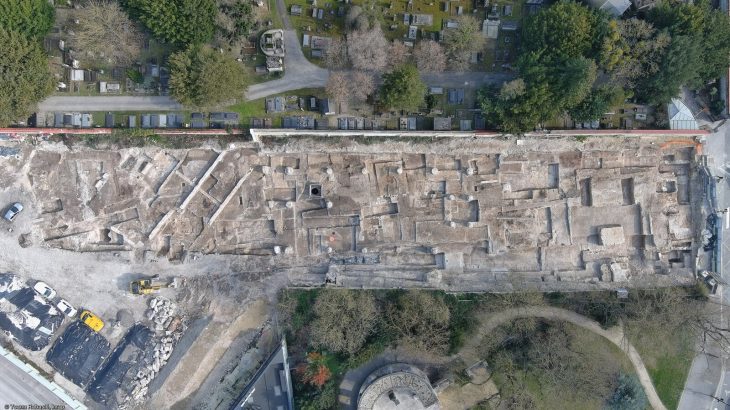
In Padula, located in the Campania region of southern Italy, authorities announced the remarkable discovery of nineteen ancient tombs during archaeological excavations, unearthing a variety of grave goods and artifacts that provide valuable insights into the area’s rich historical and cultural heritage.
On Wednesday, February 5, authorities disclosed the outcomes of a significant operation aimed at safeguarding cultural heritage. The Soprintendenza Archeologia Belle Arti e Paesaggio of Salerno and Avellino, in collaboration with the Lagonegro Prosecutor’s Office and the Carabinieri’s Nucleo Tutela Patrimonio Culturale, presented to the media and the public the results of an archaeological excavation conducted following the identification of unauthorized construction activities in Padula, located in the Campania region of southern Italy.
