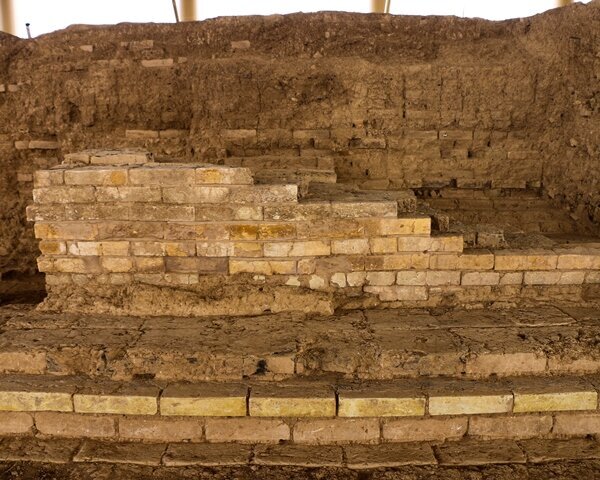
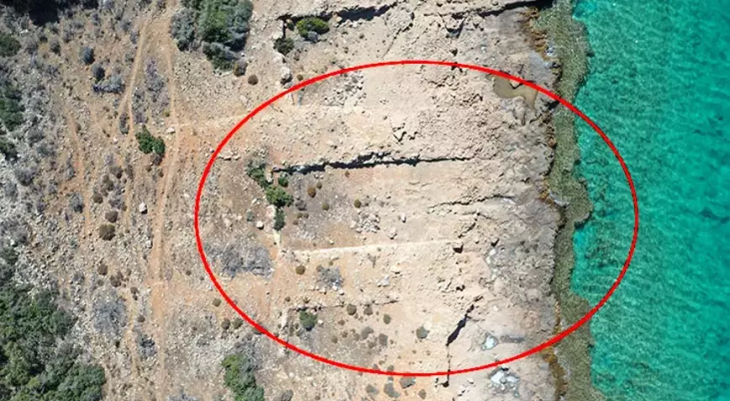
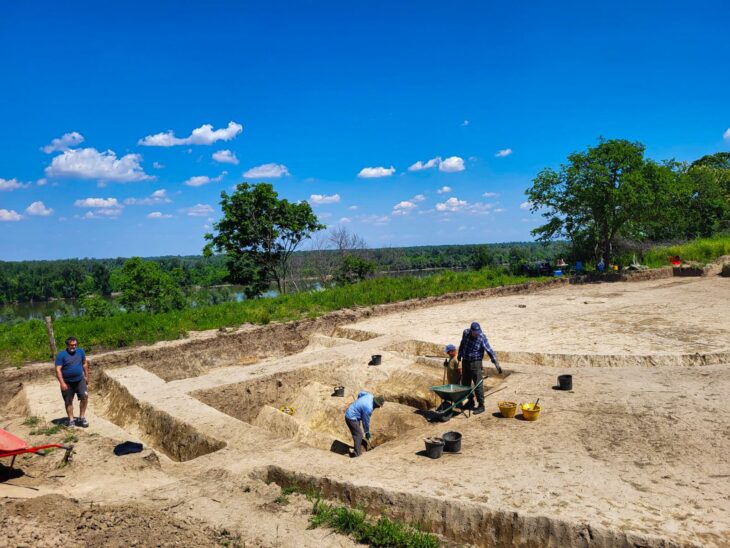
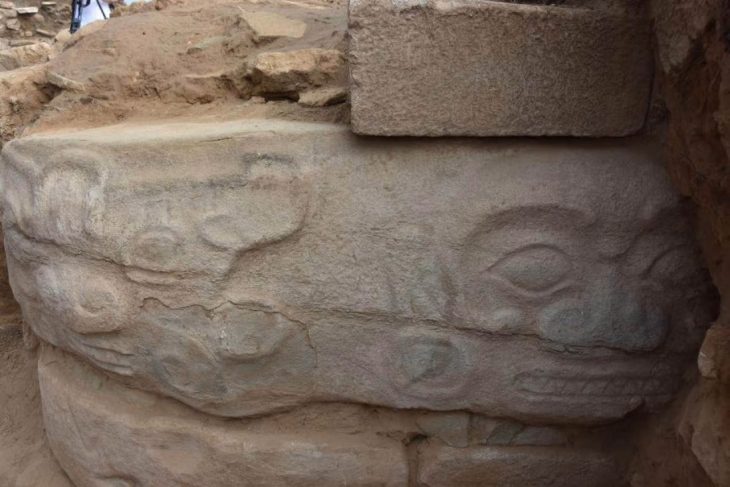
A new find at Persepolis, whose magnificent ruins rest at the foot of Kuh-e Rahmat (Mount of Mercy) in southwestern Iran, reveals the eastern wall of a large prehistoric gateway believed to have been constructed upon the order of Cyrus the Great.
