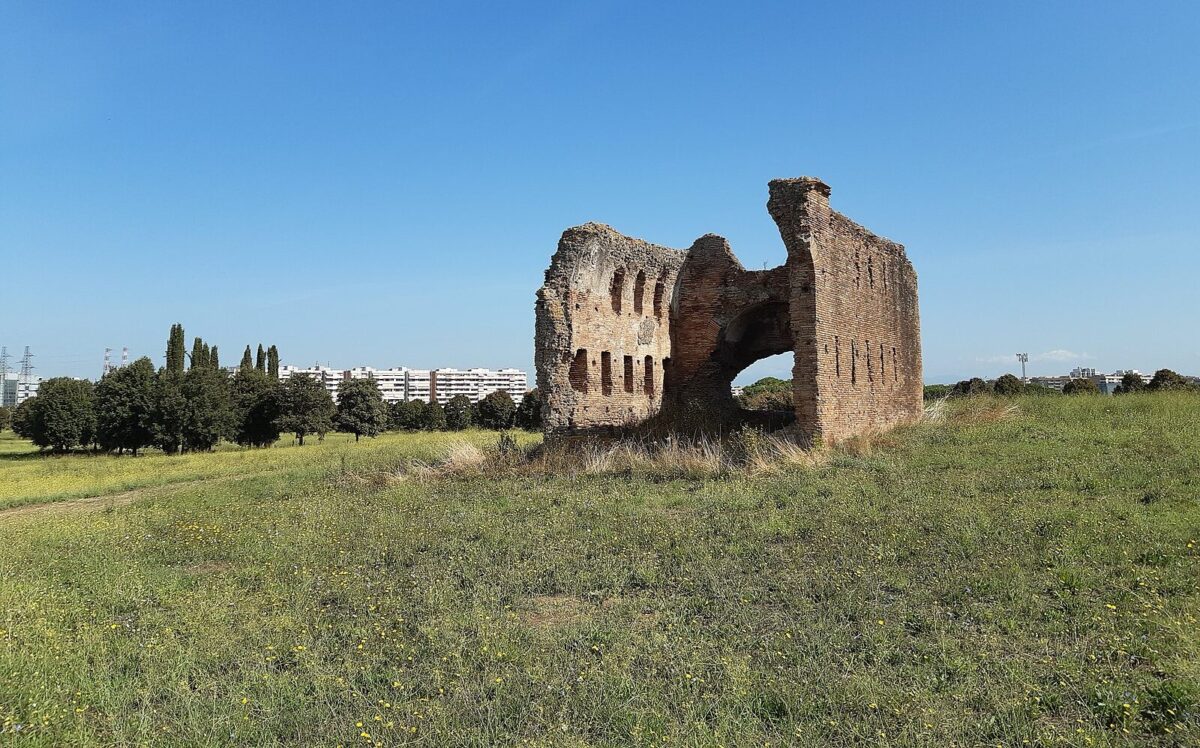
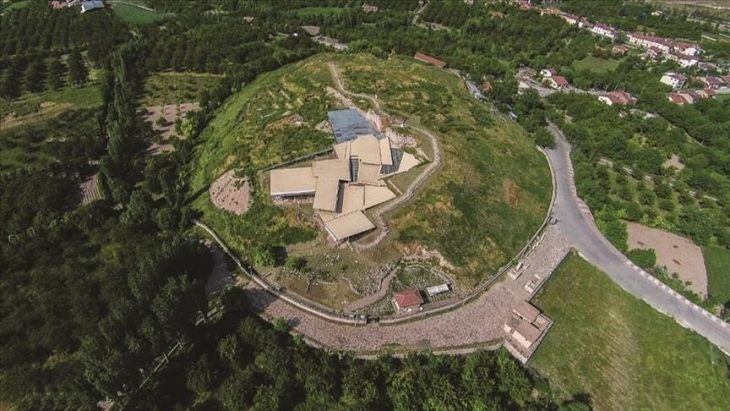
Recent archaeological excavations within the monumental complex of the Villa di Sette Bassi, situated in the southeastern outskirts of Rome, have unveiled a remarkable transformation of an ancient Roman bath complex, the Triton Baths, into an early Christian church during Late Antiquity. Constructed in the 2nd century A.D., the Triton Baths now reveal a fascinating chapter in the history of Rome’s suburban landscape and the early spread of Christianity.
