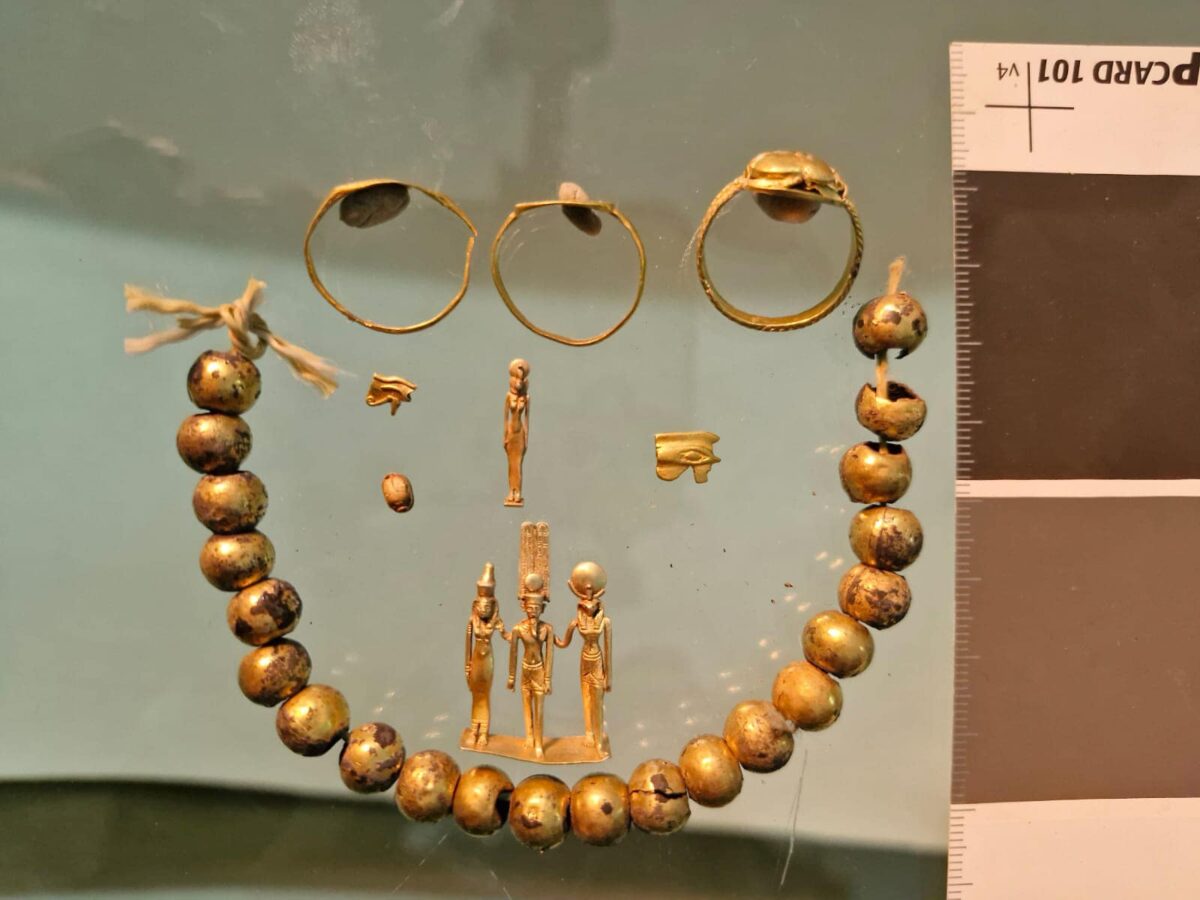
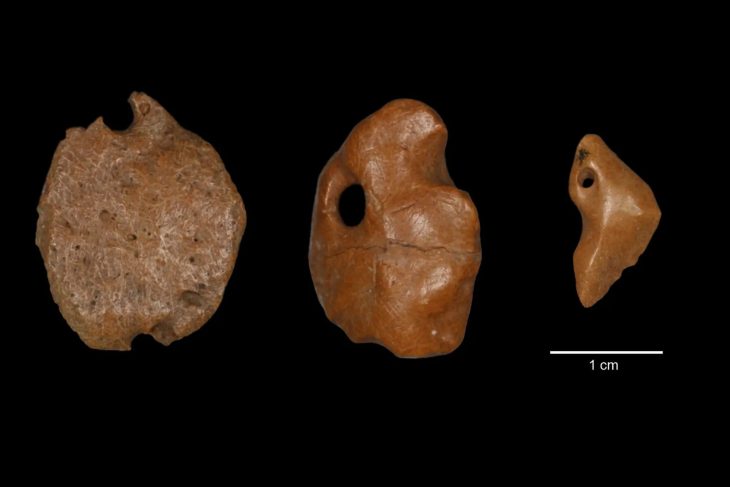
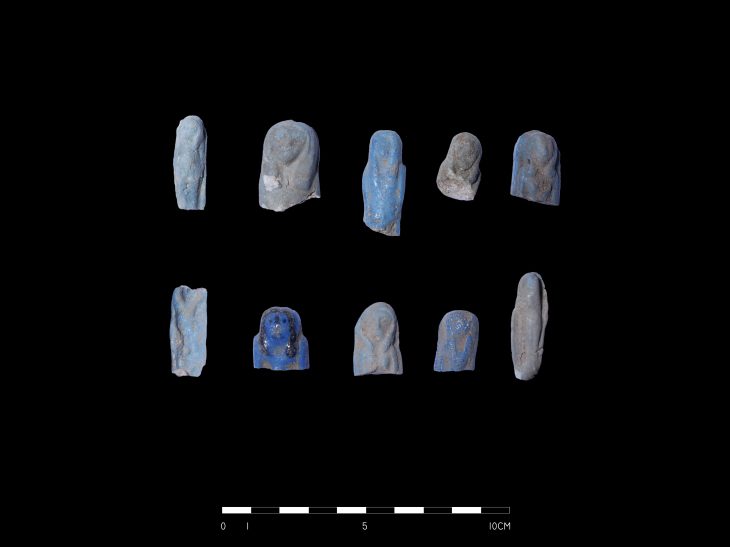
In a remarkable revelation that sheds light on ancient Egyptian craftsmanship, the Egyptian Ministry of Tourism and Antiquities, alongside the Egyptian-French archaeological mission from the Franco-Egyptian Center for the Study of the Karnak Temples (CFEETK), has uncovered a significant collection of jewelry and amulets dating back to the early 26th Dynasty (664–525 B.C.) at the Karnak temples.
During excavations in the northern area of the Karnak complex—one of ancient Egypt’s most significant religious sites—archaeologists unearthed a small, broken ceramic container that was remarkably intact. Inside, they found a stunning array of jewelry pieces in excellent condition, including several gold rings, small statuettes, and gilded amulets. Notably, the collection features a rare triptych representing the Theban triad of deities: Amun, Mut, and Khonsu. Additionally, metal brooches and amulets depicting gods in animal forms were discovered, along with numerous decorative beads, some of which are gold-coated.
