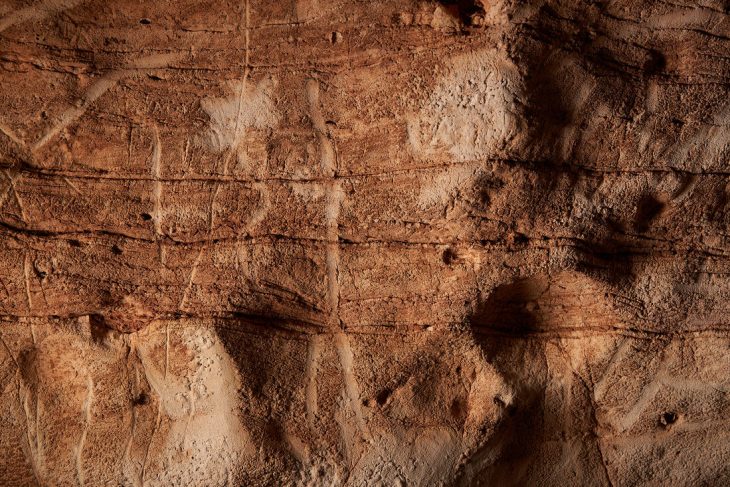
The piece, found during an archaeological dig in the village of Alqan, comprises two lines in Thamudic script and one in early Arabic.
Thamudic inscriptions belong to a South Semitic Language related to Arabic, the Thamudic language. This language is an Ancient North Arabian dialect known from pre-Islamic inscriptions carved on stones in regions stretching between the Arabian Desert and the Sinai. The Thamudic script is considered a variant of the South Arabian one.
Thamudic inscriptions usually date back to the period extending between the 4th century BC and the 3rd or 4th century AD. However, the style of the characters suggests the piece dates from the 5th century.
The discovery is a component of the commission’s ongoing archaeological survey efforts throughout the Kingdom. The inscription is thought to have been written in the fifth century AD based on research on letter forms and their evolution. The inscription is a combination between the Thamudic script and early Arabic script, standing as a living proof of the continued use of the Thamudic script in the 5th century AD.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
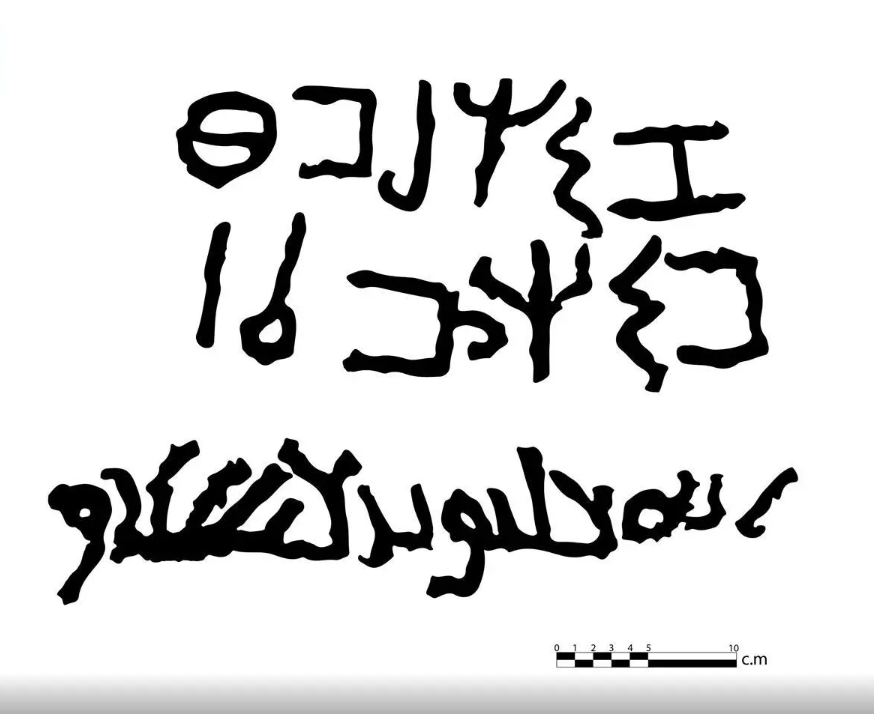
The commission also stated that the new find is evidence of the Arabian Peninsula’s ancient writing systems and styles evolving.
The discovery offers new scientific insights into the historical coexistence of Thamudic and early Arabic writing, as well as the continuity of Thamudic script knowledge among ancient communities until the 5th century AD.
It represents a significant addition to the commission’s collection of ancient Arabic inscriptions and writings and aligns with its ongoing efforts to study, document, preserve, and promote archaeological sites across the Kingdom.
Such work underscores Saudi Arabia’s commitment to protecting and showcasing its rich cultural heritage.
Saudi Arabia’s Heritage Commission
Cover Photo: SPA
