Last summer, reports emerged regarding illicit construction work on a parcel of land in the locality of Contrada Cicirelli, where a stable was intended to be erected. However, these activities resulted in significant damage to a cluster of ancient burials. Upon assessing the situation, the relevant authorities promptly secured the area and, in conjunction with the Soprintendenza, initiated an urgent intervention to recover and preserve the affected remains.

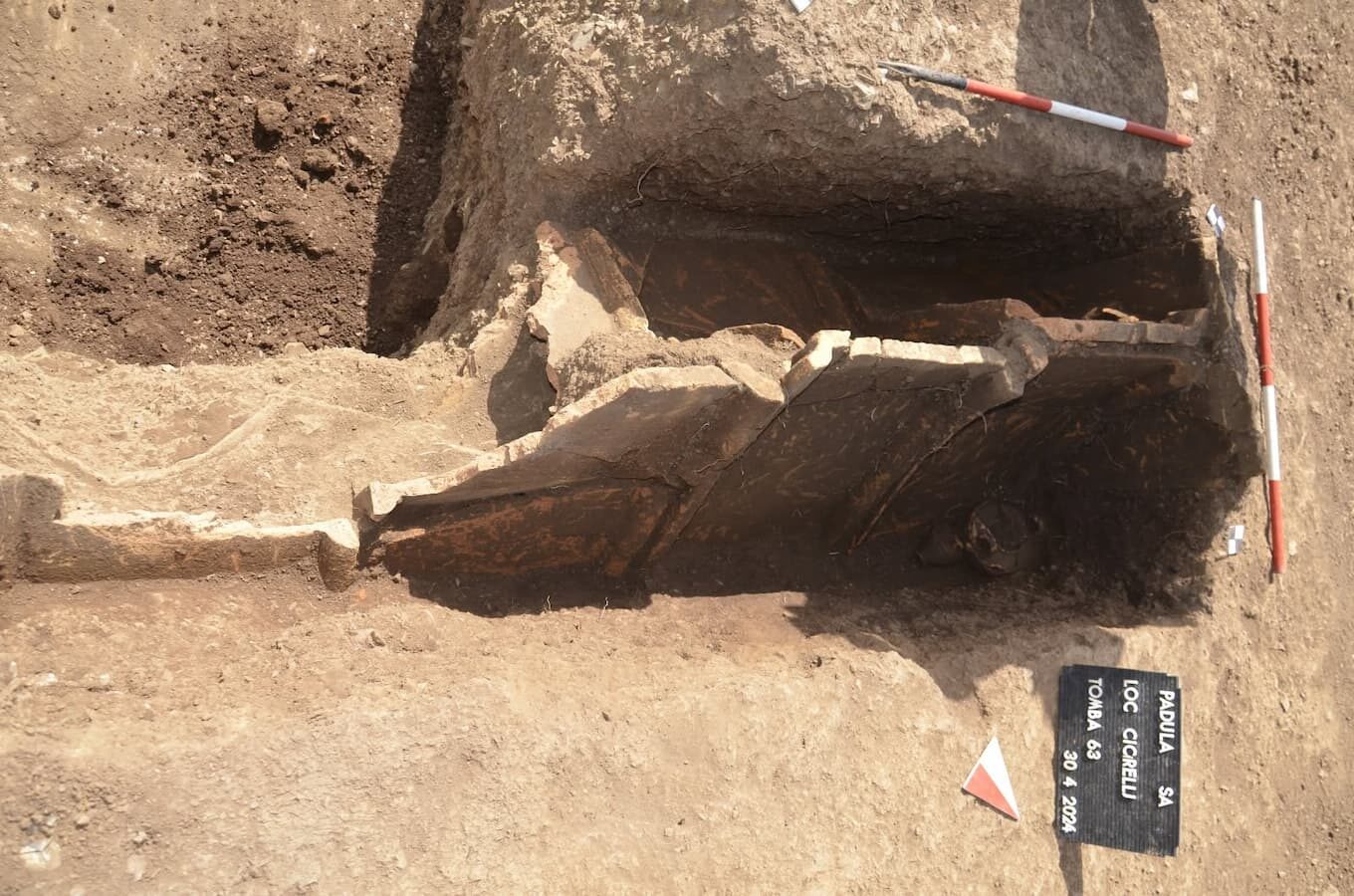
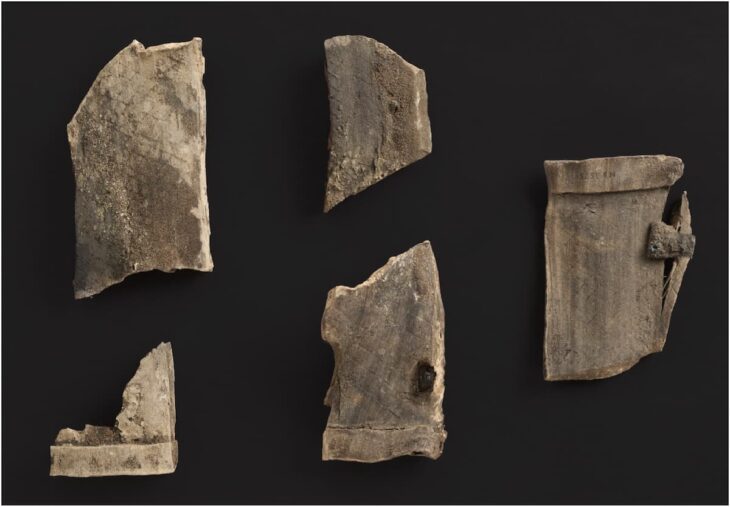
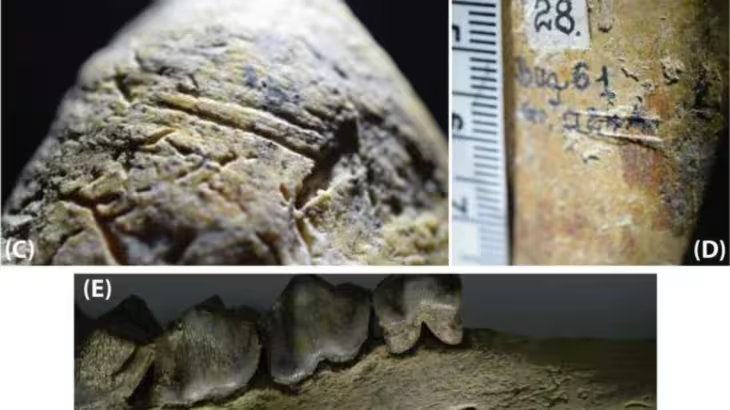
The excavations yielded the recovery of nineteen tombs, predominantly of the “a cappuccina” type, characterized by beds and walls constructed from tegulae, with the covering also composed of these ceramic slabs arranged in a gabled configuration. In certain instances, the remains were interred directly in pits excavated into the earth, marked by a large stone indicating the position of the deceased’s head.
