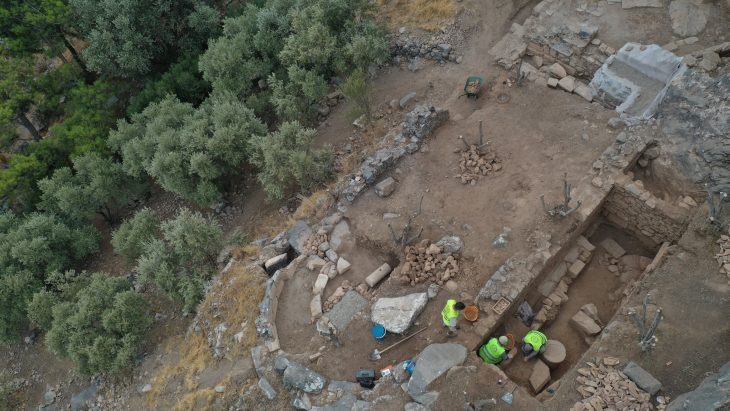
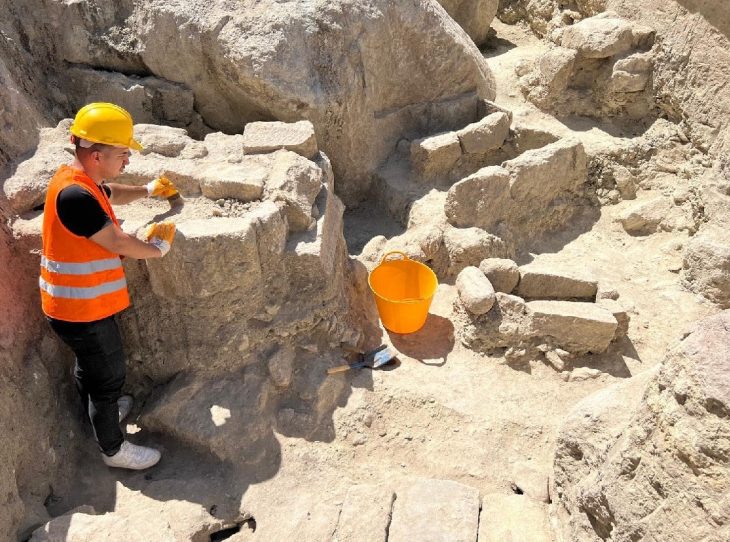
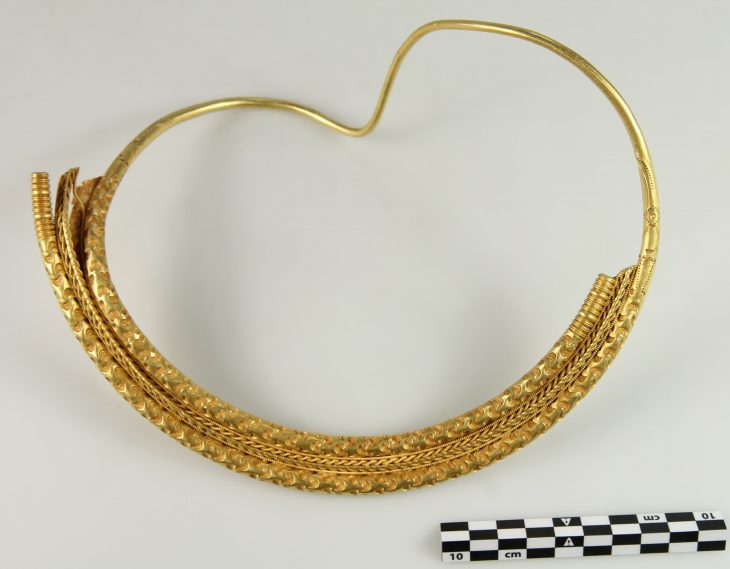
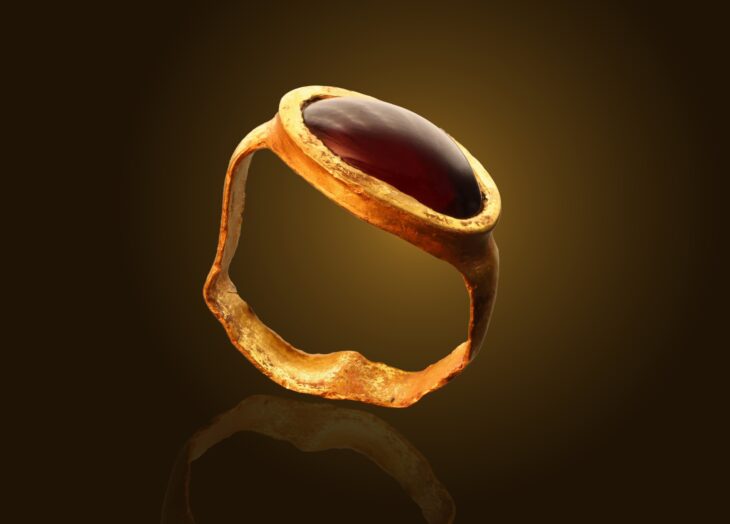
A new 3D virtual reconstruction of the Celtic gate has been made in Staffelberg, in the German state of Bavaria. The reconstruction was created based on the latest information discovered during excavations in 2018 and 2019.
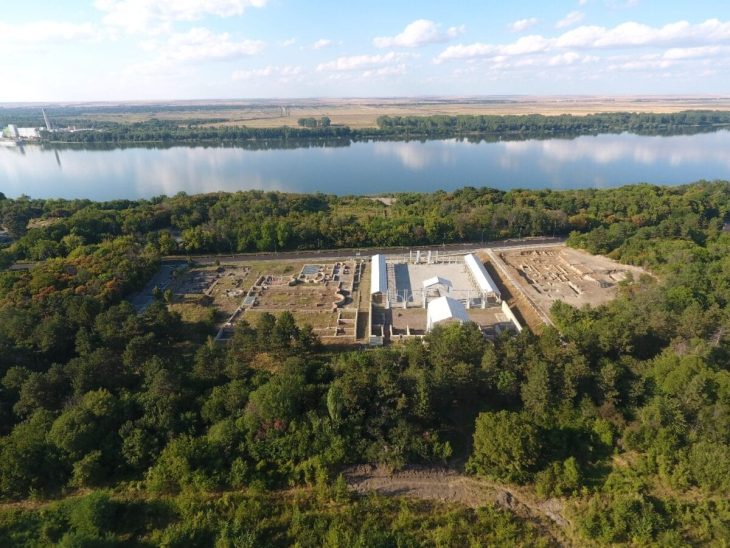
Staffelberg’s high, rocky plateau made it an ideal location for defense. This elevated area had been settled and fortified since the Neolithic (ca. 5000 BC), Urnfield, and Hallstatt periods. During the Celtic and late Iron Age periods, an additional large fortification wall enclosed