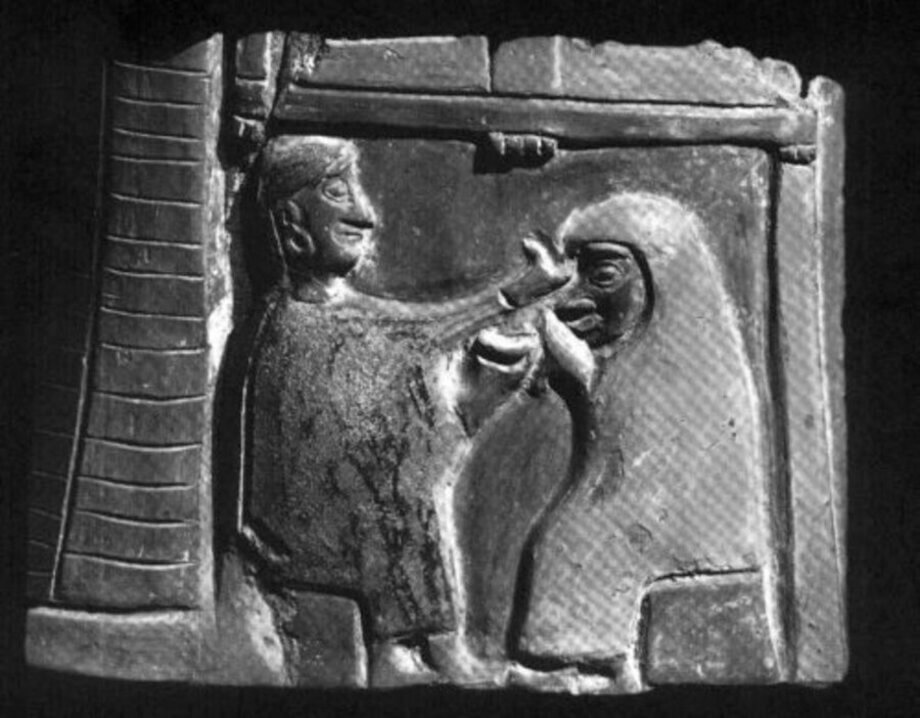
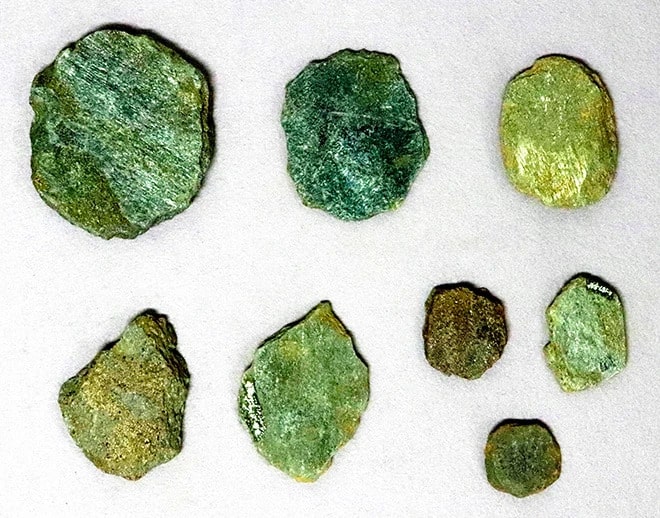
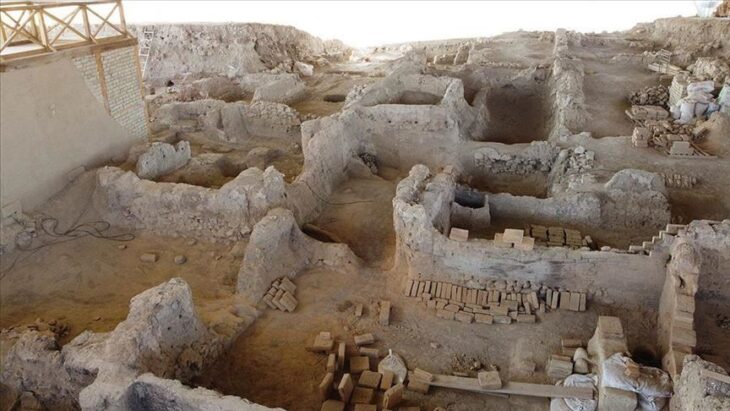
The Kültepe Tablets, discovered in the ancient site of Kültepe (ancient Kanesh) in central Anatolia, are approximately 4,000 years old and provide invaluable insights into the social, economic, and legal aspects of life during the early Bronze Age. One of the most striking features of these tablets is the prominent role that women played in various facets of civilized life, particularly in matters related to rights and inheritance.
The Kültepe tablets reveal that women were active participants in economic activities. They engaged in trade, owned property, and managed businesses. This level of involvement indicates that women were not merely passive figures in society but rather influential agents who contributed to the economic stability of their families and communities. The presence of women in commercial transactions highlights their agency and the respect they commanded in the marketplace.
The head of the Kültepe Excavation, Professor Dr. Fikri Kulakoğlu stated: “Kültepe provides us with one of the largest private archives for the ancient world. Among the documents dating back 4,000 years, we primarily find commercial records. Every event and activity related to trade has been documented here. We can say that everything of value has been recorded. Within this collection, which includes commercial documents, there are also special tablets. These records reflect the daily lives of people at that time and document financial transactions during conflicts of interest.’
