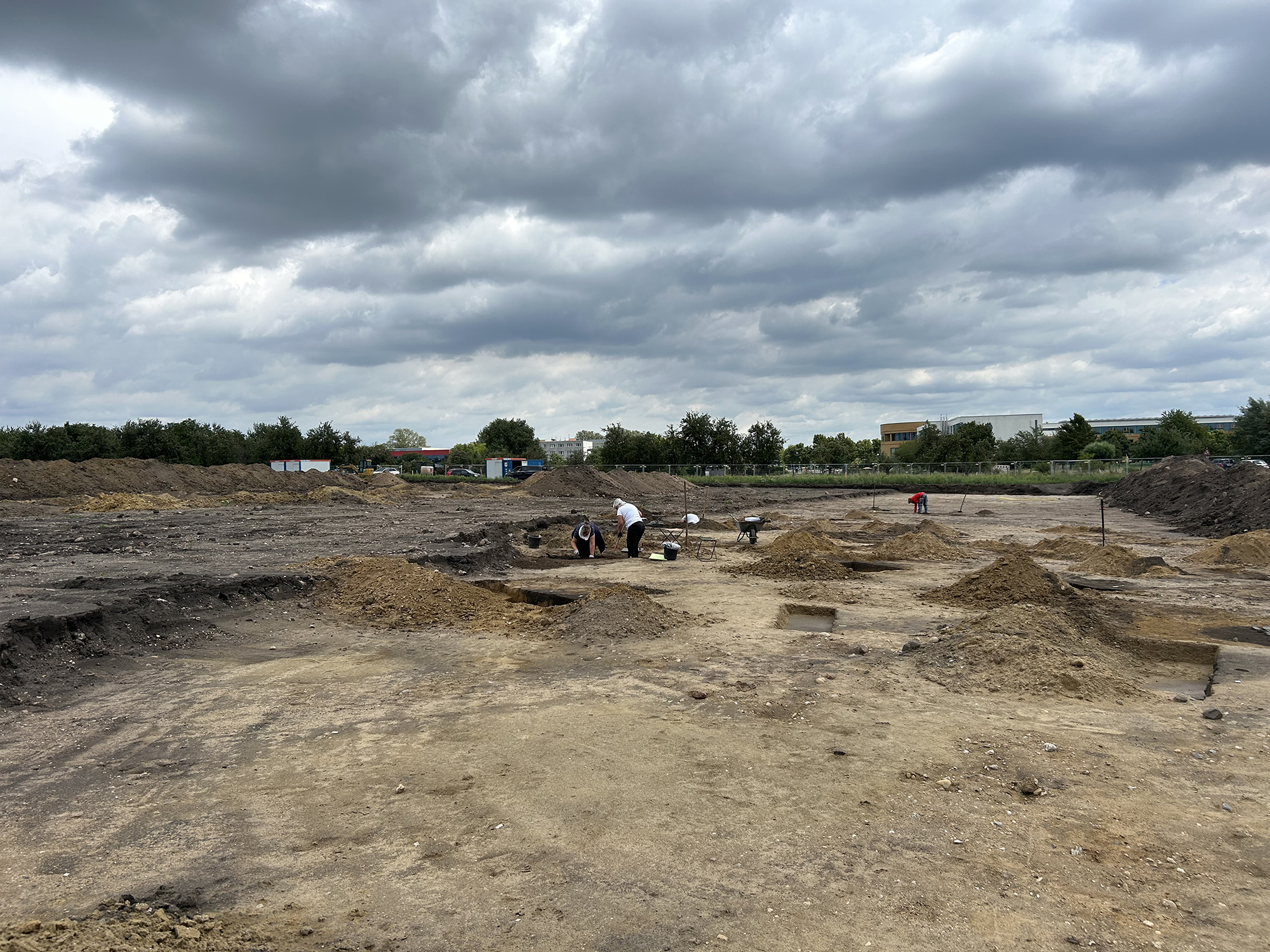
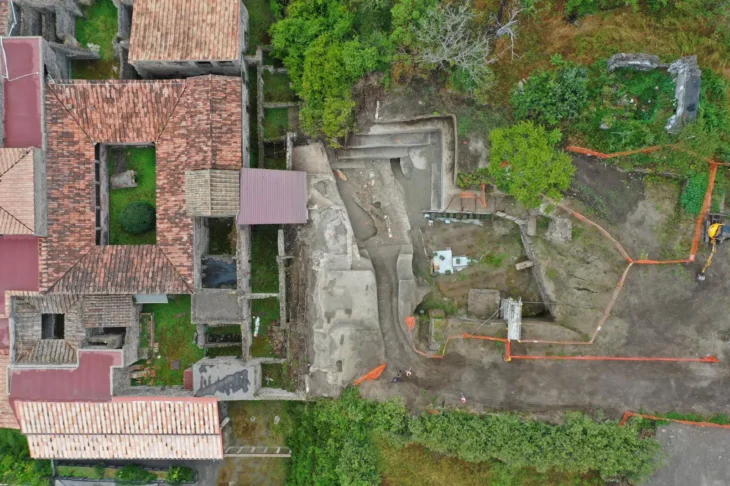
Archaeologists have uncovered an expansive Late Bronze Age settlement in Wolmirstedt, Saxony-Anhalt, ahead of the construction of a new multimillion-euro sports stadium. The discovery, made during preliminary excavations by the State Office for Heritage Management and Archaeology (LDA), reveals that this site was already considered prime real estate over 3,000 years ago.
