Archaeologists from the French National Institute for Preventative Archaeological Research (Inrap) has been uncovered a trove of artifacts, including two statues of the goddess Venus, in a Roman-era quarry-turned-trash-dump in the city of Rennes, France.
Artifacts dating back to 1800 years included statues of Venus, as well as a pottery kiln, clothes pins, and coins.
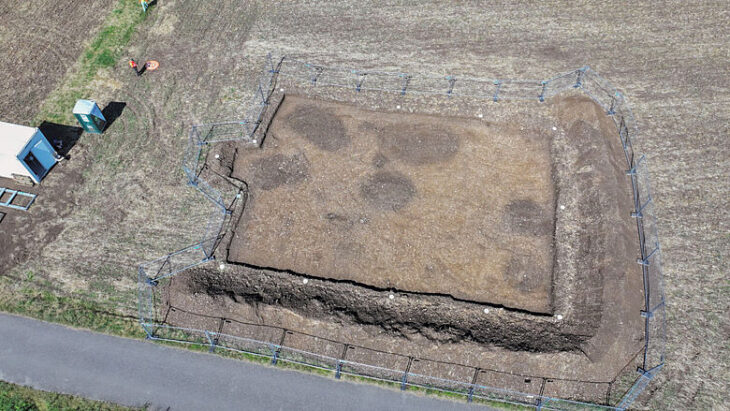
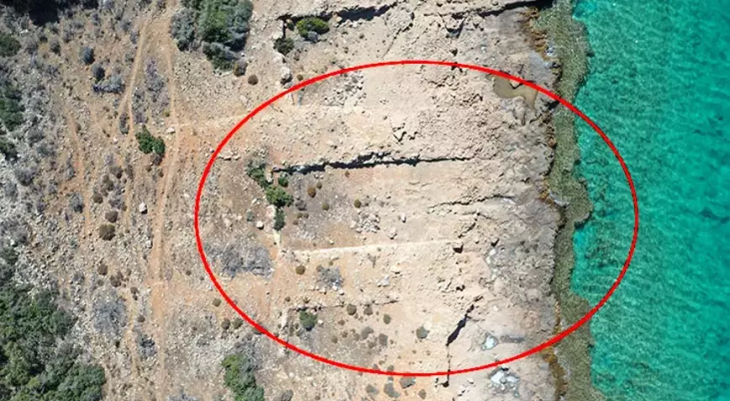
Archaeologists reported earlier this month that they had discovered a quarry that was probably important in constructing Roman Rennes while excavating before a development project.
The founding of the city of Rennes dates back to 100 A.D. Back then, it was still the Condate Riedonum, which was a Roman town. The foundations for several of Condate’s walls and streets were constructed using tiny slabs of Brioverian schist that were extracted during the first and second centuries of our era.
