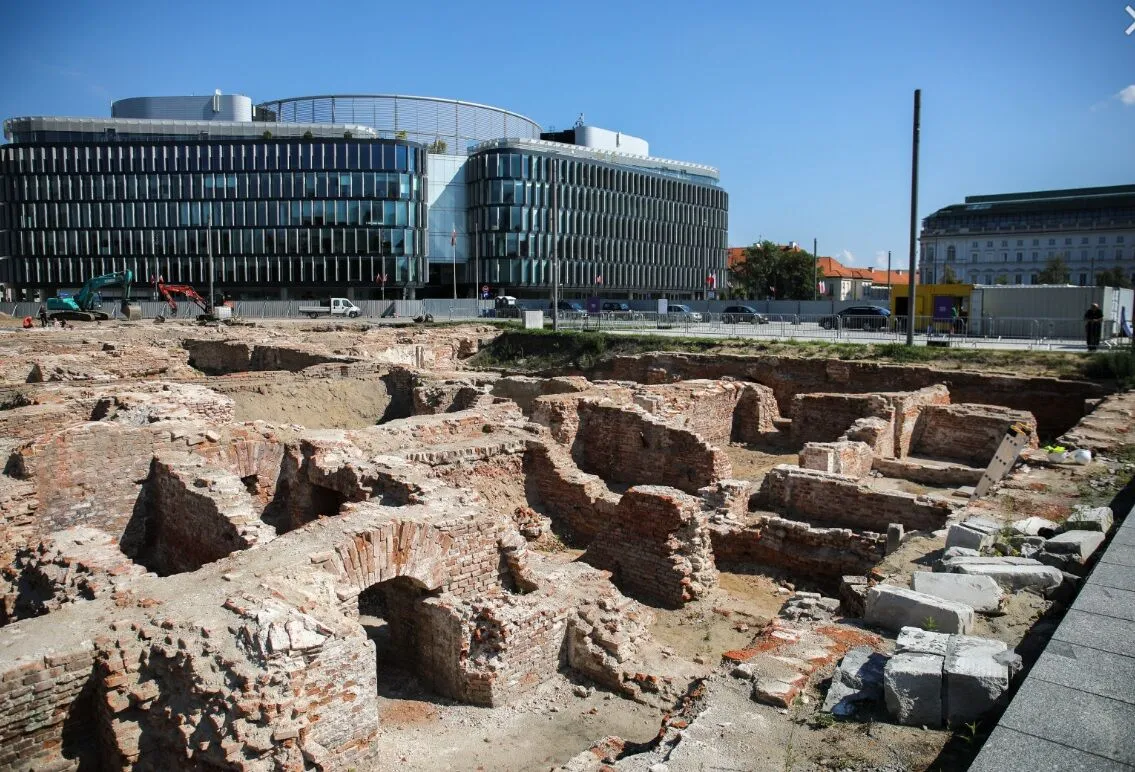
A mysterious underground tunnel was found under the ruins of the Saski Palace in Pilsudski Square in Warsaw, the capital and largest city of Poland. Archaeologists excavating the ruins of Saxon Palace uncovered a secret tunnel about 13 feet down (4 meters).
This unexpected find unsurprisingly sparked intrigue among historians and locals alike, as the tunnel does not exist in any known configuration plans of the palace.
Archaeological work currently being carried out on the site of the former Saxon Palace will continue until the end of 2023 and ultimately cover an area of approximately 4,500 square meters.
The Saxon Palace, historically significant and once resplendent, was a grand fixture of Warsaw’s architecture before being tragically destroyed during World War II. It played an important role in Polish history, making this recent discovery even more intriguing.
