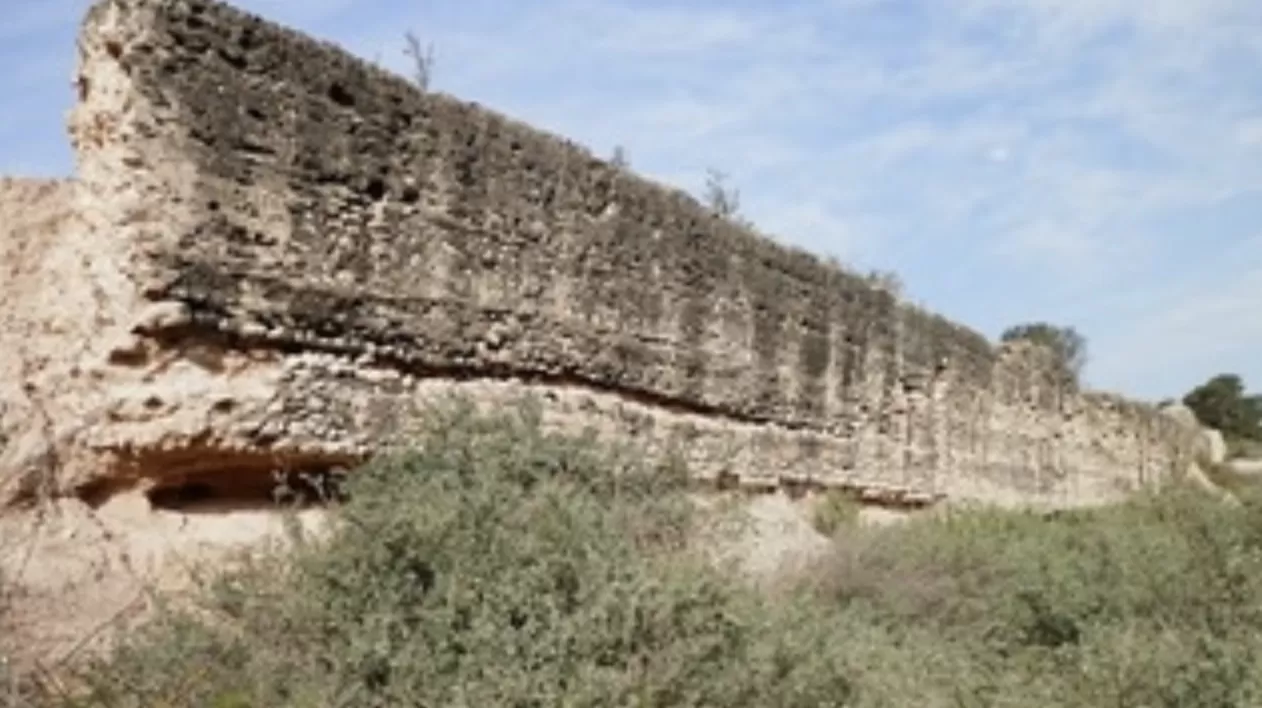
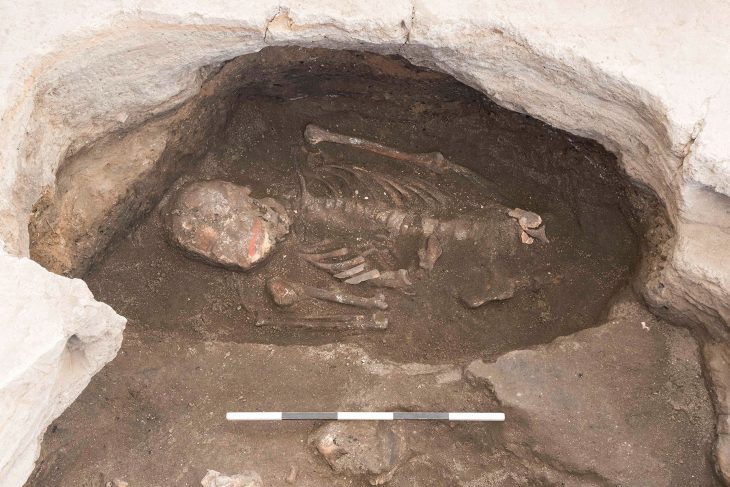
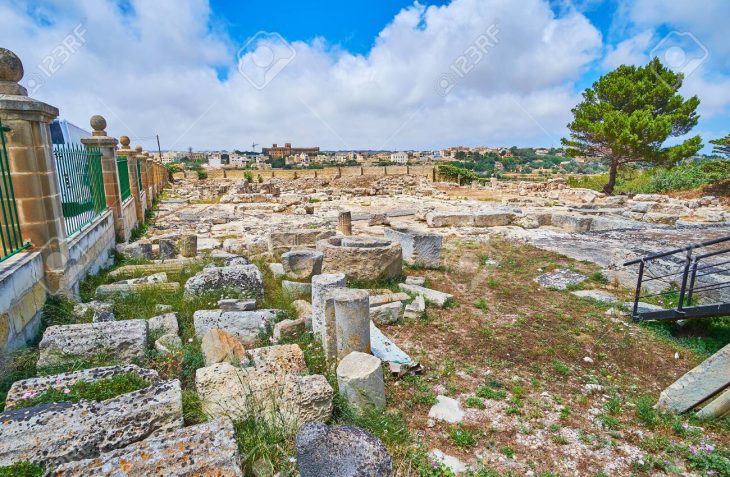
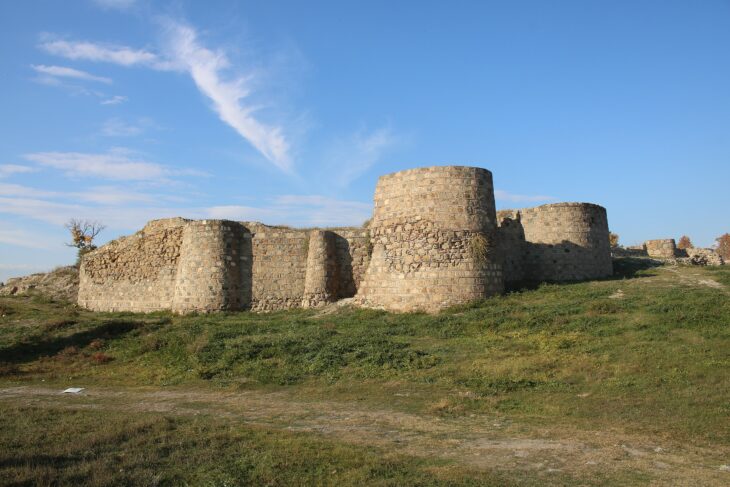
An archaeological research project has unveiled that the imposing L’Assut de l’Argamassa dam in Elche, Spain, long suspected to be of Islamic origin, was actually constructed by the Romans. The significant findings, resulting from a meticulous study led by the University Institute for Research in Archaeology and Historical Heritage of the University of Alicante (UA), were publicly announced at an event held yesterday, Friday, May 16th, at 5:00 PM at the Espai Escènic of the CCCE L’Escorxador in Elche.
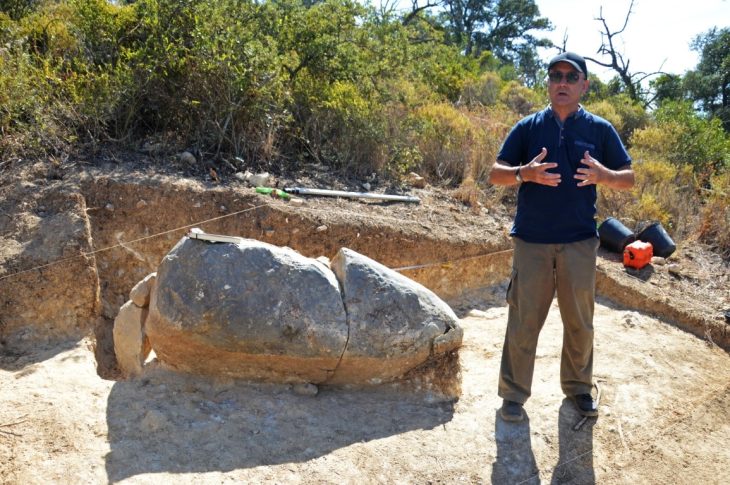
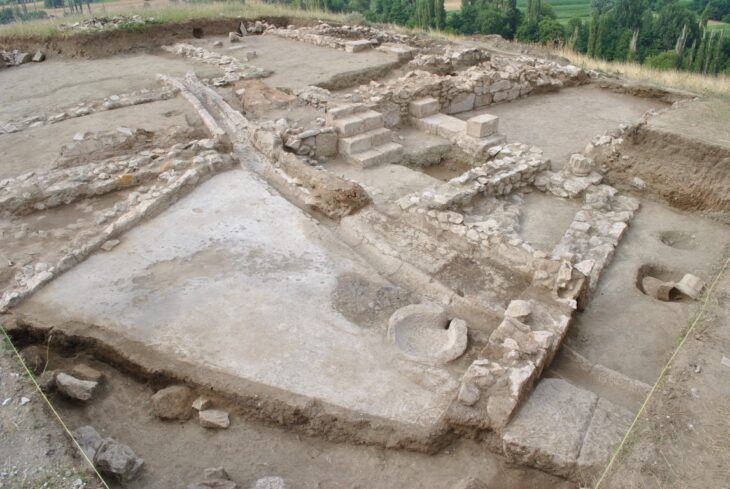
The research, spearheaded by Professor of Ancient History at UA, Jaime Molina Vidal, in collaboration with senior lecturer Daniel Mateo Corredor and Belén Carrillo Maciá from the Elche City Council, focused on the impressive hydraulic structure situated on the Vinalopó River in the Camp d’Elx region. L’Assut de l’Argamassa, stretching over 130 meters in length and standing 4 meters high, is located near the ancient Roman colony of Ilici, present-day Elche.
Ilici boasts a rich history, with its origins tracing back to Iberian settlements before becoming a significant Roman colony known as Colonia Iulia Ilici Augusta in the 1st century BC. This strategic location underscores the Romans’ advanced planning and resource management in developing the agricultural landscape (ager ilicitanus) surrounding their settlements.