Egypt’s Minister of Tourism and Antiquities, Mr. Sherif Fathy, emphasized the significance of this discovery, highlighting the fruitful collaboration between Egypt and France in archaeological endeavors. He noted that this excavation is part of a broader initiative aimed at enhancing the tourist experience at Karnak, one of the country’s most visited temple complexes. As part of this development plan, tourist routes have been modernized, a new lighting system has been installed, and the sanctuary of Amenhotep I has been restored and reinstalled in the site’s open-air museum. These efforts aim not only to preserve historical heritage but also to make the Karnak complex an even more attractive destination for both domestic and international visitors.
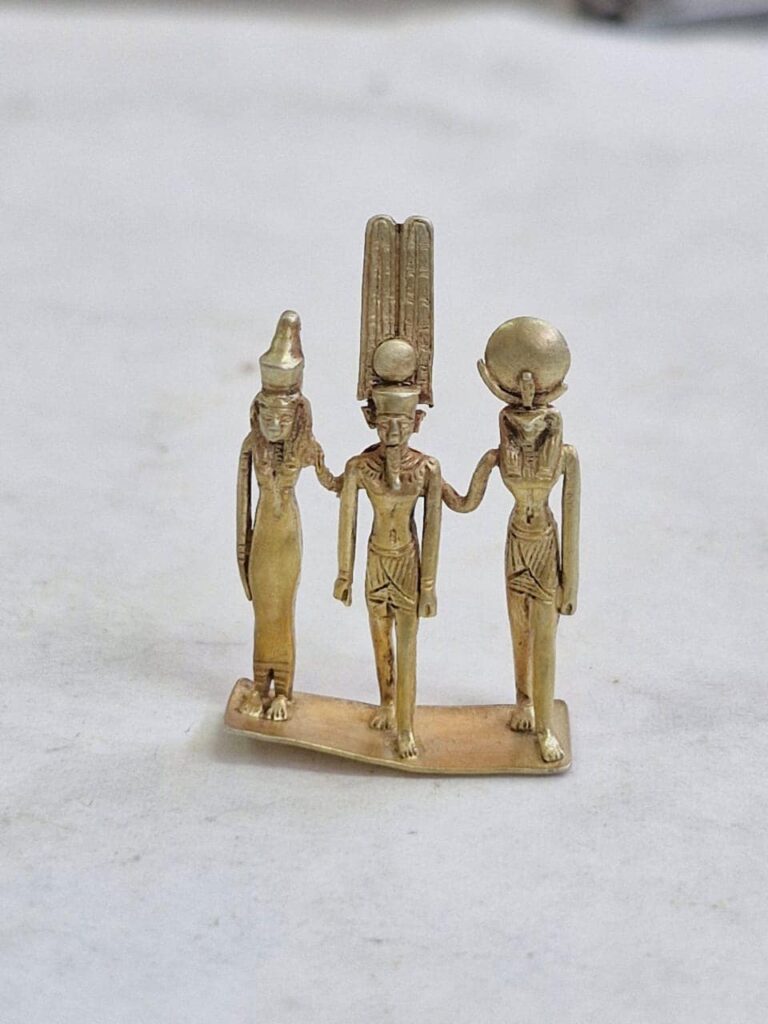

Dr. Mohamed Ismail Khaled, Secretary-General of the Supreme Council of Antiquities, remarked that this finding significantly contributes to expanding knowledge about the temple and its evolution throughout the first millennium B.C. He stated that the recovered objects will provide researchers with a clearer understanding of religious life and the use of amulets and jewelry in Egyptian society during the 26th Dynasty.