Furthermore, several of these burials contained grave goods, primarily consisting of black-glazed ceramics and vases adorned with red-figure depictions of female figures, attributed to workshops in the Lucania region, likely situated in the Vallo di Diano. Some vases were discovered outside the tombs, suggesting the performance of post-burial rituals. Experts have dated these findings to the latter half of the 4th century BC.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
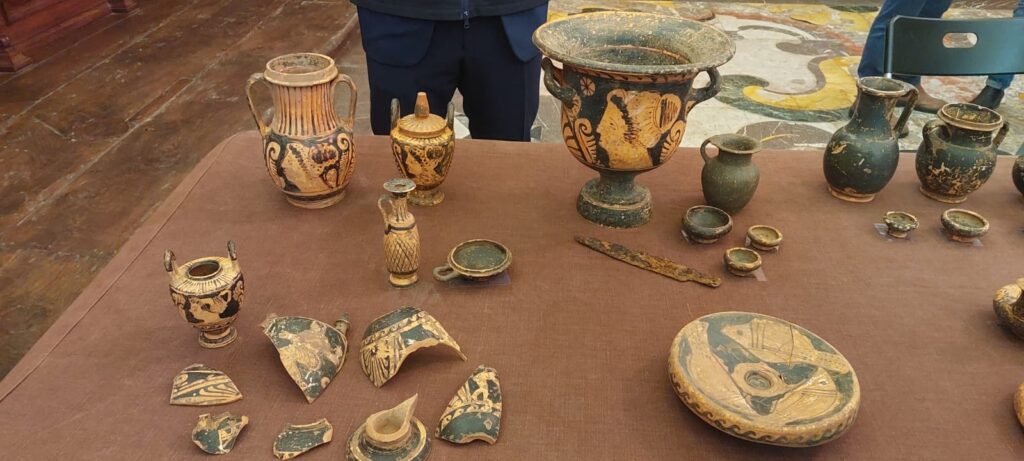

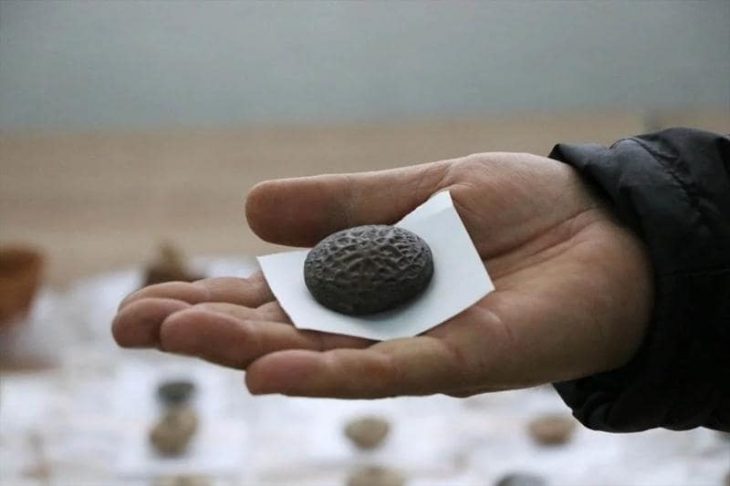
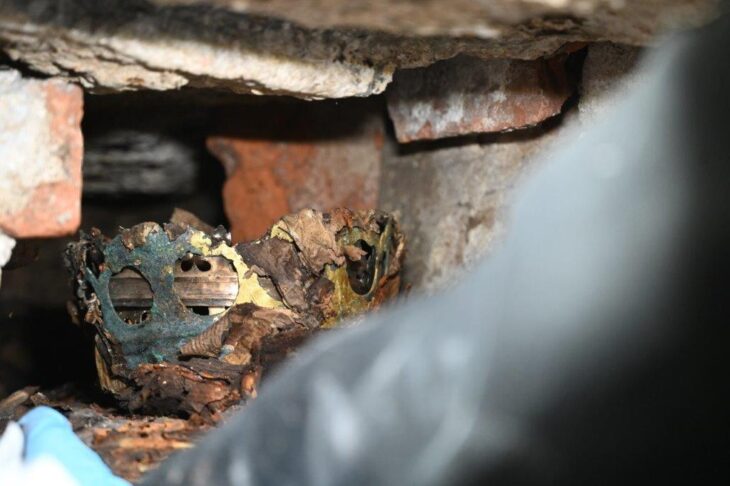
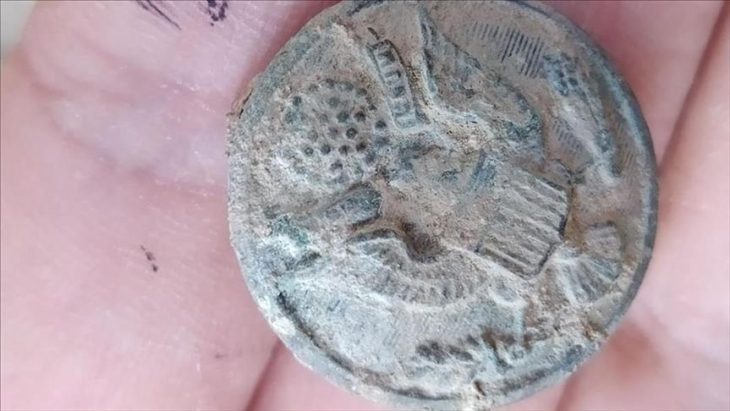
Among the most remarkable discoveries was tomb number 64, an “a cappuccina” burial that contained a funerary assemblage comprising several black-glazed vases and an undecorated small pot. Within this pot, archaeologists uncovered a silver coin, a diobol minted in Tarentum between 380 and 325 BC, featuring the image of the goddess Athena on the obverse and a representation of Hercules slaying the Nemean lion on the reverse.