Persepolis, founded by Darius I in 518 B.C., was the capital of the Achaemenid Empire. It was constructed on a massive half-artificial, half-natural terrace, on which the king of kings erected an impressive palace complex based on Mesopotamian models.
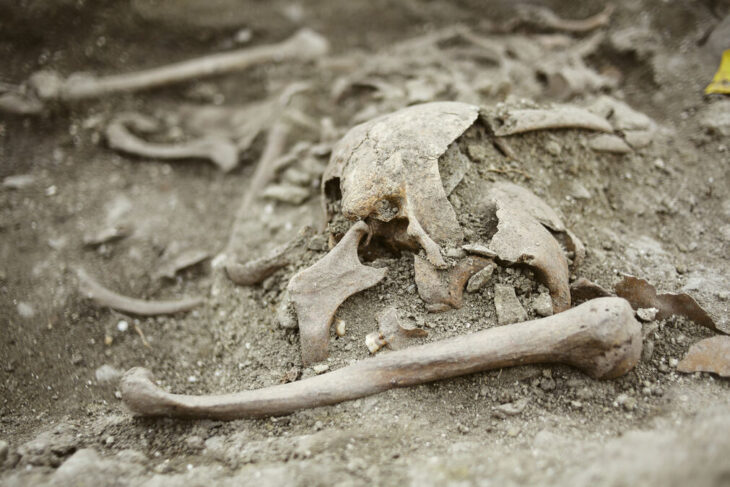
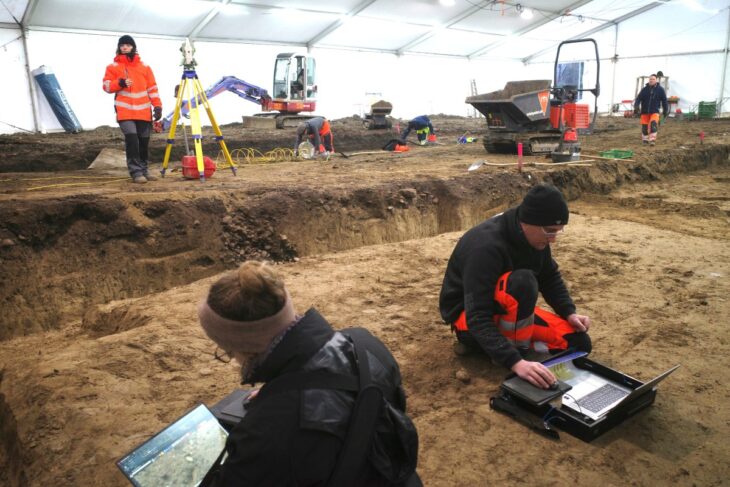
The discovery was made in a site known as Tall-e Ajori, which has been subject to archaeological work over the past decade.
The monumental structure once provided access to a royal garden known as “Paradise,” which included a grand palace that now lies in ruins at the Firuzabad site.
Adorned with striking glazed bricks, the astonishing structure, also referred to as the Gate of Cyrus, is constructed entirely from a combination of bricks and tiles. It spans an impressive 40 meters in length, and 10 meters in width, and boasts a substantial thickness of five meters.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
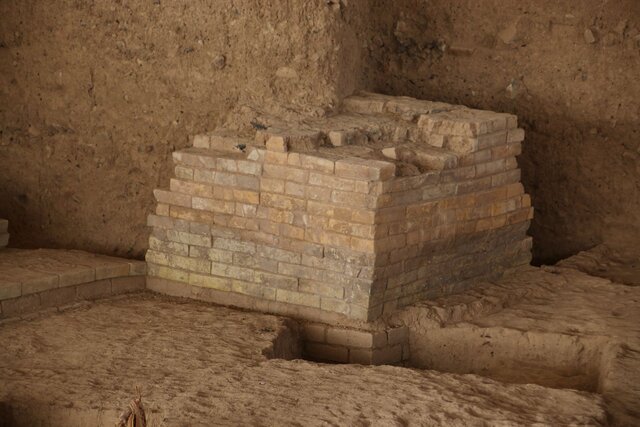

One of the charming construction techniques employed in the creation of the structure is the extensive use of bitumen mortar, Mehr reported.