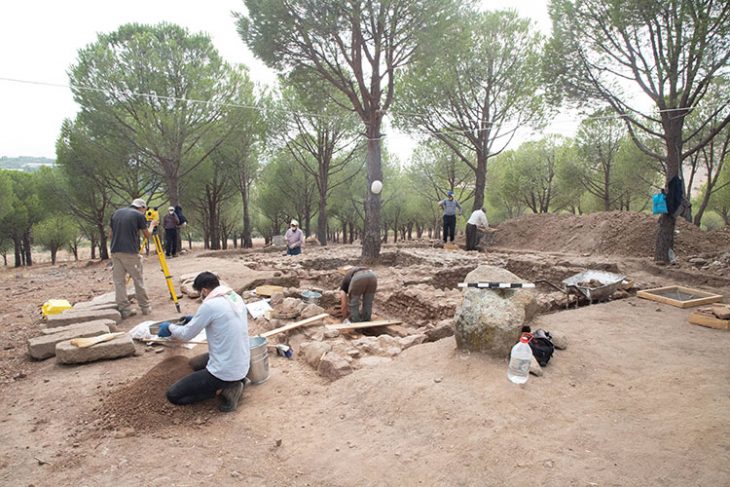
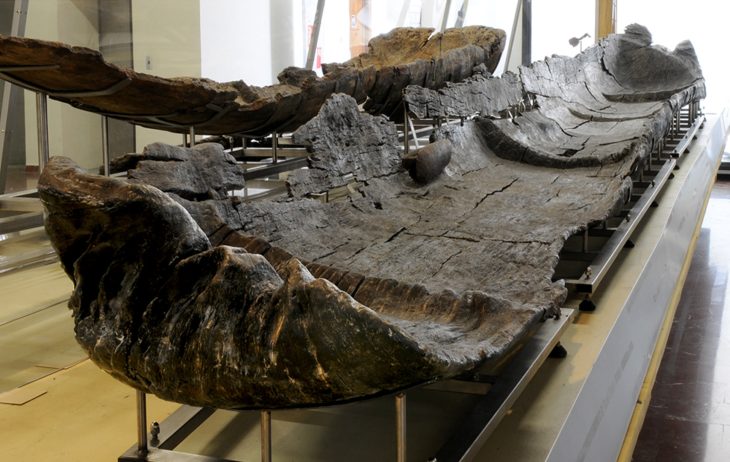
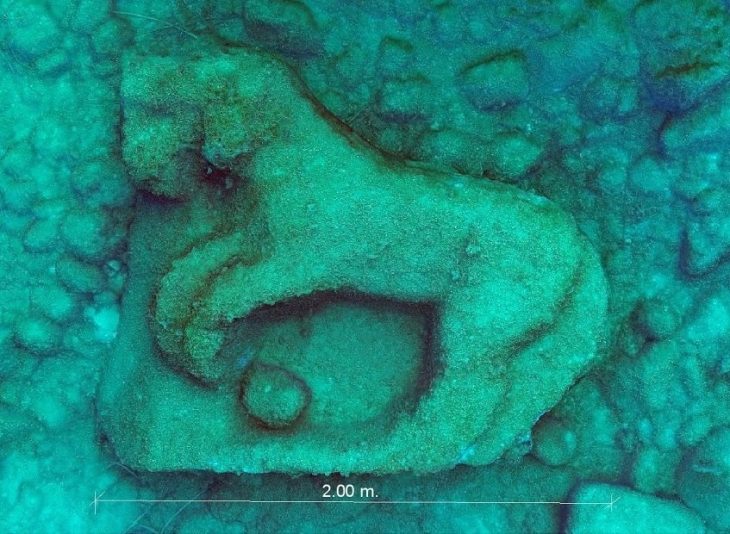
The ongoing and meticulous archaeological investigation has brought to light compelling evidence of this conversion, most notably the discovery of a well-preserved vasca, a pool meticulously lined with marble. Archaeologists interpret this structure as an ancient baptistery, specifically designed for the rite of baptism by immersion. This finding provides a crucial key to understanding the process of Christianization in the territories immediately surrounding the ancient heart of Rome.
