Over 7,000 languages are spoken around the world. This linguistic diversity, like biological traits, is passed down from generation to generation. But, as Charles Darwin originally proposed, have language and genes evolved in tandem over the last few thousand years? An interdisciplinary team from the University of Zurich and the Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology in Leipzig (Germany) has now investigated this question on a global scale.
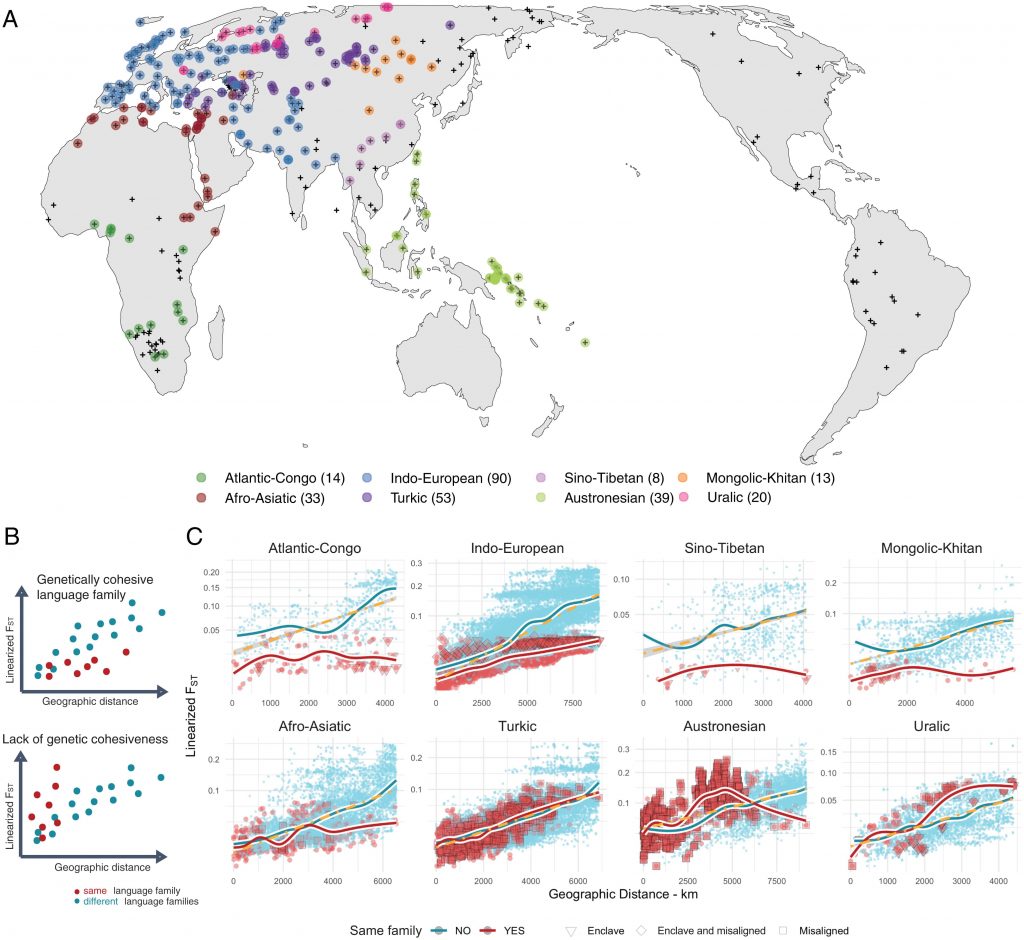
The researchers put together a global database linking linguistic and genetic data entitled GeLaTo (Genes and Languages Together), which contains genetic information from some 4,000 individuals speaking 295 languages and representing 397 genetic populations.
