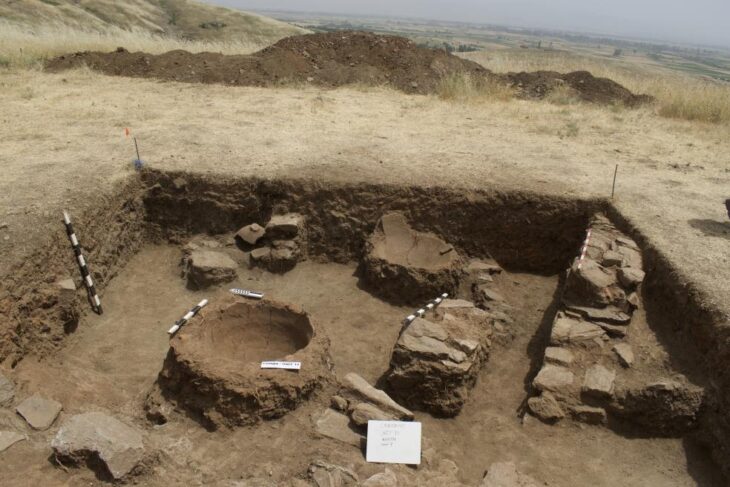
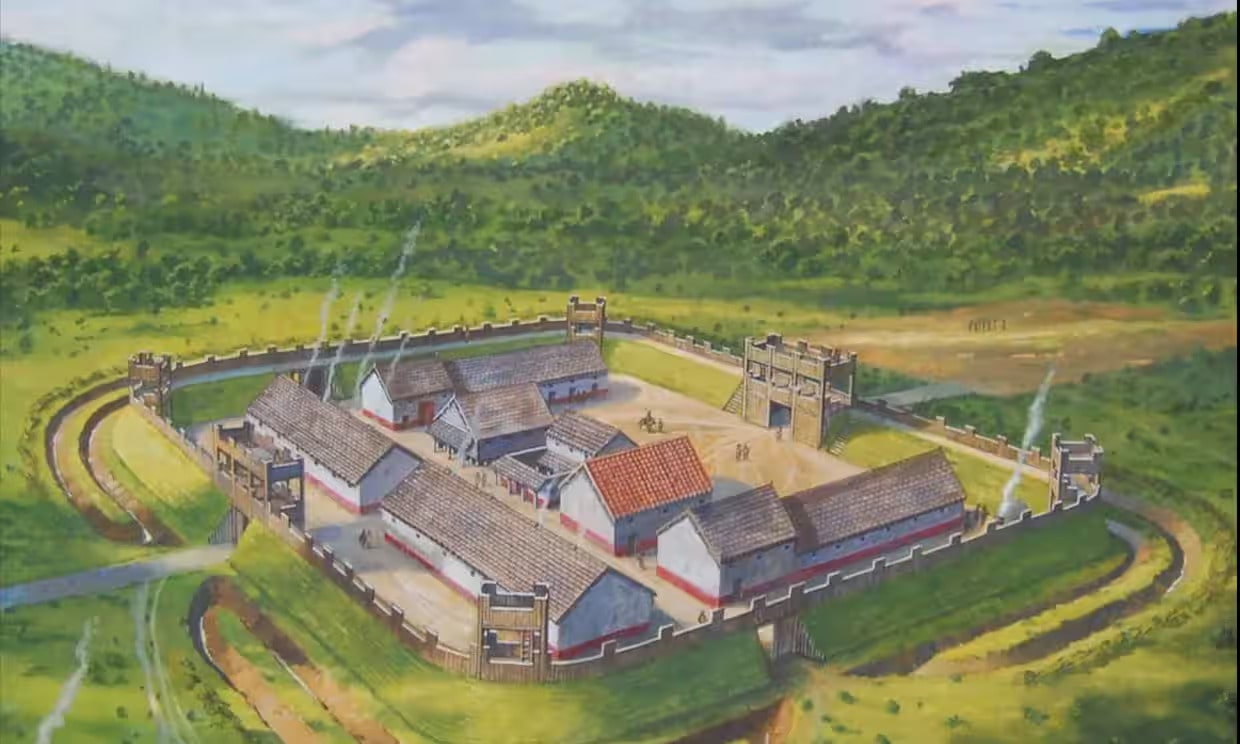
A previously unknown Roman fort has been discovered in north Pembrokeshire. The site, which has excited archaeologists, had been hidden until now beneath an enormous, overgrown field.
The discovery was made by Dr Mark Merrony who is a leading Roman specialist and a tutor at Wolfson College, Oxford.“It is a humongous fort, an incredible find of national importance,” Merrony told the Guardian, adding that he was “absolutely thrilled” about being responsible for such an amazing find.
The discovery of this previously unknown Roman fortress overturns assumptions that the region’s indigenous Celtic tribe had peaceful terms with the Roman invaders.
Dr. Mark Merrony believes the fort would have been constructed sometime between the first and third centuries AD when the Roman Empire occupied the lands of the United Kingdom. It is the second Roman fort discovered in Pembrokeshire specifically, with the other having been excavated at Wiston near the municipality of Haverfordwest in 2013.