Saski Palace spokesperson Slawomir Kulinski said that the Polish Army headquarters command was located there, and military intelligence was located on the southern wing. “The tunnel was to allow them to quickly transmit reports and information,” he said.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
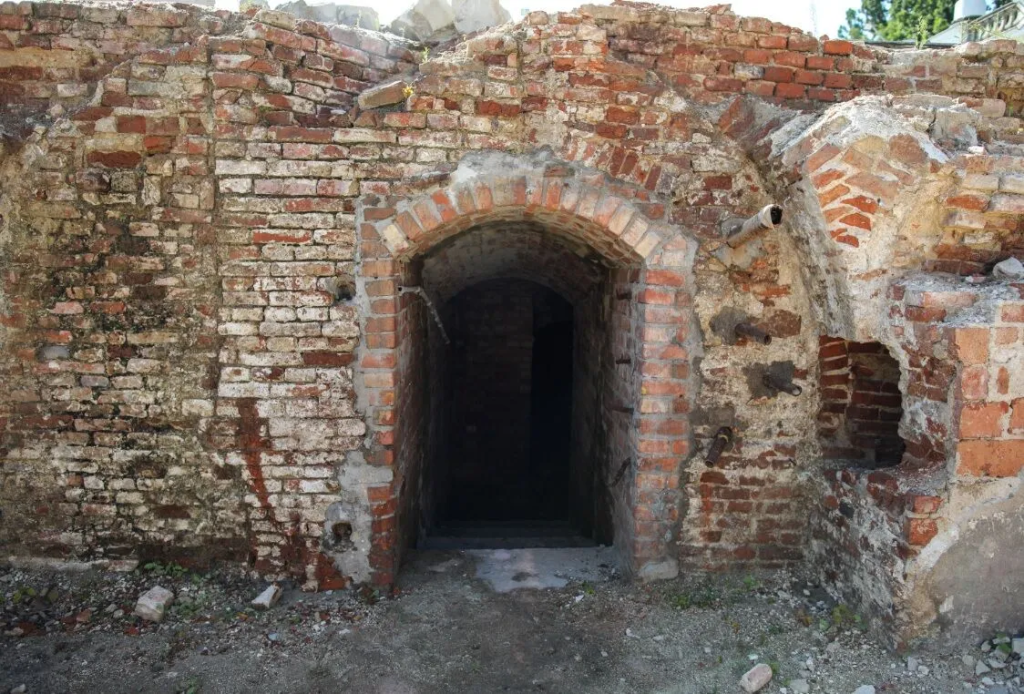

“The tunnel also had technical functions. It contained a telegraph cable and a system of heating and irrigation pipes on both sides of the palace,” he explained.
The tunnel was built in the 1930s specifically for military intelligence. It is about 45 meters long. The brick for the construction of the tunnel was supplied by the Wawrzyna brickyard, as evidenced by the brand marks on the bricks. On the fresh plaster, an unknown builder scratched the date 1933 and an eagle without a crown.
“Obviously, we are dealing with a legionary eagle, typical of the 1930s and military functions,” Kulinsky said. Another eagle, similar but smaller, is located in a third of the length of the tunnel.
The tunnel leads to the cellars of the Morshtyn period in the southern part of the Saskia Palace. There were once storerooms here, and during the interwar period, messengers ran to the generals with military intelligence reports.
The area around Brühl’s Palace, blown up in 1944 during the demolition of Warsaw, was cleared only to the ground level after World War II. The rest of the rubble was leveled, and the area became a lawn, which over time became overgrown with trees and shrubs. With the exception of a tiny fragment of one of the annexes (from the side of the Saxon Garden) that archaeologists examined in 2006, the majority of this area’s contents have remained a mystery for nearly 80 years.
At the beginning of June 2023, fieldwork began to unravel this mystery. First, the area was fenced off, then checked by sappers for the presence of unexploded ordnance. Archaeologists are currently working there.
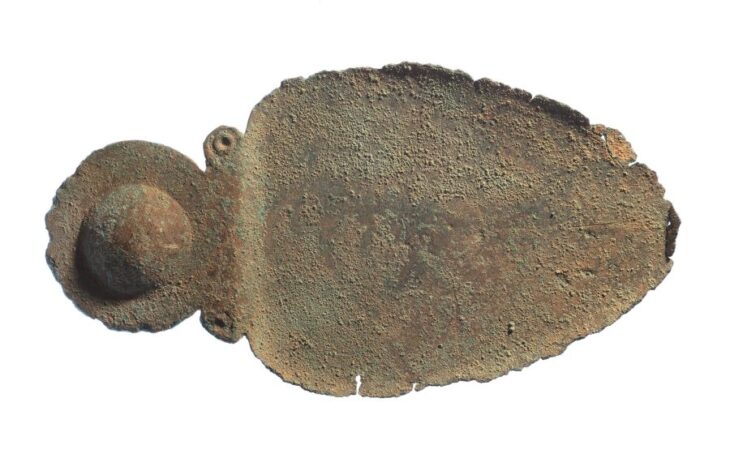
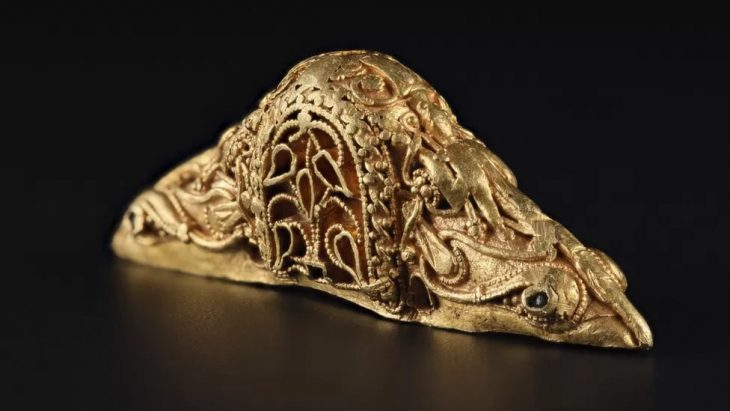
So far, nearly 46,000 artifacts have been excavated from the rubble, including coins, ornaments, medallions, and vessels with decorations or manufacturer’s signatures.