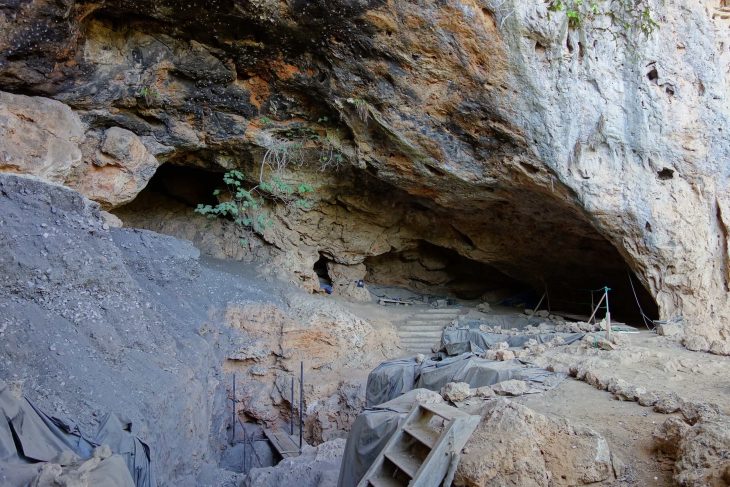
Egyptian officials have announced a groundbreaking discovery: the long-lost tomb of King Thutmose II, marking the last of the royal tombs from ancient Egypt’s Eighteenth Dynasty. This significant find comes over a century after the discovery of King Tutankhamun‘s tomb in 1922, and it sheds new light on a period that reigned from approximately 1550 BC to 1292 BC.
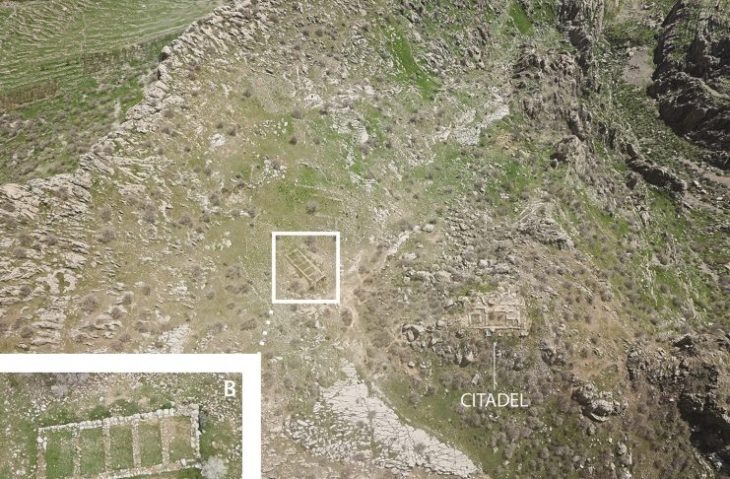
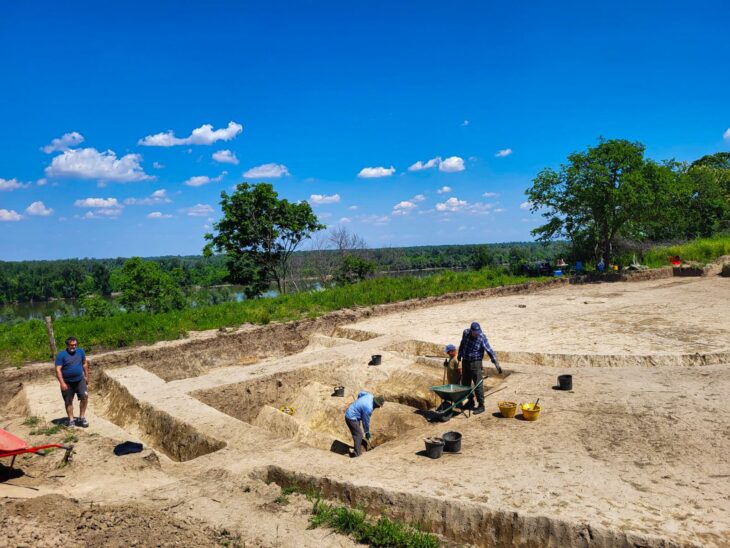
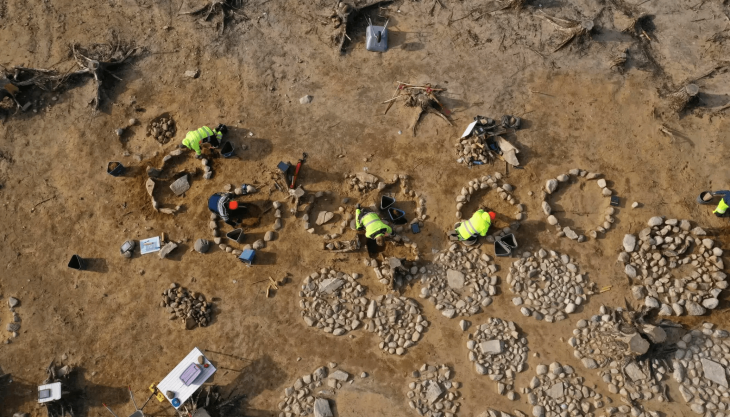
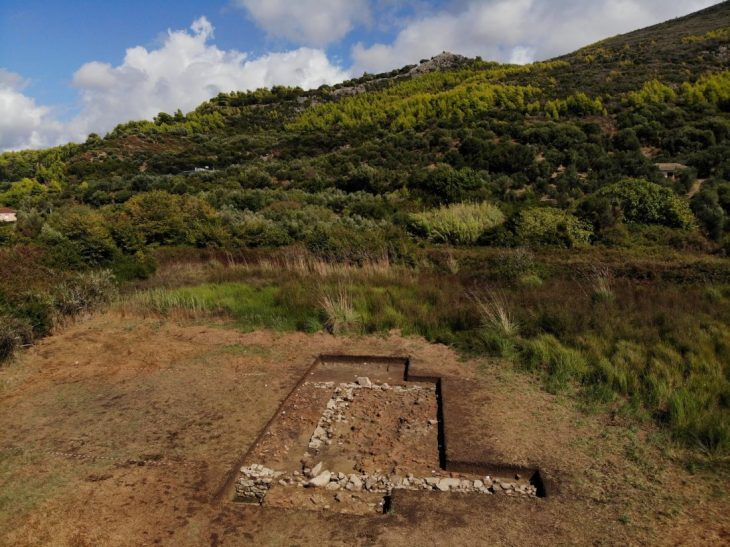
A joint archaeological mission comprising British and Egyptian teams uncovered the tomb, designated as No. C4, located a few miles west of