The archaeological team, led by Dr. Abdel Ghaffar Wagdy, Director General of Luxor Antiquities and head of the mission on Egypt’s behalf, has commenced restoration and documentation work on the discovered pieces. Once this process is completed, the artifacts are expected to be exhibited at the Luxor Museum, allowing visitors to appreciate their historical and artistic value.
From the French side, mission director Dr. Jérémie Hourdin explained that ongoing excavations in the northern area of Karnak have revealed large mudbrick structures likely used as storage facilities or workshops related to temple activities. These constructions, also dating back to the 26th Dynasty, provide valuable insights into the organization and functioning of the complex during that era.
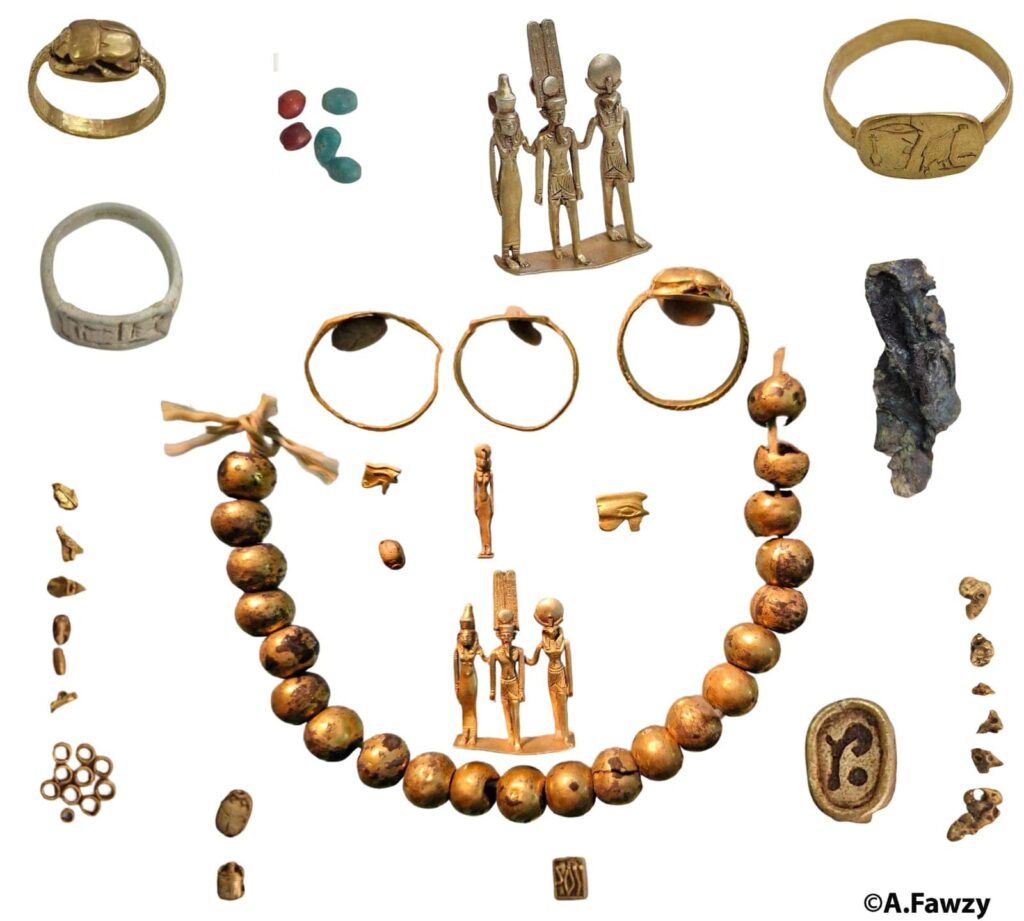

The Karnak temples continue to be an inexhaustible source of archaeological discoveries. Their vast expanse and rich history have established this site as a key reference point for global Egyptology. Each new finding, such as this collection of jewelry and amulets, allows for a more precise reconstruction of the splendor of ancient Egypt and a deeper understanding of its religious and cultural practices.
This significant discovery not only enriches the historical narrative of the Karnak temples but also underscores the importance of international collaboration in uncovering the mysteries of ancient civilizations. As the excavation efforts continue, the world eagerly anticipates further revelations from this iconic site.
The Egyptian Ministry of Tourism and Antiquities
Cover Image Credit: The Egyptian Ministry of Tourism and Antiquities, A. Fawzy