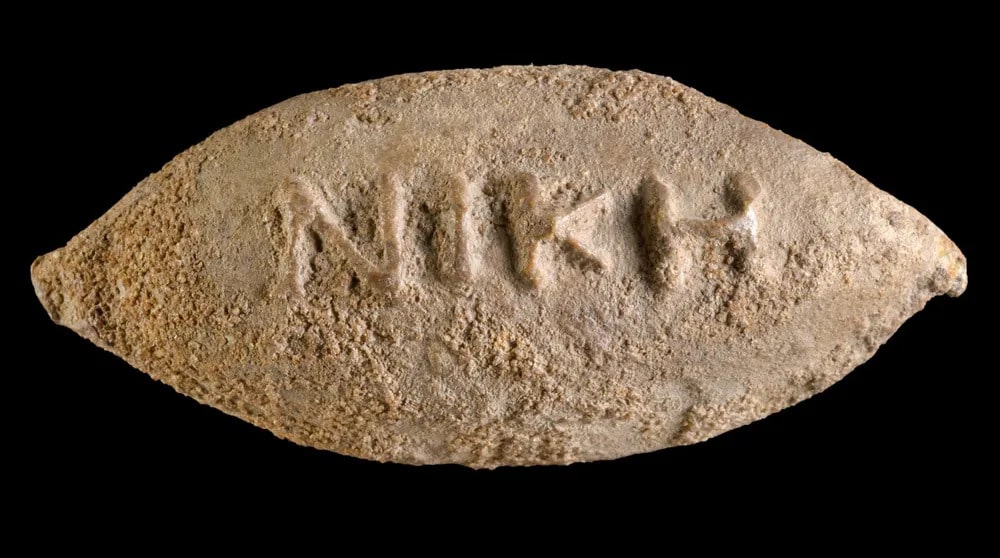
A 2,200-year-old lead sling bullet was discovered by the Israel Antiquities Authority (IAA) in the central Israeli city of Yavne, bearing a “Victory for Heracles and Hauron” inscription and which possibly belonged to a Greek soldier.
The Israel Antiquities Authority announced on Thursday that the sling bullet that bullet was discovered about a year ago and has been under examination since then.
The weapon, designed to guarantee victory in battle, may have belonged to a Greek soldier fighting in the Hellenistic Period’s conflict with the Hasmoneans. The Hasmonean dynasty was a ruling dynasty of Judea and surrounding regions during classical antiquity from c. 140 BCE to 37 BCE.
The Israel Antiquities Authority, which revealed the finding, told The Times of Israel that the sling bullet found in Yavne’s major archaeological site is 4.4 centimeters (1.7 inches) long and around 2,200 years old.

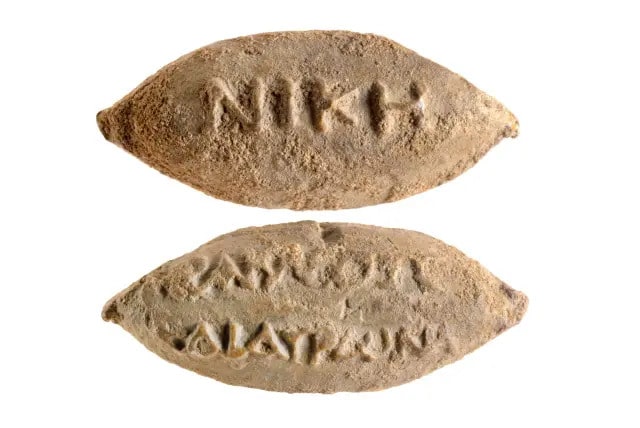
On the bullet is the Greek inscription “Victory of Heracles and Hauronas” – a pair of gods that were considered to be the “divine patrons of Yavne during the Hellenistic period,” explained Professor Yulia Ustinova from the Ben Gurion University of the Negev.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Hercules, the son of Zeus (Roman Jupiter) and the mortal Alcmena, is a Greek divine hero known for his strength and numerous far-reaching adventures. Hauronas, also known as Hauron, was an ancient Egyptian god who was worshiped in Giza.
“Actually, the inscription on a sling bullet is the first archaeological evidence of the two guardians of Yavne, discovered inside Yavne itself. Until today, the pair was only known from an inscription on the Greek island of Delos,” the professor added.
“The inscriptions convey a message of unifying the warriors with the aim of raising their spirits, scaring the enemy, or a call intended to magically energize the sling bullet itself,” noted Ustinova, who deciphered the inscription. “They were part of psychological warfare, the main purpose of which was to terrorize the opponent, and in addition, to unite the warriors and raise their spirits.”

However, the researchers acknowledged that it was unclear in what context the slingshot was used and that there was no conclusive evidence that it even belonged to a Greek soldier.
“It seems that we will not be able to know for sure if the sling bullet belonged to a Greek soldier, but it is not impossible that it is related to the conflict between the Greeks and the Hasmoneans,” said Pablo Betzer and Dr. Daniel Varga, who directed the excavation on behalf of the IAA, in the statement.
“The tiny lead sling bullets, announcing the imminent victory of the gods of pagan Yavne, is tangible evidence of a fierce battle that took place in Yavne at that time,” they added.
The story of the bullet will be presented to the public next Tuesday in a free event at the ‘Yavne and its Secrets’ lecture next week in Yavne.
Cover Photo: The word “Victory” on the sling bullet. Dafna Gazit, Israel Antiquities Authority