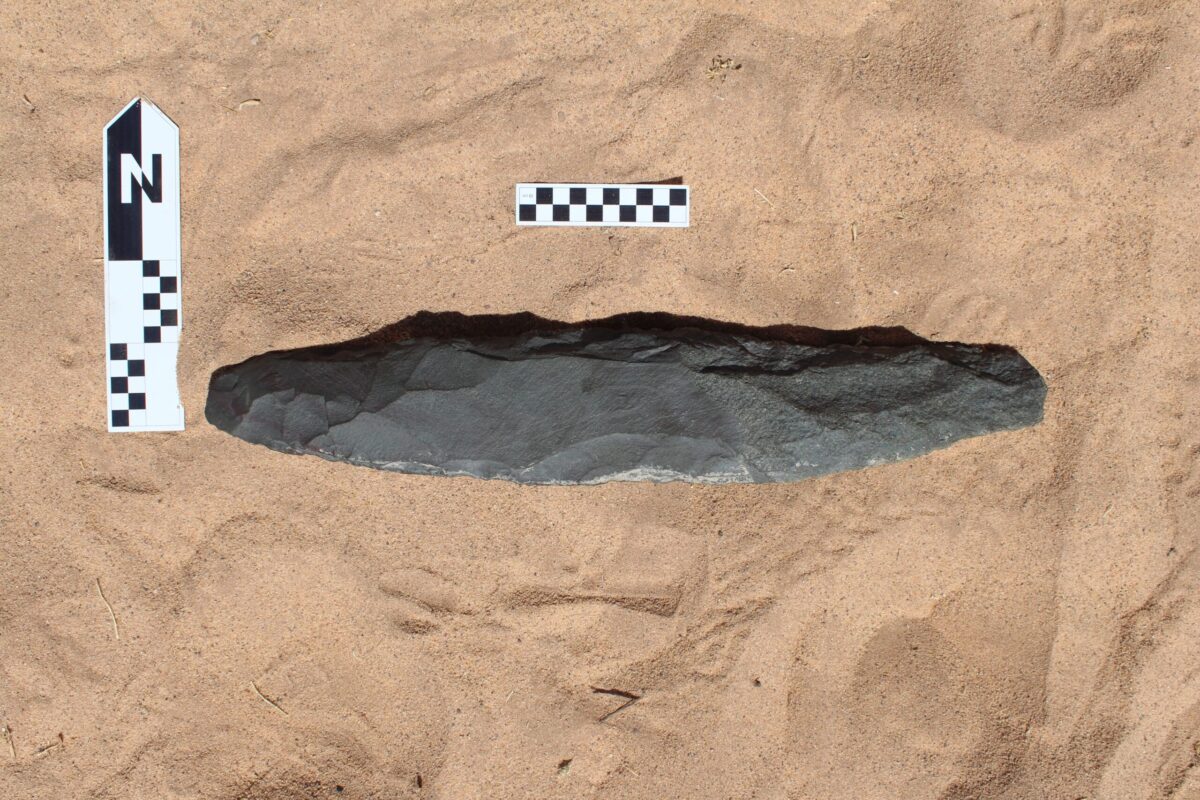
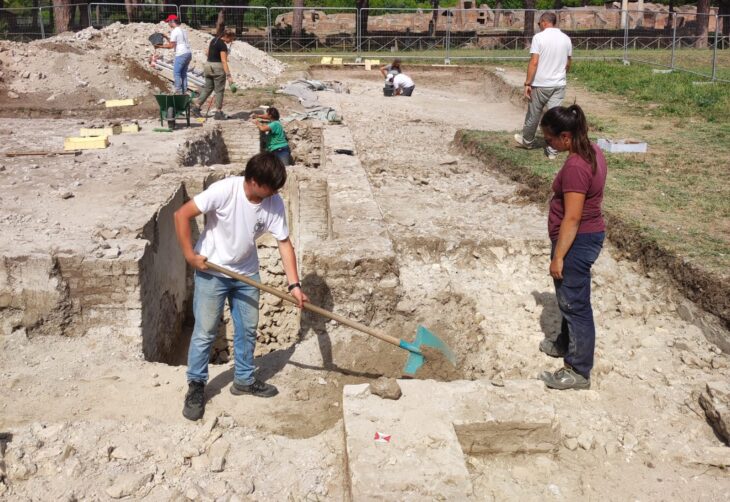
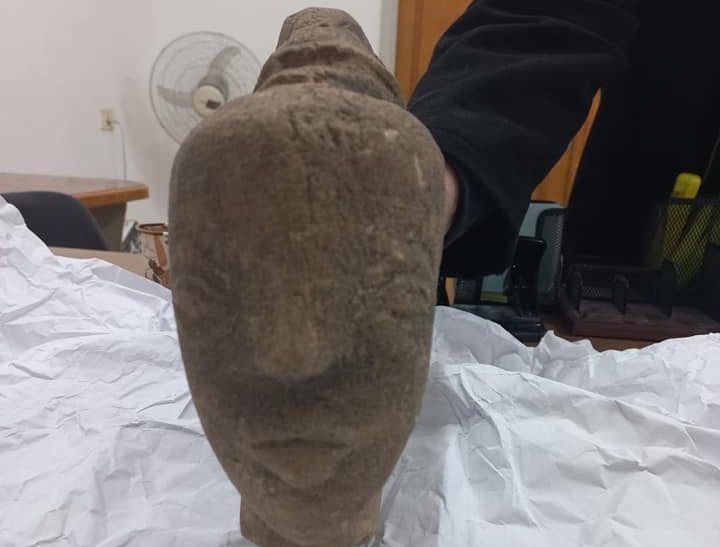
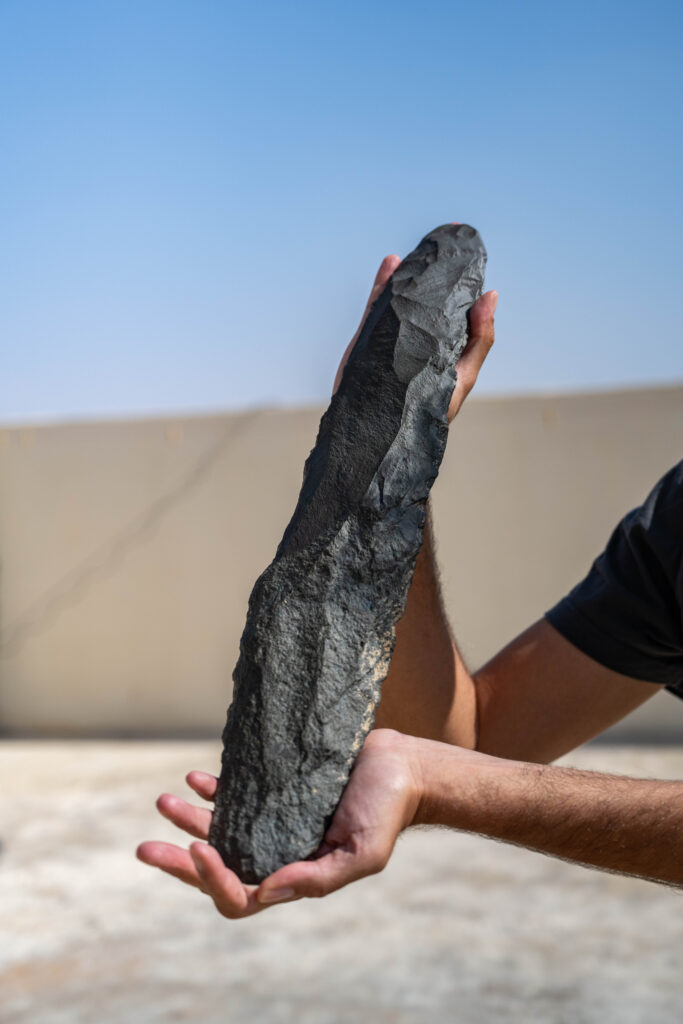
The Royal Commission for AlUla (RCU) of Saudi Arabia has announced that archeological excavation teams at the Qurh site in AlUla Governorate have discovered a Paleolithic Age hand axe estimated to be more than 200,000 years old.
Qurh (AL-Mabiyat) is located near the village of Mugheira, some 20 Kilometers south of the modern town of AlUla.