The Villa di Sette Bassi itself was a significant Roman estate, and the presence of substantial structures like the Triton Baths underscores its importance during the imperial era. These baths, typical of Roman architectural grandeur, would have served as a social and hygienic hub for the local population. The subsequent conversion of such a prominent site into a Christian place of worship highlights the profound societal and religious shifts that characterized the transition from classical antiquity to the early Christian period.
The discovered baptistery exhibits a history of adaptation, revealing at least two distinct phases of remodeling. Initially, the vasca featured a deeper basin, intentionally designed to accommodate the early Christian practice of full immersion baptism. This ritual held immense symbolic significance, representing the believer’s death to their former life and their rebirth into the Christian faith. In a later phase, the basin underwent a significant alteration, with its bottom being partially filled in, thereby reducing the overall depth of the structure.
This modification in the baptistery’s design closely mirrors the liturgical evolution of the sacrament of baptism during Late Antiquity. As Christianity spread and adapted, the practice of full immersion gradually gave way to more symbolic forms of the rite, which were less physically demanding. The two distinct phases of the vasca at Villa di Sette Bassi offer tangible archaeological evidence of this liturgical transformation within a specific community.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
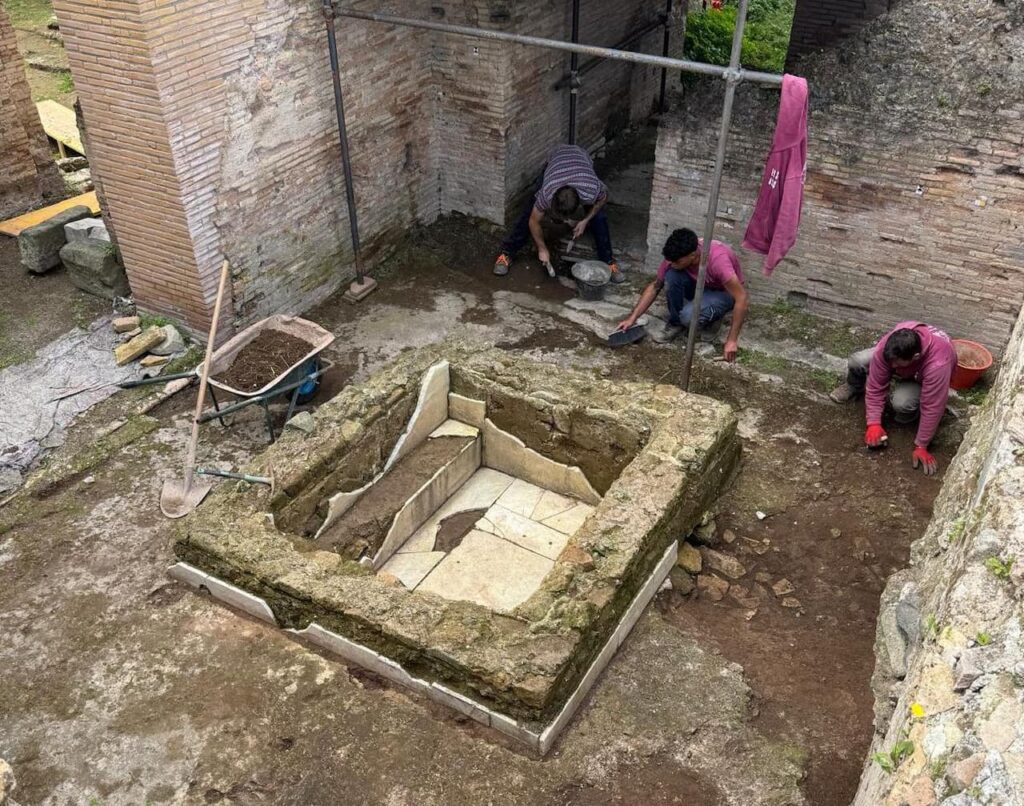

The original dimensions of the baptistery strongly suggest that the earliest and most solemn form of Christian initiation, full immersion, was practiced at this location during its initial period of use. This underscores the site’s early importance in the Christian community. Furthermore, the architectural layout surrounding the vasca, along with other structural elements unearthed during the excavation, bolsters the interpretation that this was not merely a marginal chapel but a fully established baptismal church, possessing the authority to administer the sacrament of baptism and, significantly, the right to burial.