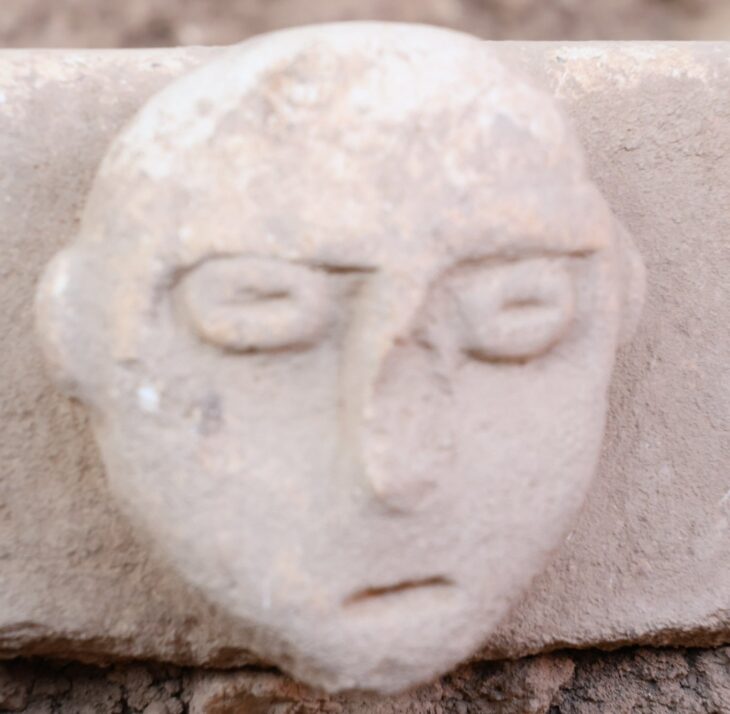
Legendary animals, eight-petaled flowers, and a palette of glazed bricks in shades of white, yellow, blue, and green constitute motifs used to decorate the gate, which was one of the most renowned ones in the ancient world.
The royal city of Persepolis, renowned as the jewel of Achaemenid (Persian) ensembles in the fields of architecture, urban planning, construction technology, and art, ranks among the archaeological sites that have no equivalent and bear unique witness to a most ancient civilization.
The complex of Persepolis is raised high on a walled platform, with five ‘palaces’ or halls of varying size, and grand entrances. The complex was added to by successive kings after its initial construction by Darius the Great in 518 BCE.
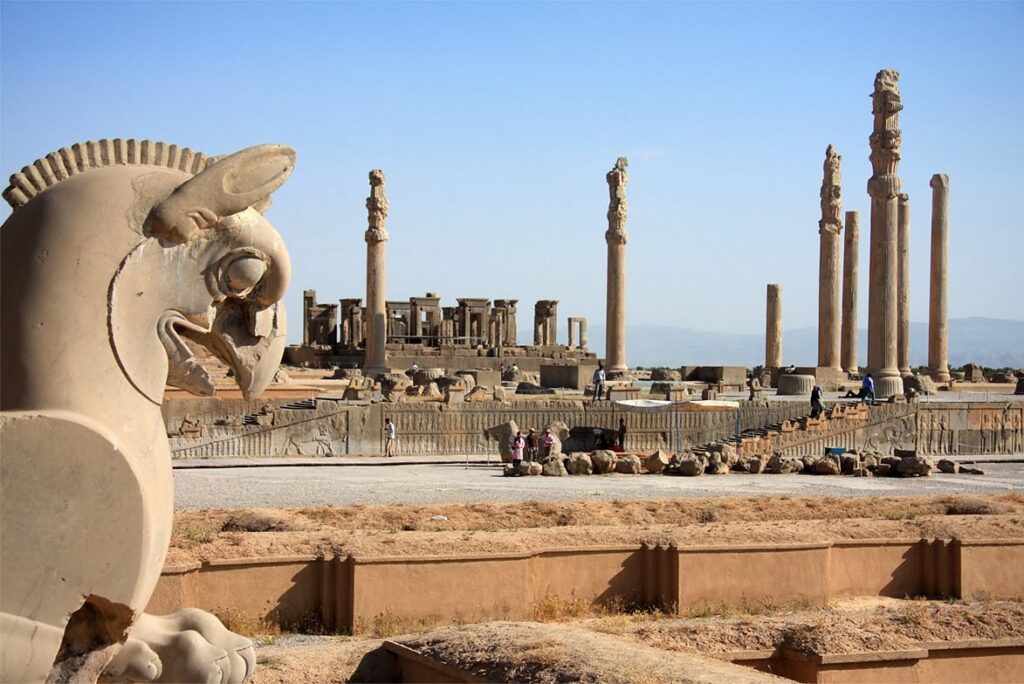

Persepolis’ function is unknown; it was not one of Persia’s largest cities, and it was not occupied all year. Instead, the grand ceremonial complex was only used seasonally, and the location of the king’s private headquarters is unknown. It was, however, the Achaemenid Empire’s seat of government, as well as a showplace and center for kings’ and their empire’s receptions and festivals.
The Macedonian conqueror Alexander the Great captured Persepolis in 330 BC, and some months later his troops destroyed much of the city. Famously, the great palace of Xerxes was set alight with the subsequent fire burning vast swathes of the city. After this destruction, the city’s prestige gradually declined and it never again became a major center of power.
Cover Photo: The eastern wall of the city gate of Parse, Persepolis, with glazed bricks. Photo: ISNA