Luxor in the area known as the mount of Thebes. The entrance and main passage were initially discovered in 2022, and while the team initially speculated that the tomb might belong to one of the wives of the kings due to its proximity to the tombs of Queen Hatshepsut and the wives of King Thutmose III, further excavations revealed compelling evidence linking it directly to King Thutmose II.
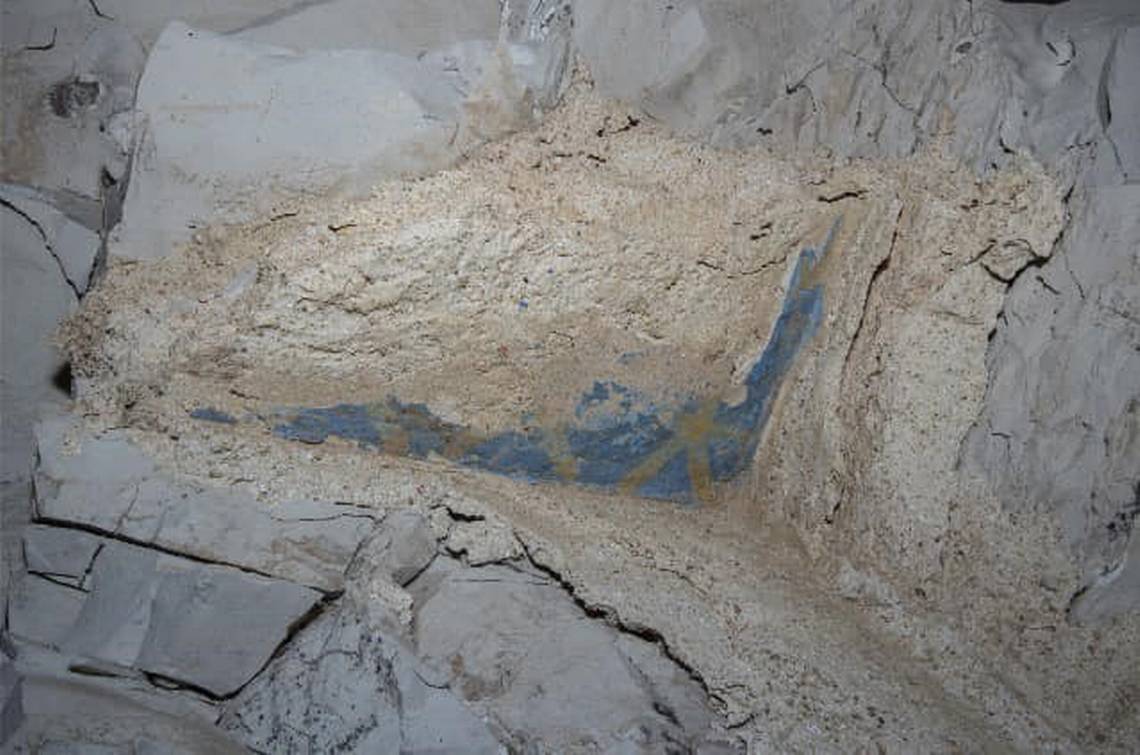
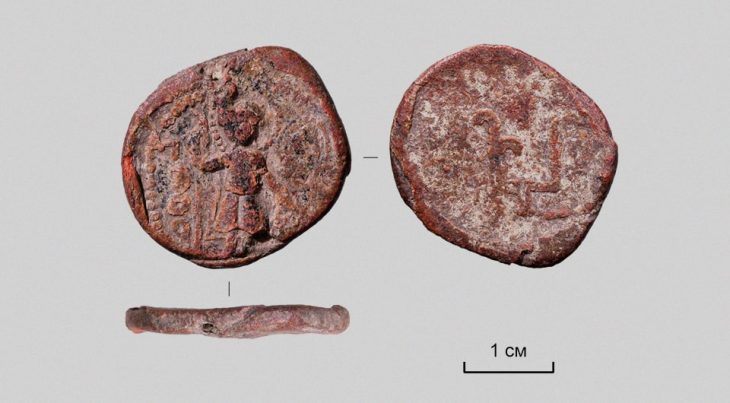
Among the artifacts found were several fragments of alabaster vases inscribed with the name of King Thutmose II, referring to him as the “deceased king.” Additionally, sections of a religious text associated with ancient Egyptian royal