One in five gene-language links point to language shifts
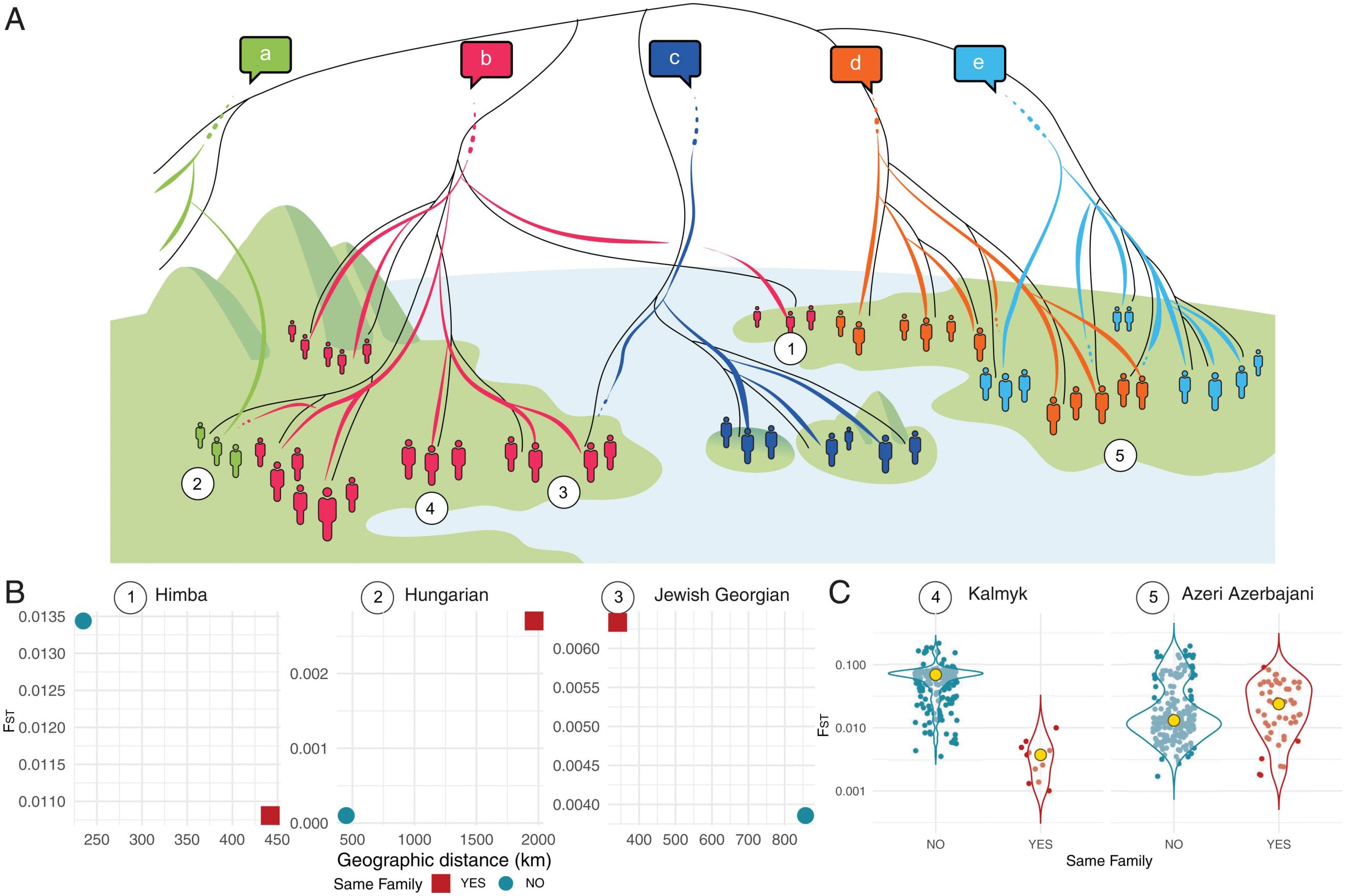
In their study, the researchers examined the extent to which the linguistic and genetic histories of populations coincided. People who speak related languages tend to also be genetically related, but this isn’t always the case. “We focused on cases where the biological and linguistic patterns differed and investigated how often and where these mismatches occur,” says Chiara Barbieri, UZH geneticist who led the study and initiated it together with colleagues when she was a postdoc at the Max-Planck-Institute.
The researchers found that about every fifth gene-language relation is a mismatch, and they occurr worldwide. These mismatches can provide insights into the history of human evolution. “Once we know where such language shifts happened, we can better reconstruct how languages and populations spread across the world,” says Balthasar Bickel, director of the National Center of Competence in Research (NCCR) Evolving Language, who co-supervised the study.
Switching to the local lingo
Most mismatches result from populations shifting to the language of a neighboring population that is genetically different. Some peoples on the tropical eastern slopes of the Andes speak a Quechua idiom that is typically spoken by groups with a different genetic profile who live at higher altitudes. The Damara people in Namibia, who are genetically related to the Bantu, communicate using a Khoe language that is spoken by genetically distant groups in the same area. And some hunter-gatherers who live in Central Africa speak predominantly Bantu languages without a strong genetic relatedness to the neighboring Bantu populations.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
In addition, there are cases where migrants have picked up the local language of their new homes. The Jewish population in Georgia, for example, adopted a South Caucasian language, while the Cochin Jews in India speak a Dravidian language. The case of Malta reflects its history as an island between two continents: while the Maltese are closely related to the people of Sicily, they speak an Afroasiatic language that is influenced by various Turkish and Indo-European languages.
Preserving their linguistic identity
“It appears that giving up your language isn’t that difficult, also for practical reasons,” says the last author Kentaro Shimizu, director of the URPP Evolution in Action: From Genomes to Ecosystems. However, it’s more rare for people to preserve their original linguistic identity despite genetic assimilation with their neighbors. “Hungarian people, for example, are genetically similar to their neighbors, but their language is related to languages spoken in Siberia.”
This makes Hungarian speakers stand out from among the rest of Europe and parts of Asia, where most people speak Indo-European languages, such as French, German, Hindi, Farsi, Greek and many others. Indo-European has not only been extensively studied, but also scores particularly high in terms of genetic and linguistic congruence. “This might have given the impression that gene-language matches are the norm, but our study shows that this isn’t the case,” concludes Chiara Barbieri, who adds that it is important to include genetic and linguistic data from populations all over the world to understand language evolution.
The study is published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
Cover Photo: Overview of linguistic and genetic similarity.