this “natural” Acropolis. A defense wall of ca. 2800 m long enclosed the Oppidum which had the Acropolis with a further fortification wall, in its entirety of 49 ha. The monumental gate was built around 130 B.C. After the year 40 BC, the site was entirely abandoned.
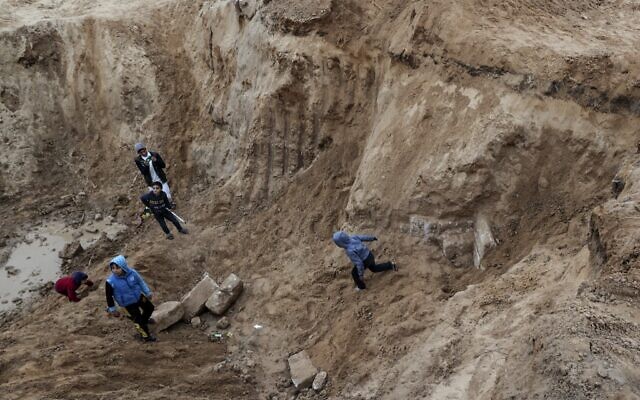
The excavation uncovered towering city walls as well as a tower three times the height of the walls at the gate. The ruins of the walls reach up to four feet in height. There have been no other Celtic oppidia with such high walls unearthed. Archaeologists also unearthed the earliest paved road segment in Bavaria. A Celtic footprint, most likely left by a construction worker, was discovered on the road.