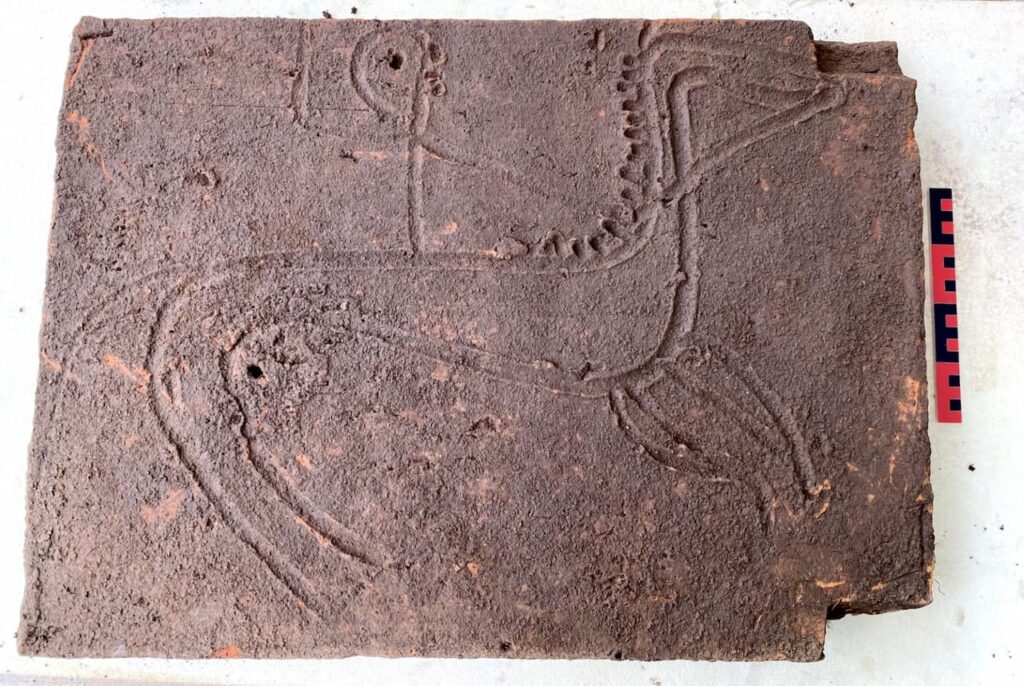
Additionally, one of the slabs covering the grave exhibited a rudimentary engraving made prior to firing, depicting a figure of a man on horseback. The horse is illustrated in full gallop, while the rider, adorned with a helmet, raises one arm as if to hurl an object, potentially a spear. This detail implies that the deceased may have been a warrior, indicative of a person of high status within the community.