The discovery of numerous burials in the immediate vicinity of the vasca further supports this conclusion. The presence of such a concentration of tombs indicates that the site held considerable religious significance and served as a central point within the ecclesiastical network of the region, rather than just a small, infrequently used place of worship.
Intriguingly, the possibility of a bishopric having been located at this site during Late Antiquity cannot be dismissed. Situated in the heart of the Roman countryside, such a high-ranking ecclesiastical presence could readily explain the notable density of burials discovered near the ecclesiastical building. This hypothesis opens up exciting new avenues for understanding the early organization and influence of the Christian Church in the suburban territories of Rome.
The very coexistence within the same architectural complex of elements characteristic of imperial-era bath architecture alongside distinctly Christian liturgical components vividly illustrates the gradual yet profound transition in the uses of space. This physical transformation directly reflects the broader social and religious upheaval that marked the decline of classical Antiquity and the ascendance of Christianity as a dominant force.
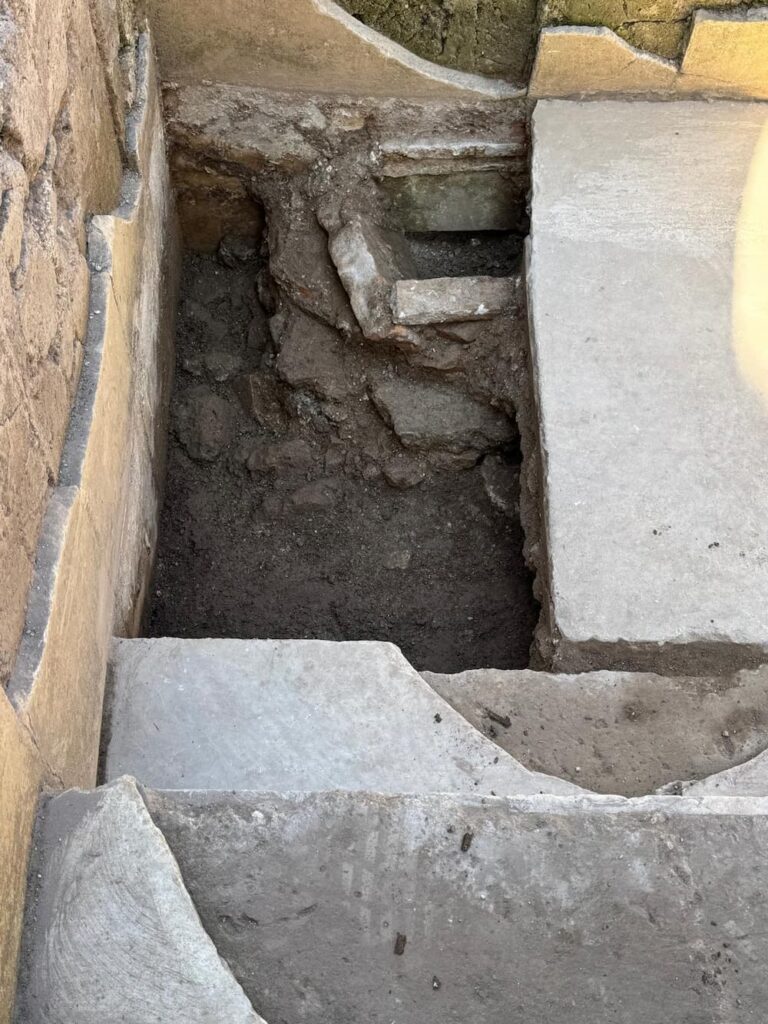

This groundbreaking discovery at the Villa di Sette Bassi has the potential to significantly reshape the historical understanding of the Christian presence and its development in the Latium region during the crucial post-imperial period. The ongoing research and analysis conducted by scholars such as Alessandra Ten, Carla Maria Amici, and Lucrezia Spera promise to yield further valuable insights into this fascinating and pivotal era of Roman history and the early Church.
In conclusion, the excavation at the Triton Baths not only sheds light on the architectural and liturgical developments of early Christianity but also opens new avenues for exploring the rich tapestry of religious life in ancient Rome. As scholars delve deeper into this site, we can expect to gain further insights into the ways in which Christianity took root and flourished in the heart of the Roman Empire.
Parco Archeologico dell’Appia Antica
Cover Image Credit: Wikipedia