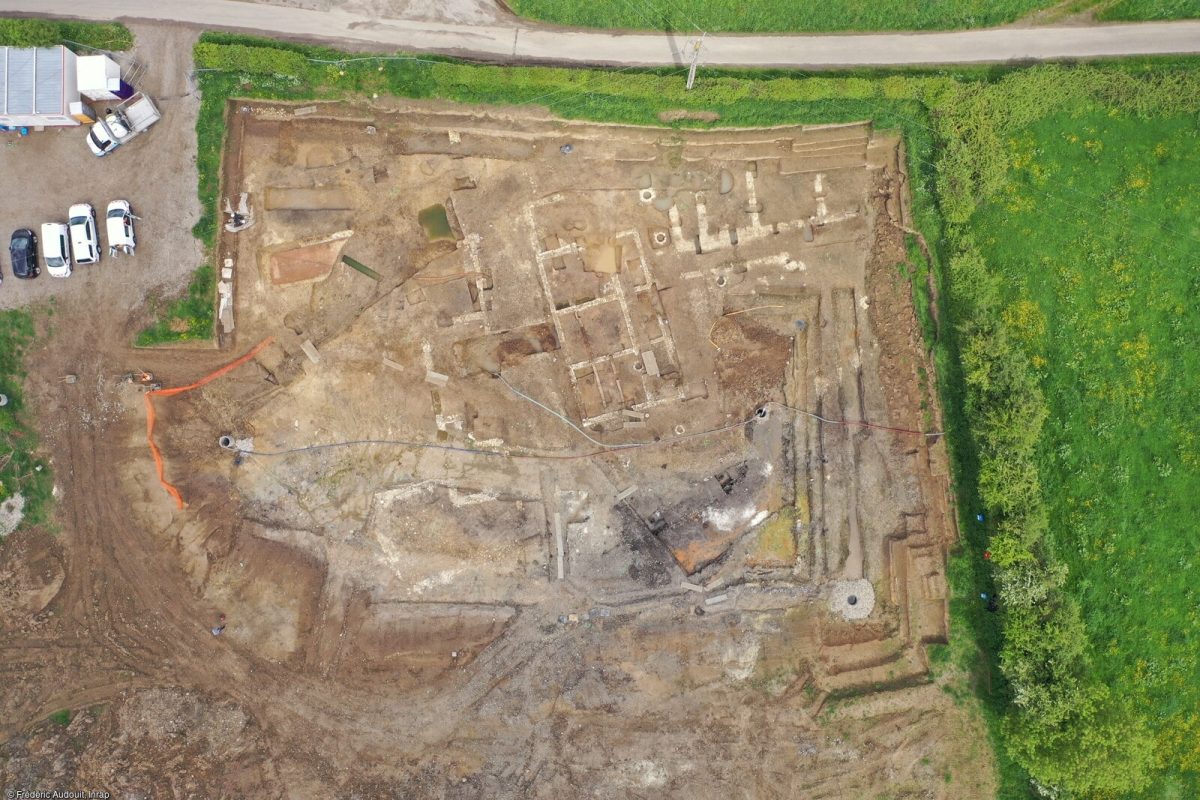
An ancient Roman craft district was discovered by archaeologists working in the southwest of the town of Therouanne near a channel, according to a news release from the French National Institute for Preventive Archaeological Research (INRAP).
The ancient site uncovered during excavations corresponds to a craft area that flourished during the Early Imperial period, along the “Lys” channel, southeast of the city.
The craft district, which was sealed by the sediment of a nearby channel, was over 1,700 years old but remarkably well preserved, according to experts.
Numerous pairs of leather shoes with rough, studded soles were found during the canal’s excavation, according to the press release. The nearly black, dark-brown leather shoes are visible in the photos. Other fragments of cut leather — pieces of unfinished footwear — indicated a shoemaker once worked in the area.
