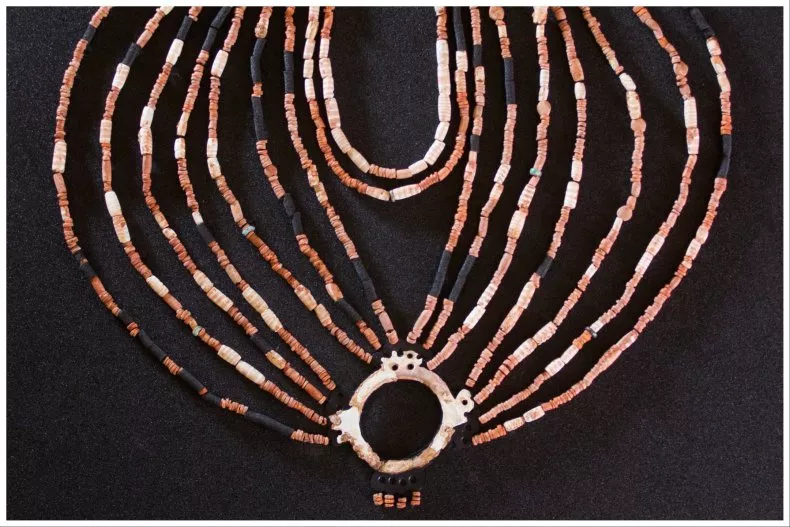
An ornate necklace found in a child’s grave in ancient Jordan about 9,000 years ago provides new insights into the social complexity of Neolithic cultures.
Researchers have described how they reconstructed the artifact several millennia later in a study published on August 2 in the online journal PLOS One.
In this study, Hala Alarashi of the Consejo Superior de Investigaciones Científicas, Spain, and the Université Côte d’Azur, France, and colleagues analyze materials that adorned the body of an eight-year-old child buried in a grave at the Neolithic village of Ba’ja in Jordan, dating to between 7400 and 6800 BCE.
The Neolithic Age began in roughly 10,000 BCE and is considered the later part of the Stone Age. This period was known for polished stone tools, more permanent settlements and villages instead of hunter-gathering societies, domesticated plants and animals, and some pretty strong women.
Body adornments are powerful symbols that communicate cultural values and personal identities, and they are, therefore highly valuable in studying ancient cultures.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!

The grave was found in 2018, with the child in a fetal position alongside more than 2,500 colorful stones and shell beads on the chest and neck, a double perforated stone pendant, and a delicately engraved mother-of-pearl ring.
After analyzing the craftsmanship, composition, and spatial layout of these items, the team believes that they likely belonged to a single composite multi-row necklace that has fallen apart over time. They created a physical reconstruction of the necklace as part of the study and it is currently on display in the Petra Museum in Wadi Musa, Jordan.
The ornament indicates that the child had significant social status, according to the researchers.
“The abundance of beads composing the necklace, which is a common trait of ornaments found in other burials at Ba’ja, hints to wealth and prosperity,” the authors said. “Adornments with a large number of beads—over 2,500—are unprecedented among contemporary Neolithic villages in the Levant.”
The production of the necklace appears to have involved meticulous craftsmanship. It also required the importation of certain exotic materials from other regions. This provides evidence for complex social dynamics among the people who once lived at Ba’ja—including artisans, traders, and authorities who would have commissioned such an ornament.
The study’s authors said analysis of the necklace highlights a high level of connectivity between the ancient people of Ba’ja and the wider World.
Cover Photo: ALARASHI ET AL., 2023, PLOS ONE, CC-BY 4.0