Traditionally, the dam’s origins had been attributed to the Islamic period without solid evidence. However, the recent investigation employed detailed morphological analysis combined with cutting-edge Optically Stimulated Luminescence (OSL) dating techniques. These advanced methods conclusively revealed that the dam was built between the late 1st century BC and the early 1st century AD, firmly placing its construction within the Roman era.
Professor Molina emphasized the dam’s crucial function in regulating the flow of the Vinalopó River. He also suggested a potential secondary role in facilitating irrigation systems on the right bank of the river, known as the Alebus during Roman times. The dating strongly suggests a direct connection between the dam’s construction and the establishment of the Roman colony of Ilici, as well as the subsequent development of the fertile ager ilicitanus, the agricultural land surrounding the city. This discovery highlights the sophisticated water management infrastructure implemented by the Romans in the region from the earliest days of their settlement.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
While initial investigations into the dam began over a decade ago, the research reached its culmination with the development of innovative OSL dating methodologies for lime mortars and the crucial financial support from various national and regional scientific projects.
The significant findings were first presented to the international archaeological community at the Landscape Archaeology Conference (LAC2024) in 2024 and were met with considerable enthusiasm. Recognizing the importance of this research, it will be featured in a forthcoming monographic volume dedicated to Roman hydraulic infrastructures, titled: “Molina Vidal, J., Mateo Corredor, D. (in press): L’Assut de l’Argamassa (Elche, Alicante, Spain): a Large Roman Hydraulic Structure in the ager Ilicitanus, in P. Trapero, A. Carneiro, J. García (eds.) Water uses in rural economic activities: evidences for the Roman period in Hispania and the Roman West. Archaeology of the Mediterranean World, Brepols.”
This pivotal research was made possible through funding from the STILA programme (“Irrigated landscapes, market gardens and smallholdings in Roman times. Analysis of intensive agrosystems and their economic and social logics” – PID2022-142712NB-I00), supported by the Spanish Ministry of Science and Innovation.
Yesterday’s public presentation offered a deeper insight into this remarkable discovery and its profound implications for understanding Roman influence and engineering prowess in ancient Spain, shedding new light on the early development of the Elche region.
Note: This article is based on a press release from the University of Alicante and has been translated from Spanish.
Cover Image Credit: University of Alicante