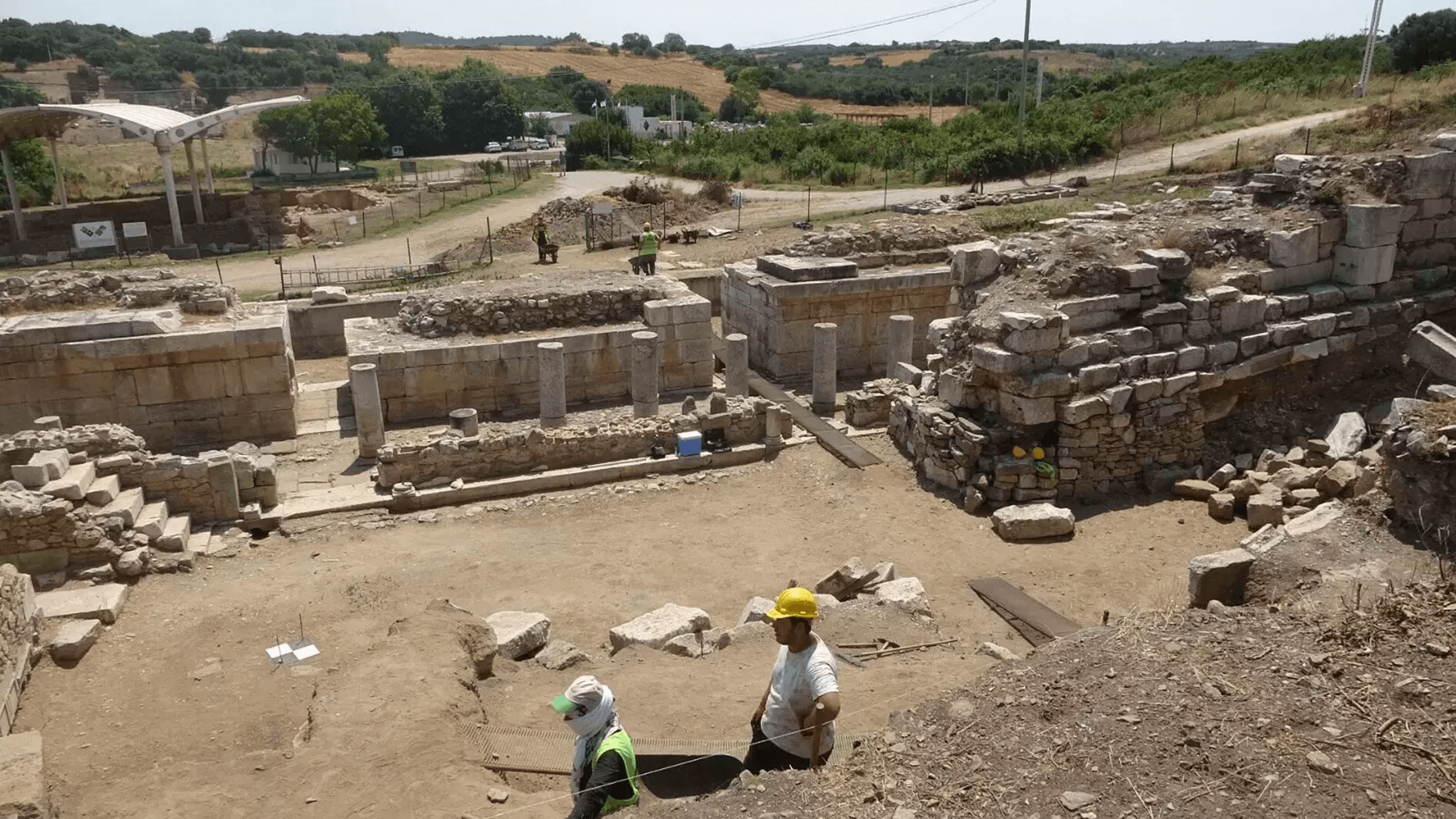
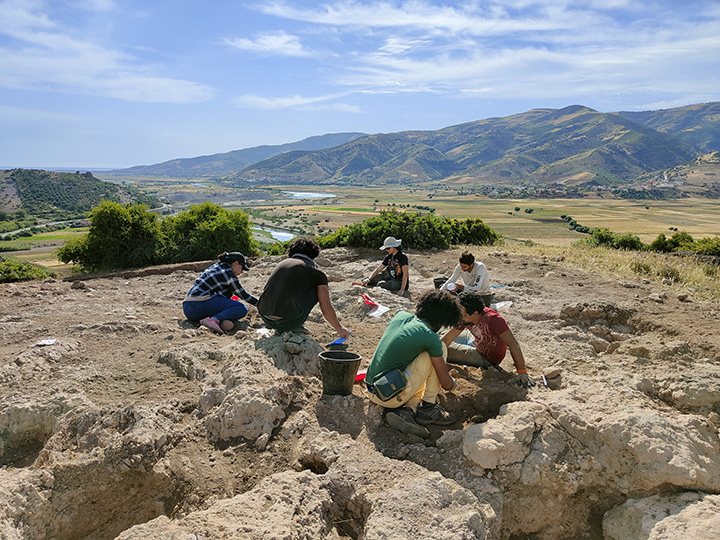
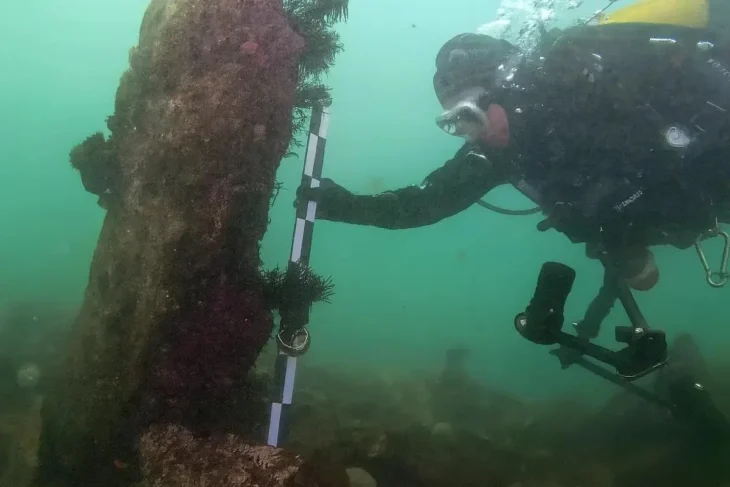
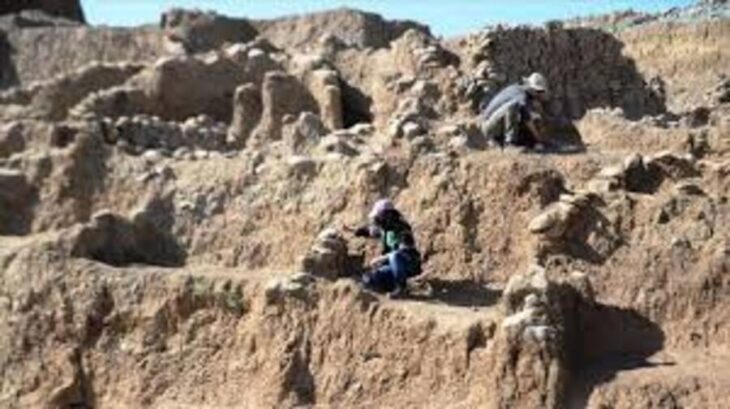
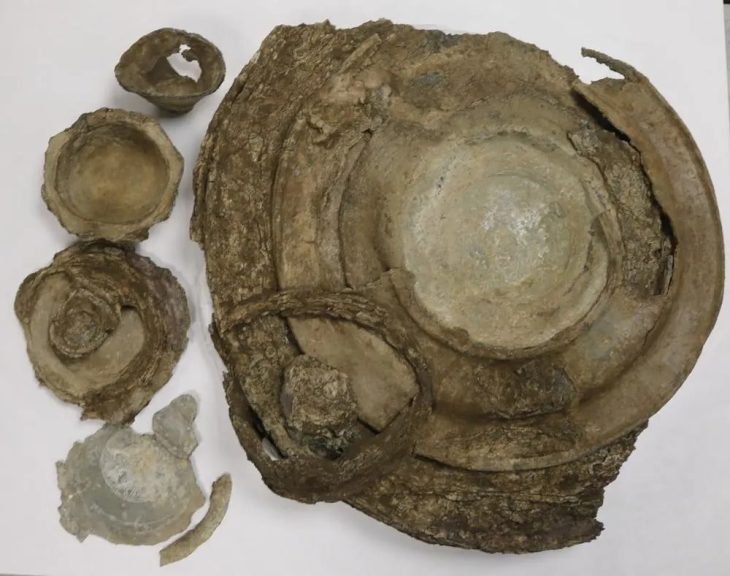
