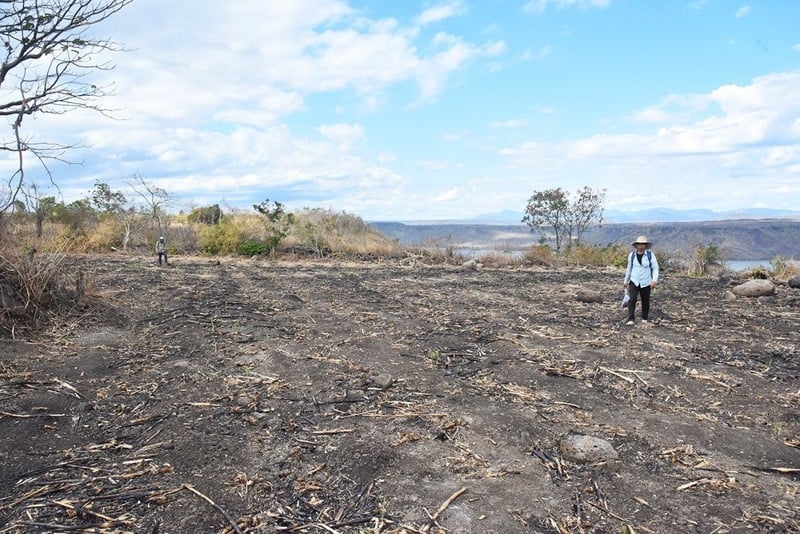
Archaeologists in Vietnam’s Gia Lai province have uncovered a remarkable prehistoric site dating back more than 3,500 years. Excavations at Plei Ring, located in H’Bong commune of Chu Se district, revealed not only a vast opal stone workshop but also one of the most intriguing musical discoveries in Southeast Asia: a set of prehistoric lithophones, or stone xylophones.
The findings were announced during a conference on August 15, organized by the Pleiku Museum in collaboration with the Southern Institute of Social Sciences. Leading Vietnamese scholars hailed the site as a key hub in the prehistoric network of tool production and cultural exchange across the Central Highlands.
A 3,500-Year-Old Opal Stone Workshop
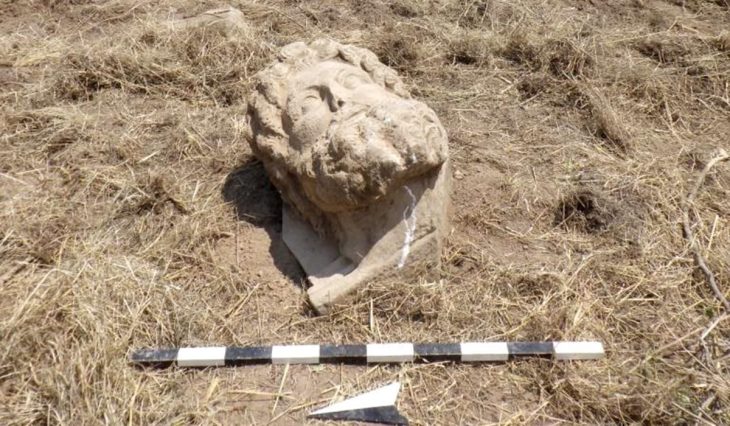
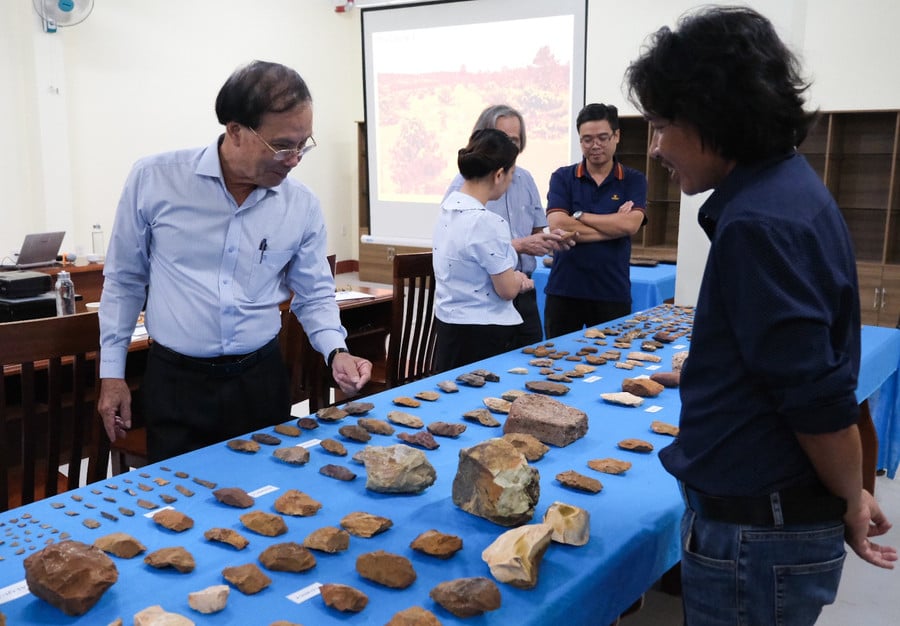
Excavations between March and June 2025 showed that Plei Ring was more than just a settlement. According to Dr. Nguyen Quoc Manh, deputy director of the Archaeological Center, the site functioned as a large-scale opal stone workshop around 3,500 to 3,000 years ago. Craftsmen there mastered chipping and carving techniques to produce an array of tools that supplied not only local communities but also neighboring regions.