Bronze Age Life Revealed on the Banks of the Ohre River
Located on the western edge of the town near the Ohre River and close to its ancient confluence with the Elbe, the 21,000-square-meter site offers rich insights into one of the most dynamic cultural borderlands of the Late Bronze Age (ca. 1300–750 BC). The region served as a crossroads between two significant cultural groups — the Nordic Bronze Age circle and the Lusatian culture — with local expressions like the Elb-Havel and Saalemündung groups emerging in this area.
Excavation manager Juliane Huthmann and her team have so far documented 322 archaeological features and recovered over 1,000 artifacts, including ceramics, bronze tools, animal remains, and a surprising number of architectural structures.
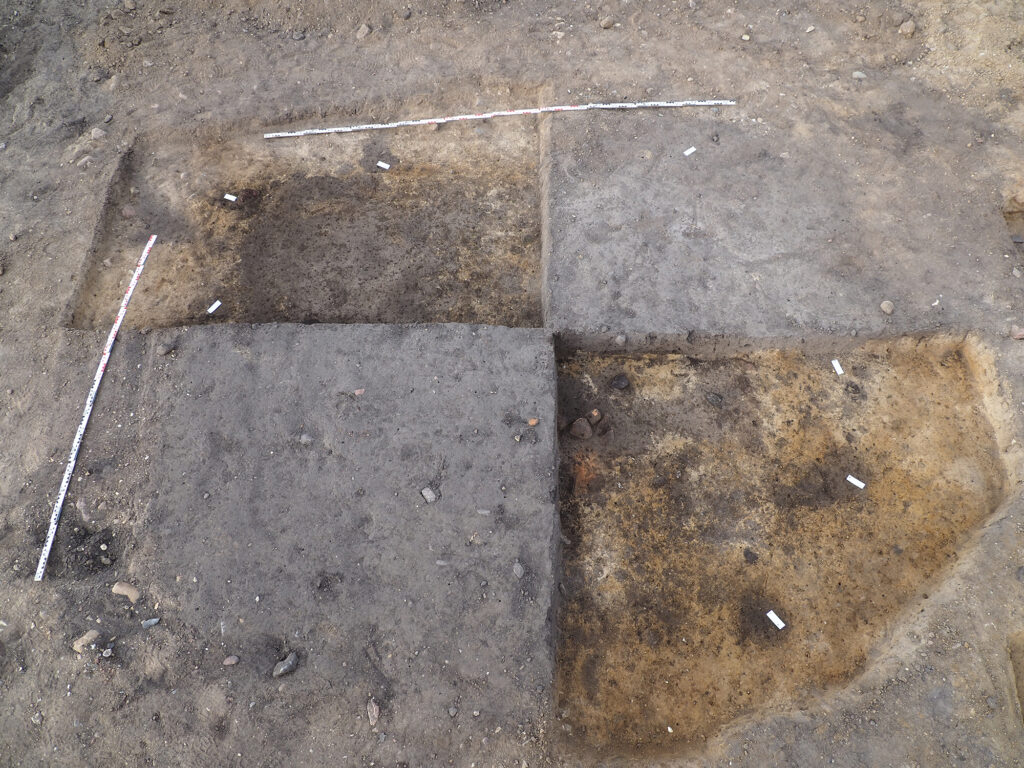

Key Findings: Ovens, Storage Pits, and a Glimpse into Bronze Age Daily Life
The archaeological team uncovered a wealth of structures and artifacts that offer an intimate look into everyday life during the Late Bronze Age. These findings shed light not only on how people lived, but also on how they cooked, stored food, created textiles, and managed resources more than 3,000 years ago.