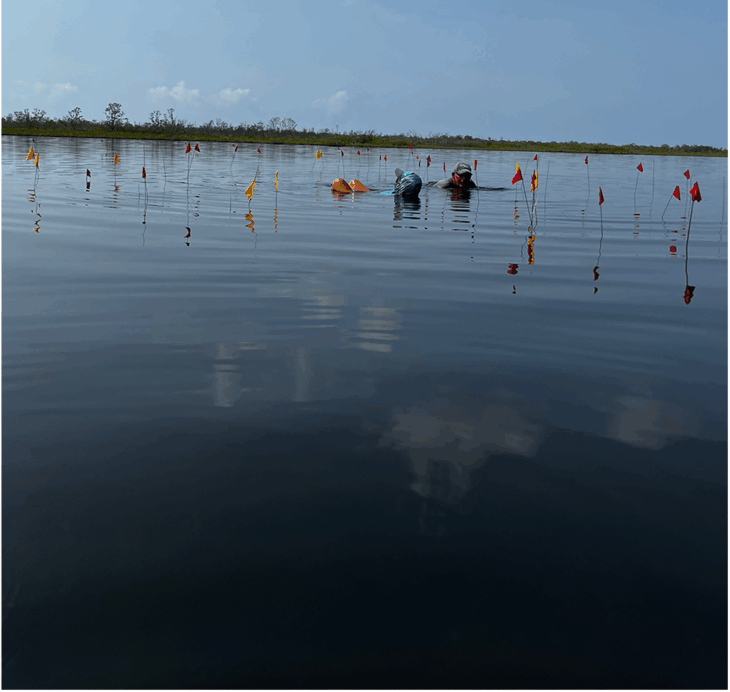
Underwater studies in Parion, a 2,700-year-old port city from the Roman Empire in Kemer village of Biga district of Çanakkale in northwestern Türkiye, revealed the second ancient port of the city.