Evidence of mass production was clear: numerous discarded and broken artifacts were found, suggesting a strict quality control system and an early division of labor. This discovery highlights the sophistication of prehistoric craftsmanship and the gradual development of an agricultural economy that relied heavily on durable stone tools.

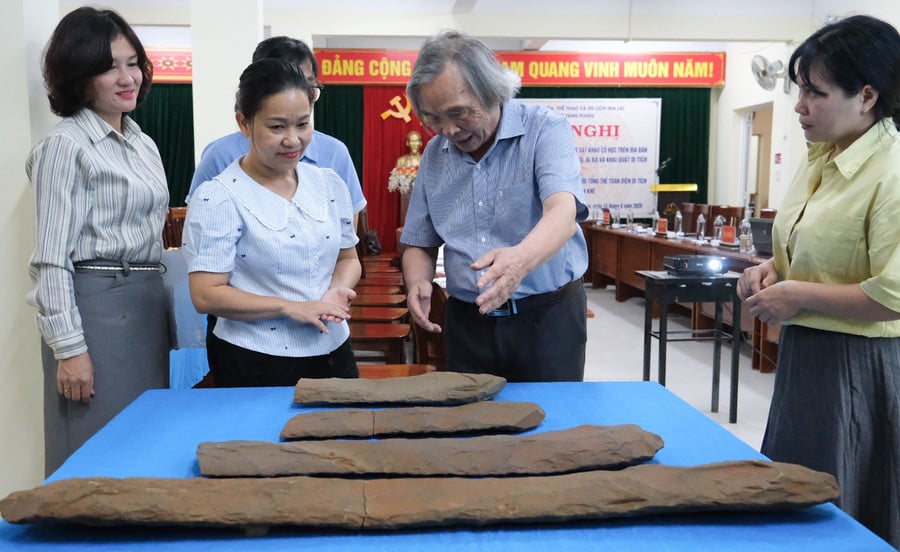
The Discovery of Lithophones
Among the most striking finds at Plei Ring was a set of lithophones, an ancient musical instrument made from carefully carved stone slabs. When struck with wooden mallets, these stones produce resonant tones similar to those of a xylophone. Lithophones are considered one of the oldest known musical instruments in human history, with some examples in Vietnam dating back at least 3,000 years.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
In traditional contexts, lithophones were likely used in ritual ceremonies, communal gatherings, and perhaps even agricultural festivals. Their haunting, bell-like sounds connect present-day listeners with the spiritual and cultural lives of prehistoric communities.
Cultural and Historical Significance
The discovery of lithophones at Plei Ring not only enriches the understanding of prehistoric music but also demonstrates the cultural creativity of early Vietnamese societies. Unlike stone tools designed for survival, lithophones represent a deeper dimension of human expression: the desire to create sound, rhythm, and art.
Archaeologists suggest that lithophones in the Central Highlands may have served both practical and symbolic purposes, reinforcing social cohesion and spiritual beliefs. Their presence within a large workshop site also indicates that music was not an isolated practice but an integrated part of community life.

Toward Heritage Recognition
Experts at the conference emphasized the importance of preserving the Plei Ring relic and incorporating it into broader heritage programs. Discussions also touched on linking the research with other key archaeological sites, such as Roc Tung-Go Da in An Khe, in order to prepare a future UNESCO World Heritage dossier.
With over 52 newly identified relics in Chu Se district alone, the Central Highlands is emerging as one of the most important regions for studying Vietnam’s prehistoric past. The dual discovery of stone tools and lithophones underscores the balance between utility and creativity in ancient societies—an enduring legacy that continues to fascinate researchers and music lovers alike.
A Legacy That Resonates Today
For modern audiences, the lithophone offers more than archaeological curiosity. Contemporary musicians in Vietnam have revived the instrument, adapting it for concerts and cultural showcases. Its deep, resonant tones remind listeners that the roots of music stretch back thousands of years, connecting us with the imaginations of our ancestors.
The findings at Plei Ring reaffirm Vietnam’s role as a cradle of prehistoric innovation, where stone was not only a tool for survival but also a medium for art and sound. As archaeologists continue to uncover the secrets of this site, the 3,500-year-old lithophones of Gia Lai stand as a symbol of both human ingenuity and cultural heritage that still echoes across time.
Cover Image Credit: Plei Ring archaeological site plan. Huynh Ba Tinh