Storage Pits with Ingenious Design
One of the most common features found on site were circular storage pits, originally designed for preserving food. These pits were typically lined with woven wickerwork, a sophisticated method that provided ventilation while protecting contents from spoilage. Over time, many of these storage structures were repurposed as waste disposal areas, providing archaeologists with a layered timeline of use and adaptation.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Ancient Clay Ovens and an Unusual Culinary Clue
Three clay ovens were identified based on their burnt clay walls and surrounding charcoal deposits. In two of the ovens, log impressions preserved in the clay indicate the use of wooden superstructures or oven covers, a detail rarely found with such clarity. Perhaps the most intriguing oven contained the shell of a pond turtle, unearthed alongside ceramic fragments. Laboratory analyses are underway to determine whether this animal was consumed, which would offer rare insight into the Bronze Age diet and possibly ritual practices.
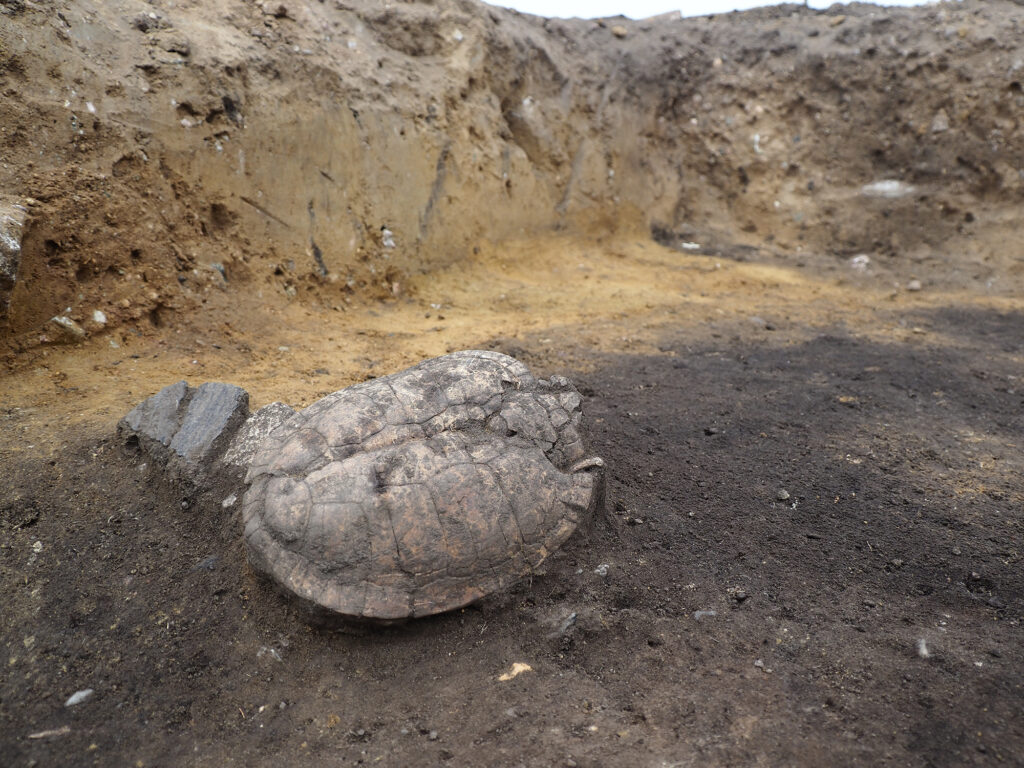

Remains of Residential and Utility Structures
Evidence of post holes across the site points to a variety of buildings, from domestic residences to storage sheds. A particularly noteworthy structure is a two-aisled residential house, measuring approximately 4 meters wide by over 6 meters long — a substantial home for its time. Additional post configurations suggest the presence of smaller utility and storage buildings, likely used for daily farming or household activities.
A Rare Bronze Age Weaving House
Among the most significant architectural discoveries is a recessed weaving house, roughly 4 by 3.3 meters in size. The building was identified by a line of pyramid-shaped loom weights, which were used to hold tension on vertical threads in a standing loom. This setup allowed for the production of textile strips about 60 centimeters wide, indicating that textile manufacturing was a regular part of domestic life in the settlement.
Ceramics and Domestic Tools
Thousands of pottery fragments were recovered, showcasing a wide array of Bronze Age ceramics. These include rough-walled storage jars and cooking pots, as well as more refined and decorated jugs and cups. Together, they reflect both utilitarian and ceremonial use, hinting at the social and economic diversity of the community.
Food Remains Paint a Dietary Portrait
The excavation also yielded numerous animal bones, including those of cattle, pigs, and sheep or goats. These remains are mostly food scraps and provide direct evidence of the community’s meat-based diet. Combined with the ceramic cooking vessels and storage solutions, these finds help reconstruct Bronze Age food preparation and consumption practices in the region.