The origin of its name is not clear, but one theory suggests that it may have been named after Parion, the son of Iason or Demetria from Erythrai, or even Paris, the prince of Troy. Having been established as a port city, the Parion Ancient City is known as the largest ancient city within the region with a diameter of approximately 4 km. In ancient times, Parion functioned as an important harbor for the surrounding settlements.
In 546 BC, Parion became a Greek city under Persian rule, and later in 334 BC, it fell under the sovereignty of Alexander the Great after he invaded Asia Minor. After his death, the city was taken over by the Attalid from Pergamon. As a part of the Pergamon Kingdom, Parion was handed over to the Romans by the will of Attalos III in 133 BC.
For years, excavations have been conducted in the village of Kemer in the Biga district of Çanakkale to uncover the historical and archaeological heritage of Parion Ancient City. With the permission of the Ministry of Culture and Tourism, scientific excavations at Parion Ancient City, led by Prof. Dr. Vedat Keleş, Dean of the Faculty of Humanities and Social Sciences at Ondokuz Mayıs University (OMU), have reached their 20th year with the 2024 season.
Excavation head Vedat Keleş said: “This harbor, compared to the southern harbor, which served as a commercial port, is slightly smaller and filled with alluvium deposited by the river running through the city. Parion was a legion colony, so there is a possibility that this harbor could have been a military port.”
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Underwater work was carried out for the first time this year in the city and during these works, the second ancient harbor of Parion has been unearthed.
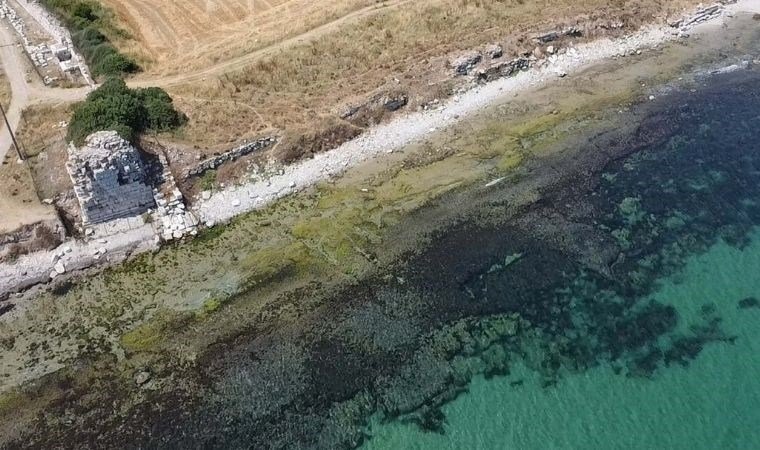

Stating that this is the 20th year of the excavations in Parion, Keleş said, “This is an important source of pride for us. When we look at 20 years, I think that the Parion work has done its part in the past 20 years in terms of excavation, restoration-conservation, publication and training of scientists. This year, we initiated underwater studies. As we all know, Parion is an important port city in the Northern Troas. We already knew that we had a southern port. This is mentioned in ancient sources. We were thinking there could also be a northern port. But this was always a question mark in our minds. With the underwater studies, we have determined that this place is also a port.”
Stating that Parion was a legion colony, Keleş said, “However, this port is a little smaller in size than the southern port, which is the trade port, and its interior is filled with alluviums accumulated by the stream passing through the city. Parion is a legion colony. Therefore, there may be a possibility that this place is a military port. The underwater studies we will carry out will give us more detailed information on this issue.”
Keleş noted that excavations continued in two places during the excavation season: “One is theater, the other is the agora. Foreign faculty members work in the agora. We work in the theater. The theater work is difficult because it is destroyed. Because a city wall was built over the stage building and almost all the seating rows and architectural parts of the theater were used within this city wall. Therefore, the structure seems to have changed considerably in the late period. Even though we have some trouble due to this destruction, our work progresses slowly. Apart from this, restoration work also continues.”
Keleş expressed their aim to elevate Parion to its deserved status in the near future, stating: ” As a young excavation team, the city we are excavating has a high level of destruction. We need to fully uncover the city. Therefore, we need labor support. I would like to appeal to local authorities. If they support us, especially by providing labor support, we can continue our excavations uninterrupted throughout the year, as the climate permits.”