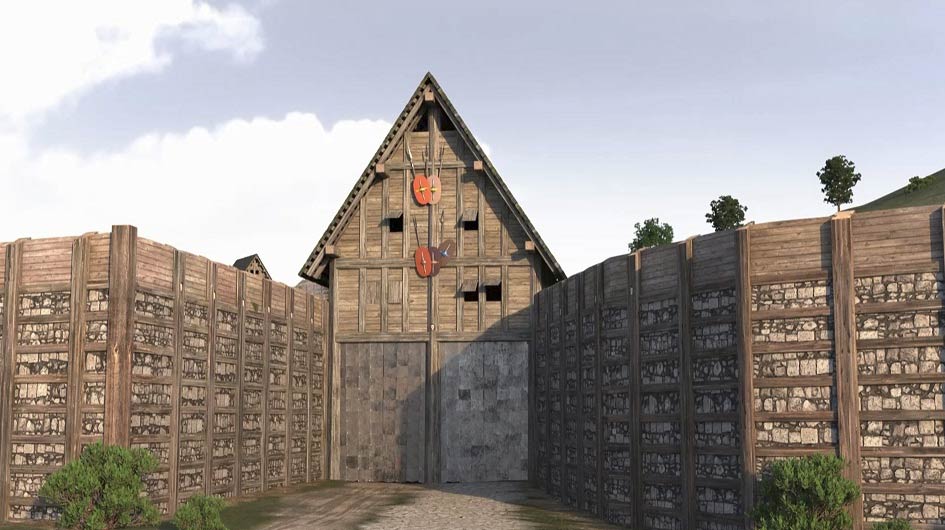

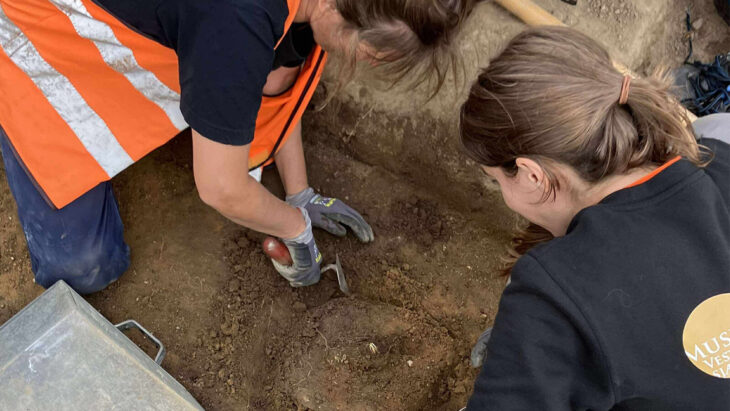
More than 30 human skulls decorated the town entrance. Never before has a Celtic city gate been documented in such detail as the Franconian Staffelberg.
More than 30 human skull fragments were found during the excavations. Archaeologists believe the skulls were placed in niches and on wooden posts in the gate. Ancient sources describe Celts adorning their gates with skulls.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
“Everything indicates that the nobility who lived on the summit plateau of the Staffelberg wanted to show what they could afford with this gate. It is a demonstration of its richness and the high level of technology,” explains Dr. Markus Schußmann, who led the research excavation at the west gate of the oppidum…. According to current knowledge, the residents probably set the oppidum on fire themselves when they abandoned it around 40 B.C. Using the traces left by the foundations, the charred wood of the gate and the iron nails and fittings in the ground, the archaeologists meticulously did detective work to reconstruct the presumed structure of the complex.
Bavarian State Office for the Preservation of Monuments, emphasizes: “The Celtic Gate opens our eyes to the pre-Christian past. It reveals a lot about the life of the Celts: for example, that traffic on the oldest known street in Bavaria was on the right at the time.”