burials and plaster fragments adorned with blue paint and yellow stars were discovered. These findings have led archaeologists to conclude that Tomb No. C4 was indeed the final resting place of King Thutmose II.
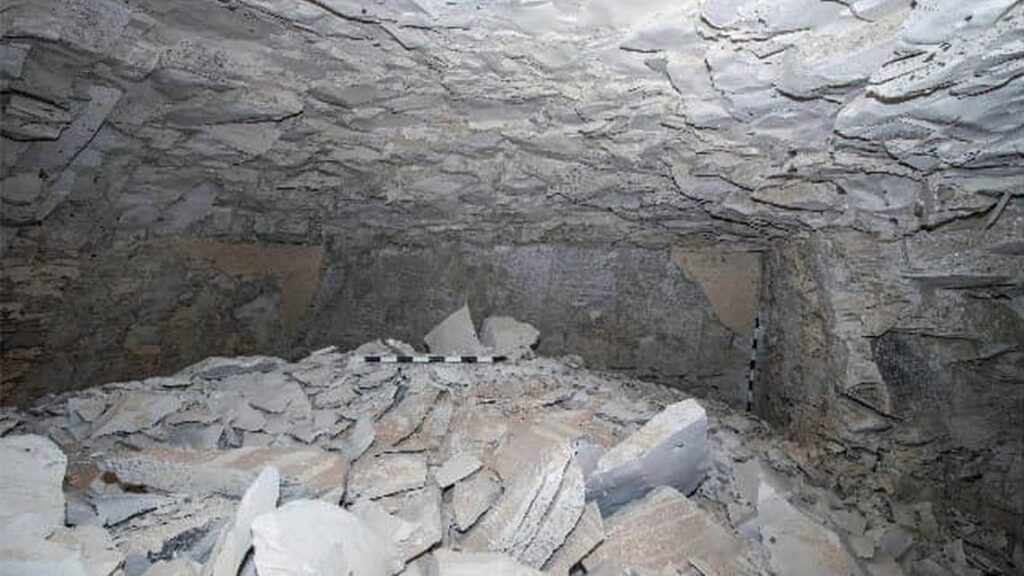

Dr. Mohamed Ismail Khaled, Secretary-General of Egypt’s Supreme Council of Antiquities, emphasized the importance of this discovery, describing it as one of the most significant archaeological finds in recent years. The tomb, however, is in a poor state of preservation, likely due to flood damage shortly after the king’s death. Initial studies suggest that many of the original contents of the tomb may have been relocated following these ancient floods.