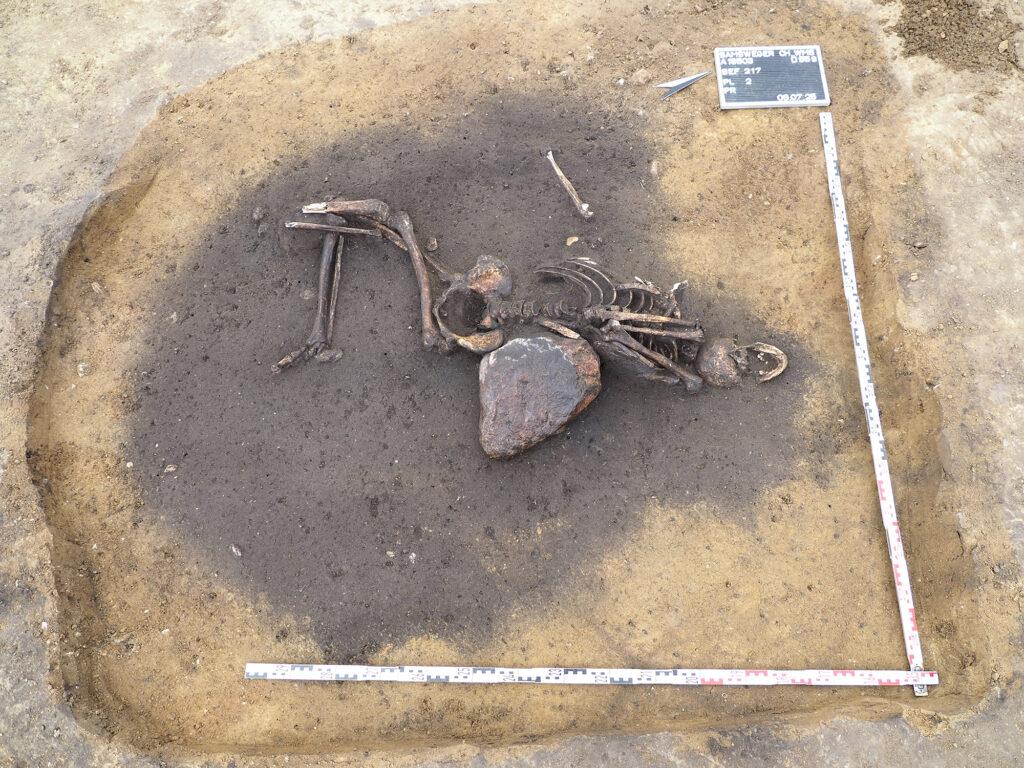

The Mystery of the Squatting Skeleton
Adding a layer of intrigue, archaeologists discovered an unusual human burial within the settlement boundaries. The skeletal remains of a strong adult male, buried in a squatting position with a twisted head, deviate from the typical cremation customs of the time. The purpose of such irregular burials remains unclear — theories range from ritual practice to social stratification.
Looking Ahead: History Beneath the Stadium
The ongoing excavations are scheduled to continue through October 2025, with full analysis and cataloging expected to follow. The construction of Wolmirstedt’s new multifunctional stadium — the town’s largest investment since 1990 — is set to begin in March 2026. With funding support of €4.3 million from the state of Saxony-Anhalt, the €10.5 million project will include a grandstand, a full-size pitch, and modern athletic facilities, culminating in a grand opening ceremony planned for September 4, 2027.
Cultural Heritage Meets Modern Development
This exceptional find showcases how modern development and archaeological heritage can go hand in hand. As Wolmirstedt prepares to build for the future, it simultaneously uncovers deep connections to its distant past — revealing a vibrant community that once thrived on this very ground more than three millennia ago.
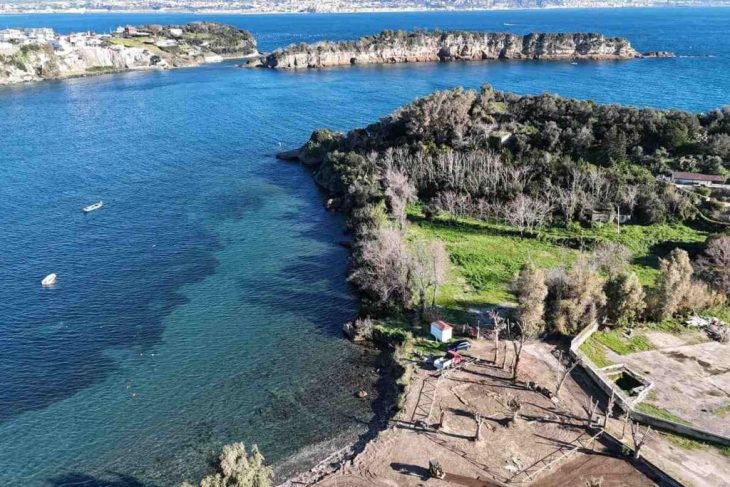
Cover Image Credit: View over the excavation area in Wolmirstedt. Credit: State Office for Monument Preservation and Archaeology Saxony-Anhalt, Barbara Fritsch.