The excavation of such a set can teach archaeologists more about the management and organization of the quarry, as well as the gestures of the quarry workers (tools used, extraction techniques), the evolution of the working face over time, and the development of the quarry in successive levels.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!

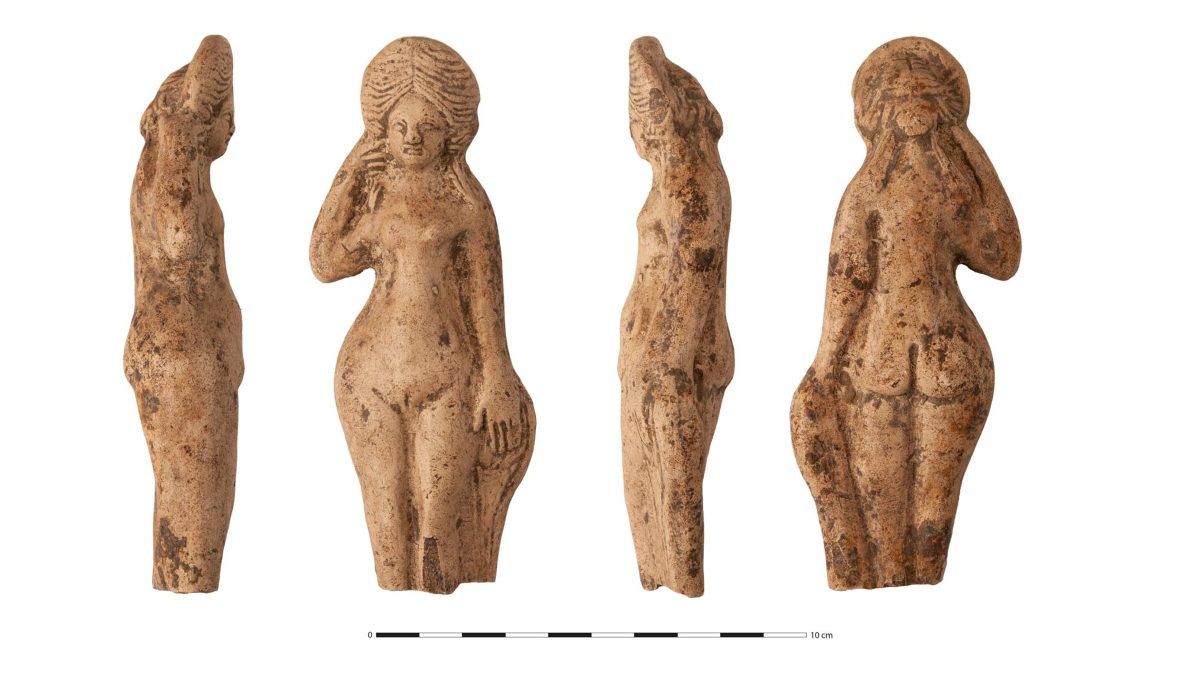
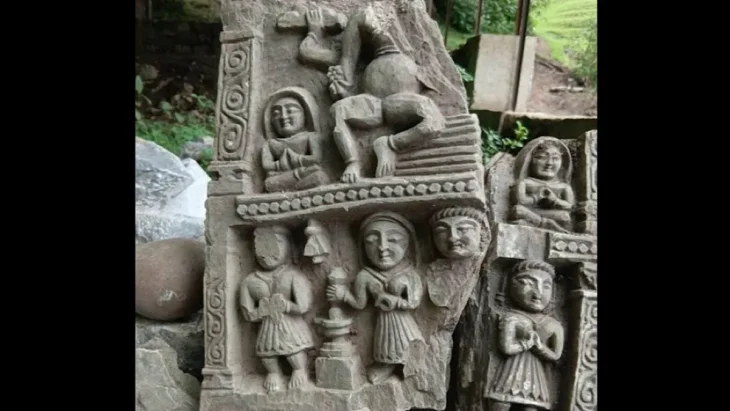
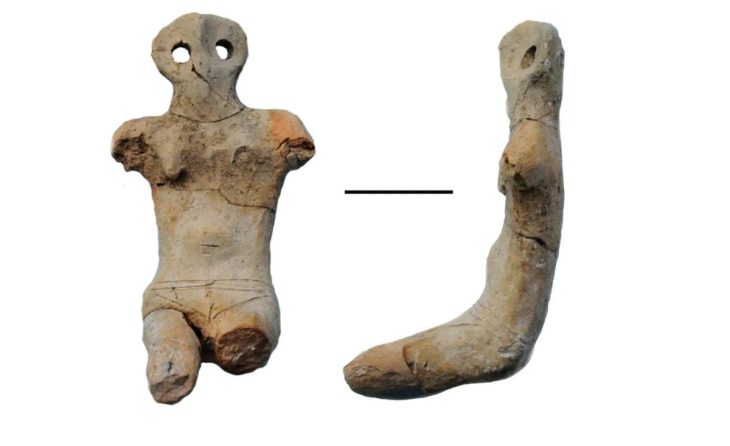
During the quarry excavation, a piece of the mother-goddess Venus genetrix, depicted with her chest covered in fabric, was found. The statuette dates from between the 1st to 2nd century AD and depicts a 10cm tall naked Venus made from terracotta. She is shown holding her hair which is held in place by an imposing headdress.
The second and more thorough example is Venus Anadyomene, who emerged from the sea. She is naked and is wringing the water from her hair with her right hand.
Venus is a Roman goddess associated with love, beauty, desire, sex, fertility, prosperity, and victory. According to Roman mythology, she was an ancestor of the Roman people through her son, Aeneas, who survived the fall of Troy and fled to Italy.