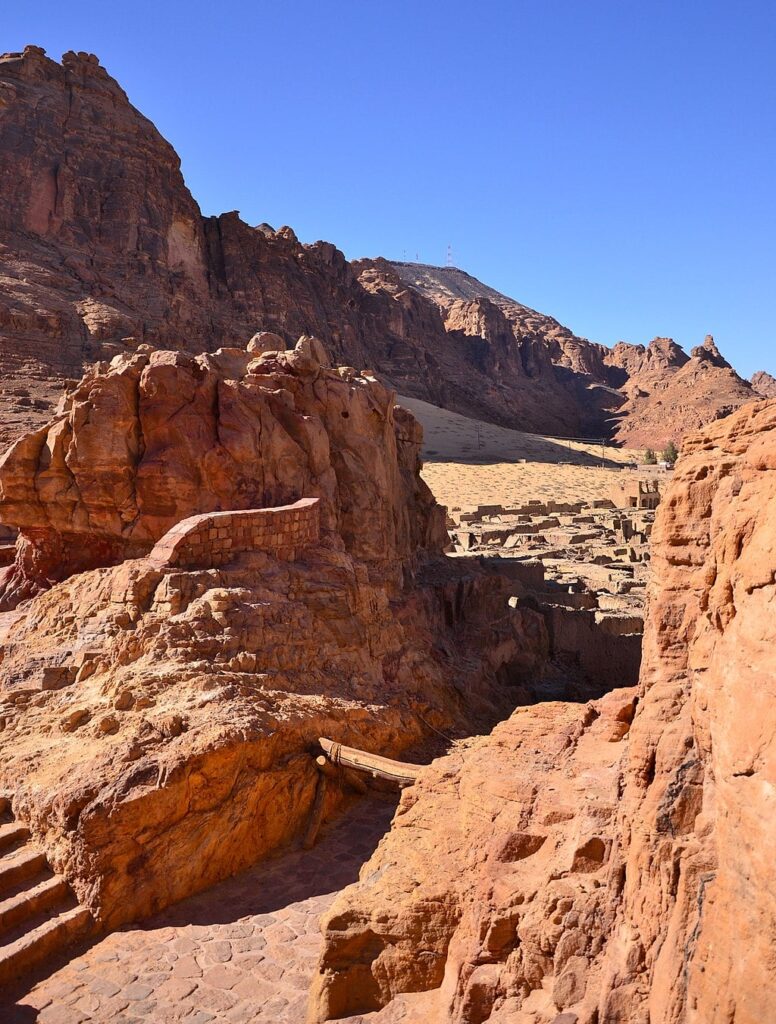
Qurh, a website with historic significance from the early Islamic intervals, stands as one of many Arabian Peninsula’s essential city locales, concealing a wealth of secrets and techniques and historic treasures.
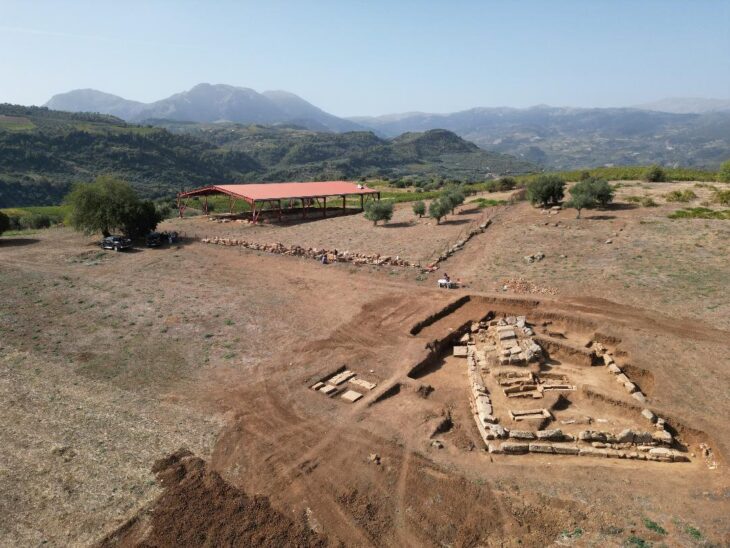
The archaeological site covers a large area and includes several open trenches from previous archaeological campaigns as well as several free-standing or exposed architectural elements such as sections of the city wall. The visible remains include a variety of architectural elements, the majority of which are made of earthen materials, as well as brick and stonework.

It is known as Deira (The town). Inside the town, there are ancient heritage buildings, mosques and markets, dating back to about 7 centuries. Its birth long pre-dates Islam but it prospered and flourished between 800 and 1100 CE.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
This ancient tool was discovered by a team of archaeologists from the heritage consultancy TEOS Heritage.
This strong instrument, crafted from comfortable basalt stone and measuring 51.3 cm in size, reveals traits indicative of chopping or chopping functions. Ongoing studies aim to precisely ascertain the tool’s intended use.

The hand axe discovery is hailed as a transformative chapter in the history of humanity both within and beyond the Arabian Peninsula.
RCU at present oversees 11 specialized archaeological initiatives in AlUla and Khyber as a part of its dedication to unraveling the mysteries of historic occasions.
The commission attaches great importance to archeological discoveries as part of its AlUla comprehensive development plan to become a world-leading destination for natural and cultural heritage.