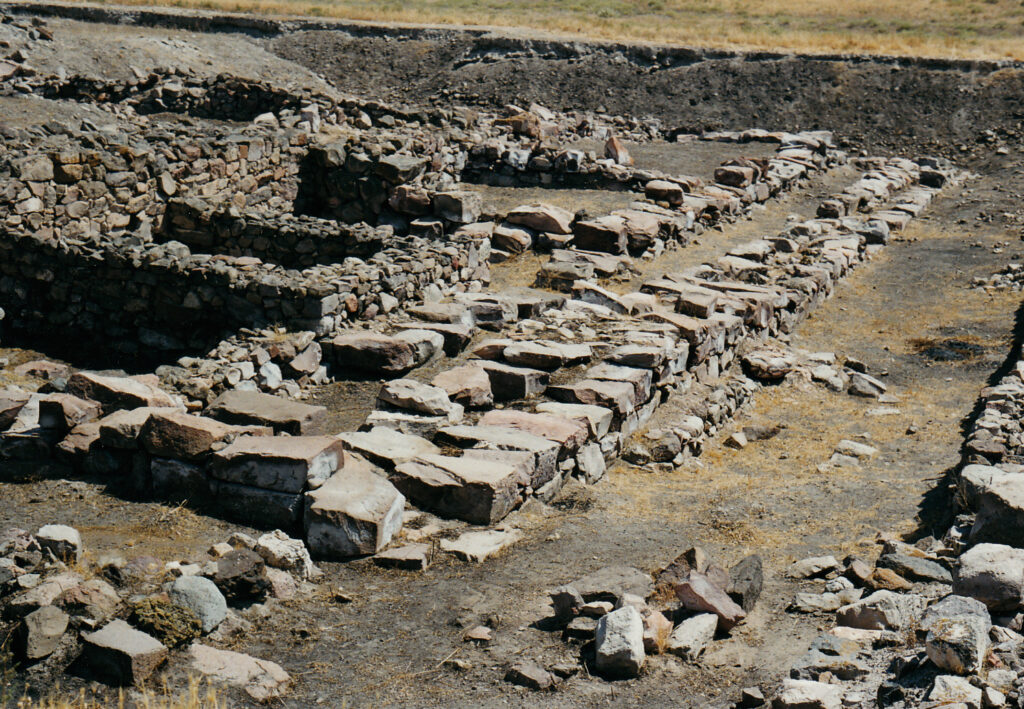

Legal Rights and Inheritance
One of the most significant aspects of women’s rights reflected in the Kültepe tablets is their entitlement to inheritance. The tablets contain references to women inheriting property, which was a crucial aspect of their legal status. The woman inherits 50% of the property as an heir, highlighting her significant legal rights and status within the family and society.
Professor Dr. Fikri Kulakoğlu, stated that the concepts of “wills” and “inheritance” existed 4,000 years ago, with individuals leaving written documents to secure the future of their spouses and children after their death. “We are talking about a time that is very early, 4,000 years ago. In fact, the legal regulations regarding wills and inheritance are relatively new in the modern world. Therefore, people in that era wanted to secure the future of the generations that would come after them and ensure the well-being of their spouses. One of the most important aspects is the equality of women with men; the fact that women inherit 50% of the property is likely something that is not found in other cultures. One of the unique features of the Kültepe tablets is the prominent role that women play in civil life,” he emphasized.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
This right to inherit not only provided women with economic security but also allowed them to maintain a degree of independence within a patriarchal society. The ability to inherit property signifies a recognition of women’s contributions to family and society, challenging the notion that women were solely dependent on male relatives.

Marriage and Family Dynamics
The Kültepe tablets also shed light on the institution of marriage and family dynamics. Women had the right to negotiate their marriage contracts, which often included stipulations regarding their rights to property and inheritance. This indicates that women were not merely passive participants in marriage but had a voice in determining their futures. The existence of such contracts suggests a level of mutual respect and negotiation between spouses, which is essential for understanding the social fabric of Kültepe society.
Marriage was an institution, much like today, but mutual interests were also documented. Marriage contracts are frequently encountered documents in Kültepe. Additionally, we find specific clauses that outline the rules of marriage. The marriage contract includes penal clauses in the event of a potential divorce. For example, a man has recorded that he would pay a compensation if he divorced his wife before marriage. People also planned for the future of their spouses and children. In the event of a father’s death, he documented how much he would give to his wife and children. Just as in modern times, people established rules for the distribution of their assets upon their death. For instance, the wife has the right to inherit 50% of all the property left by her husband. This was established as a fundamental rule. Upon his death, 50% of his assets and property go to the wife, while the remaining portion is distributed equally among the children according to the rules set by the guardian. This is not a rare occurrence; there are numerous tablets related to wills. Some of these documents are found in envelopes. These wills are not limited to those written by a single individual; there are also those signed in the presence of witnesses, which can be considered almost as official documents.”
In conclusion, the Kültepe tablets serve as a testament to the significant role women played in the social, economic, and legal spheres of early Anatolian civilization. Their rights to inheritance, participation in economic activities, and involvement in marriage negotiations reflect a society that recognized and valued women’s contributions. By examining these ancient texts, we gain a deeper understanding of the historical context of women’s rights and the evolution of gender roles, which continue to resonate in contemporary discussions about equality and justice.
The Kültepe tablets remind us that the fight for women’s rights has deep historical roots, and the lessons learned from the past can inform our ongoing efforts toward achieving gender equality today.
Cover Image Credit: The Vase of İnandık. AA