The architectural design of the tomb is characterized by simplicity, featuring an entrance, a sloping main corridor, and a burial chamber. Dr. Piers Litherland, head of the English team at the site, noted that the mission would continue to investigate the tomb and seek to uncover any additional secrets that may lie beneath the earth.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
While the mummy of King Thutmose II was discovered in the 19th century at another site known as the Deir el-Bahari Cachette, this recent discovery provides a crucial link to understanding his life and reign. As work at the tomb progresses, many questions remain regarding the circumstances surrounding the removal of the king’s mummy from its original burial site.
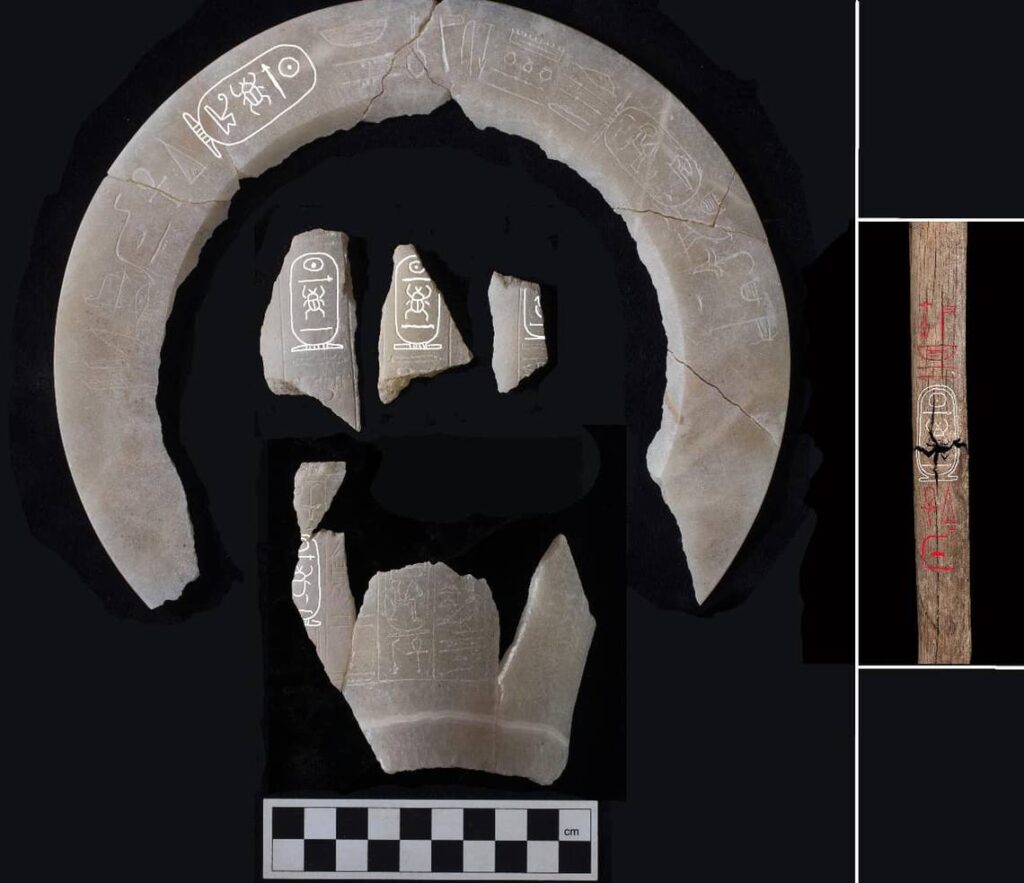

This remarkable discovery not only enhances our understanding of King Thutmose II’s life and reign but also underscores the importance of continued archaeological efforts in revealing the complexities of ancient Egyptian history. As researchers delve deeper into the tomb and its artifacts, they are poised to uncover further insights that could reshape our knowledge of this pivotal era in Egypt’s past.
Egypt’s Ministry of Tourism and Antiquities
Cover Image Credit: A section of tomb No. C4, identified as the burial site of King Thutmose II. Credit: Egypt’s Ministry of Tourism and Antiquities