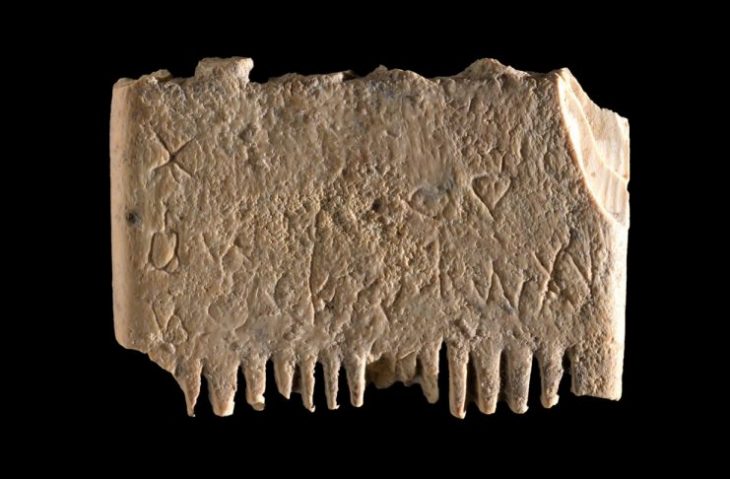
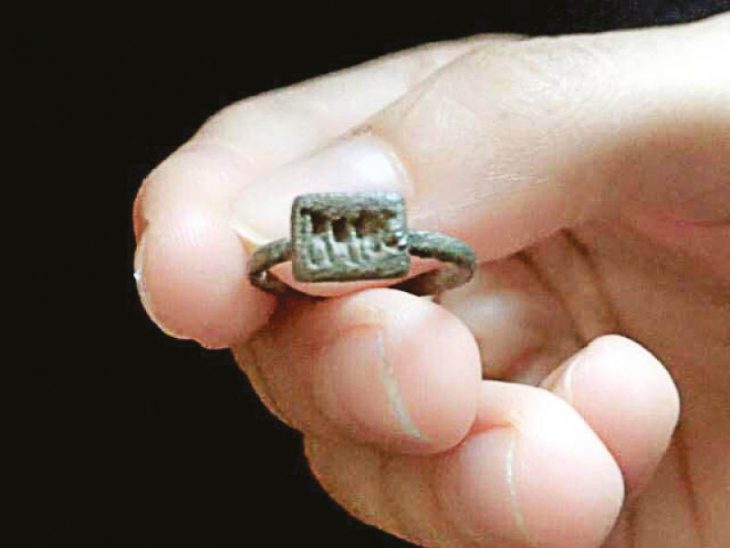
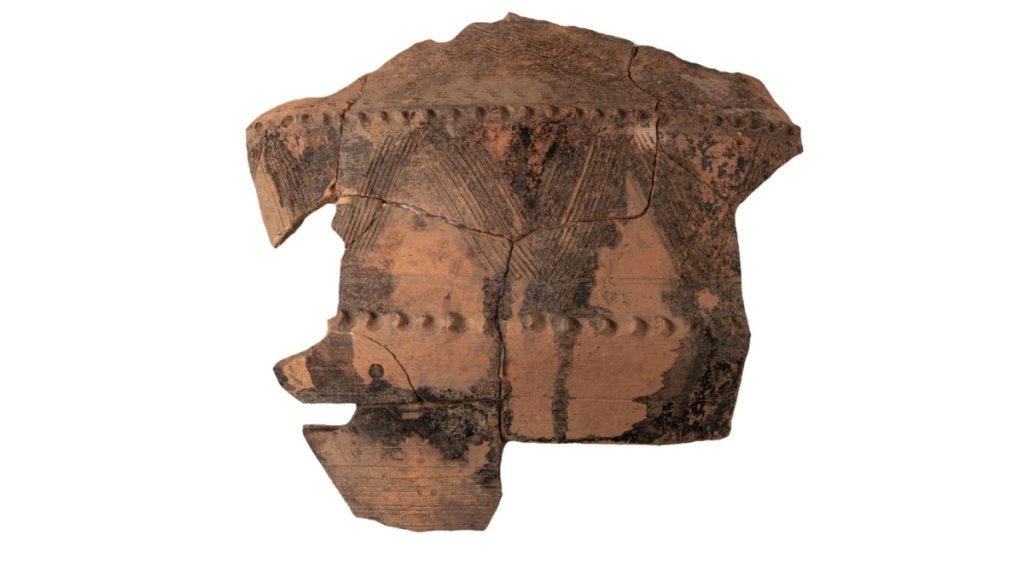
Excavations of the accumulated layers of Roman rubbish has revealed a multitude of finds, including fragments of ceramic tableware, several terracotta statuettes of deities, coins and items of adornment (fibulas).
Cover Photo: Emmanuelle Collado