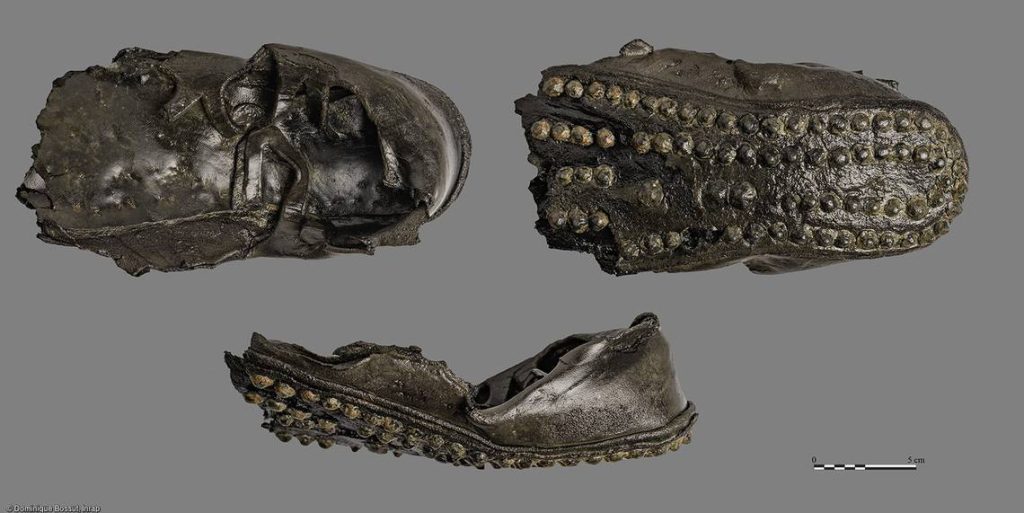
Here, leather work is represented by the discovery, still in the fillings of the canal, of numerous leather shoes with studded soles and numerous triangular scraps of leather, clues to the probable presence in the sector of a shoemaker and a tannery which, like the butchers, would have used the river as a dumping ground.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Archaeologists also discovered a structure with several ovens. According to the release, they found two blue glass cylinders inside the ruins, one in the oven and another off to the side. The unfinished projects indicated the structure was a glassmaker’s workshop.
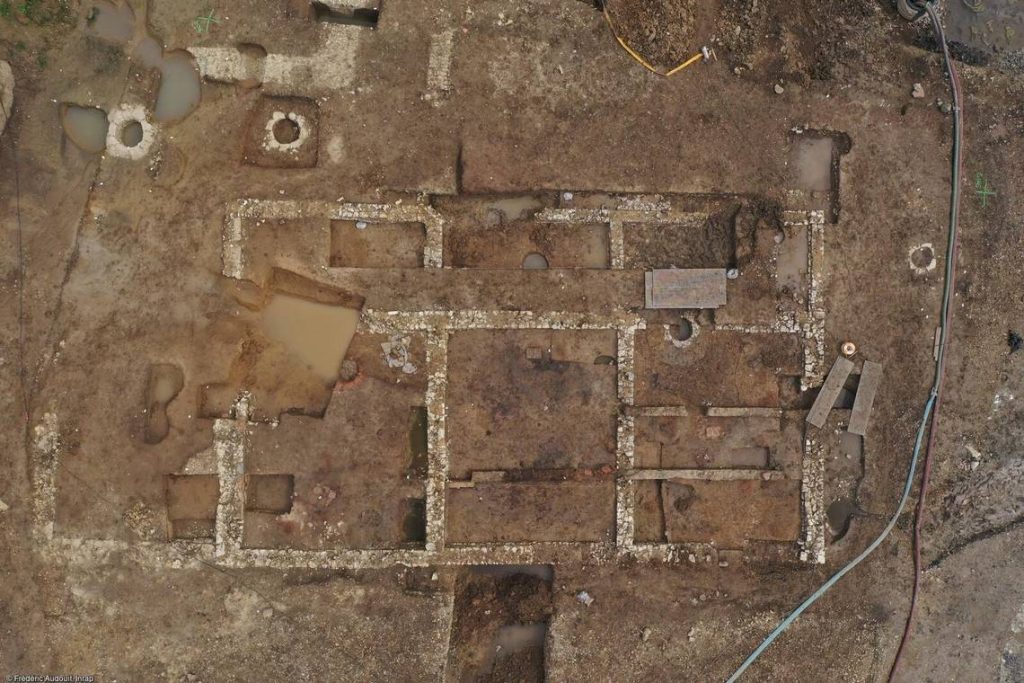

In the canal, archaeologists found a significant number of one kind of cow bone. According to the press release, the bones were leftovers from a nearby butchery and bore signs of butchering.
Ruins of a canal, road and another large structure were found nearby, archaeologists said. The discovery of a canal built during the ancient period is the first in Nord-Pas-de-Calais.
Cover Photo: General view of the Thérouanne excavation complex (Pas-de-Calais) in 2023. Photo: Frederic Audouit, Inrap