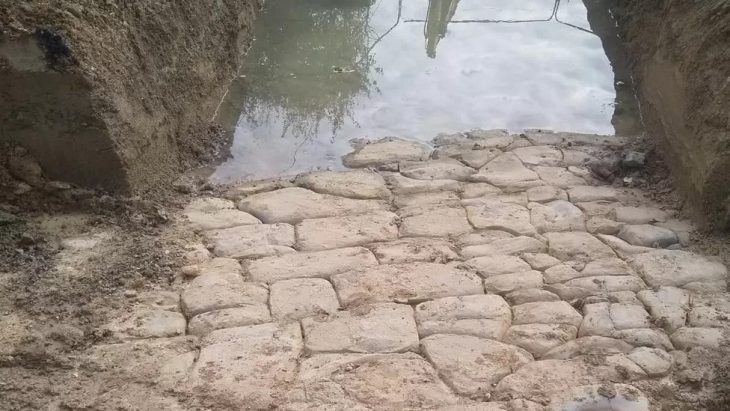
Apart from discovering the ruins of the fort, Merrony also confirmed that a road that ran alongside it originated from the Roman Empire. He was able to do this because the road connects the fort in the field with the second one located at Wiston.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
When considered collectively, the two forts demonstrate the strength of the Roman military’s influence in the area during the Roman era. This goes against expectations because it has long been believed that the Celtic Demetae tribe, who were present in Wales 2,000 years ago, got along well with the Romans and posed no real threat. However, it appears that this wasn’t the case given the existence of a network of forts.
“I now don’t think they [the Demetae tribe] were pro-Roman at all, but that the Romans were hitting the area with an iron fist,” Dr. Merrony stated.
A native of Pembrokeshire, Dr. Merrony had often traveled along a particularly straight road – wondering whether it was Roman – and, when he looked at satellite imagery recently, his eye was drawn to a field with dimensions likely to be a Roman fort. This was not visible through the brush that covered the field when standing at ground level, but quite clear when viewed from above.
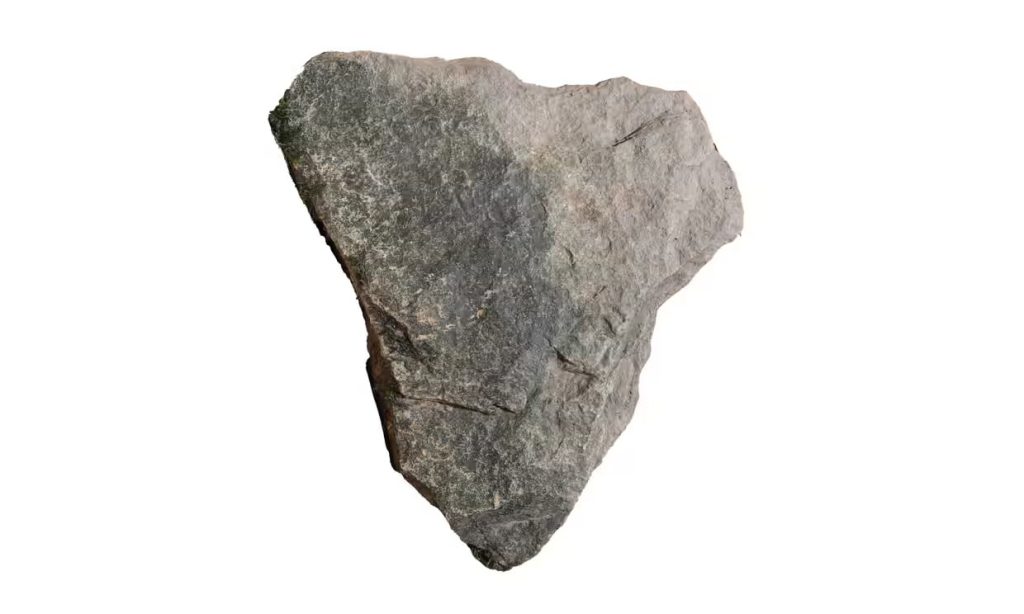

In order to determine whether his initial suspicions were correct, Dr Merrony began examining the site for Roman material.
“Sticking out of the ground was a triangular piece that looked like a Roman roofing slate,” he said. “I thought: ‘Surely not?’ I pulled it up and lo and behold, it’s an archetypal Roman roofing slate, an absolute peach. Flip it upside down and you can see underneath a diagonal line where it was grooved to fit into the one that was underneath it. It’s a real beauty. That was the diagnostic evidence I was looking for, which is a miracle, because it’s a huge site.”
He told the farmer about his discovery of the roofing piece, and the farmer told him that there was slate and stone buried just beneath the earth all around the site (which is why the field was unplowed and essentially abandoned).
“That suggests there’s a lot of material under the ground,” Merrony said. “That’s because there’s obviously several collapsed buildings here. The slates are left, the timbers have rotted.”
Further surface-level examinations have led to the discovery of more roofing slate pieces, which are covered in streaks of rust from decayed nails and feature marks that show the pieces had been chiseled and attached to other slate tiles.
“These are diagnostically consistent with other slates from Romano-British buildings,” Merrony confirmed.
Dr. Merrony estimates that when the fort was erect, its total area would have been between 5-7.5 acres (2-3 hectares) based on its outline. According to his estimation, the fort would have been big enough to accommodate the deployment of roughly 500 Roman soldiers, which suggests that it served more as an auxiliary fort than a primary defensive position.
To protect the discovery, its location won’t be disclosed to the public until a geophysical survey is carried out.
Cover Photo: Roman Fort Project