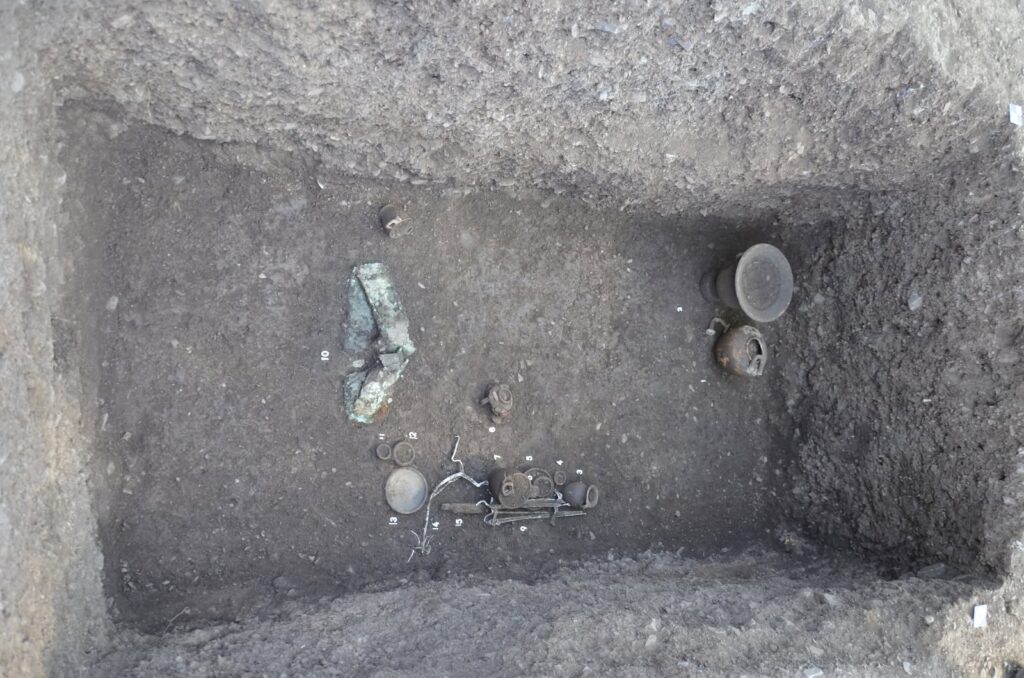

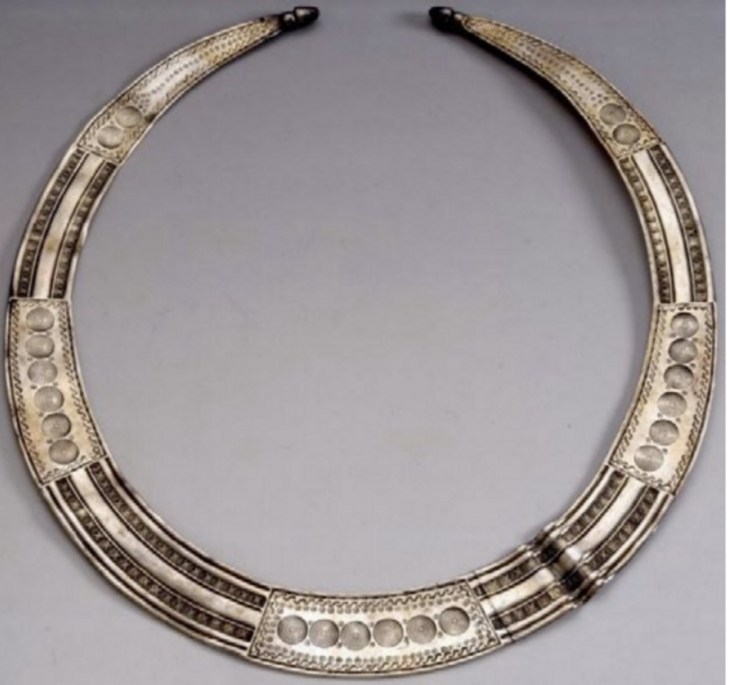
In another burial, researchers identified a grave assemblage consisting of numerous black-glazed and red-figure vases, including a krater, a vessel associated with symposium rituals, embellished with female imagery. Accompanying the ceramic artifacts were an iron knife, a bronze belt worn by the deceased at the time of burial, several metal spits, two fire supports, and a lead candelabrum.
The presence of the belt suggests that the deceased was also a warrior, while the household items further reinforce the notion of his significant role within both the domestic and social spheres. The distribution pattern of the tombs and their characteristics have led experts to hypothesize a potential association with an ancient settlement or agricultural site from the period.
Soprintendenza Archeologia Belle Arti e Paesaggio of Salerno e Avellino
Cover Image Credit: Soprintendenza Archeologia Belle Arti e Paesaggio of Salerno e Avellino