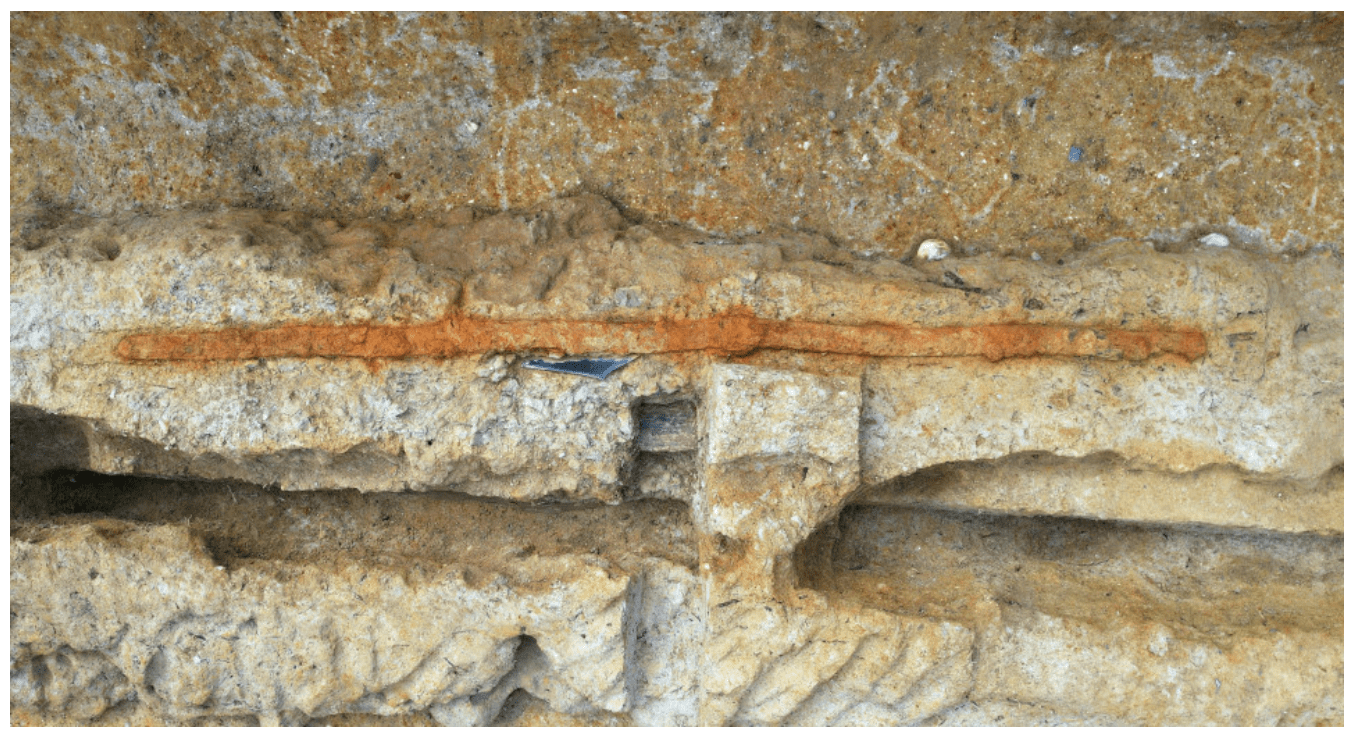
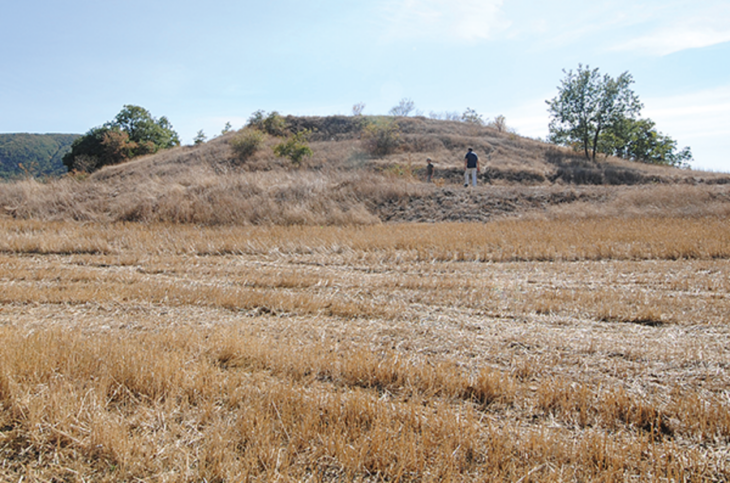
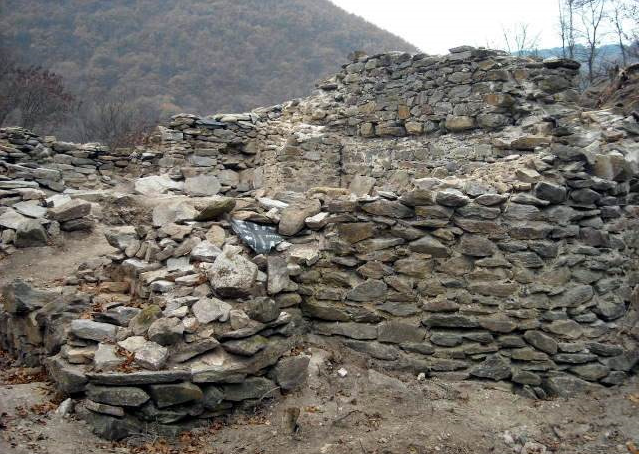
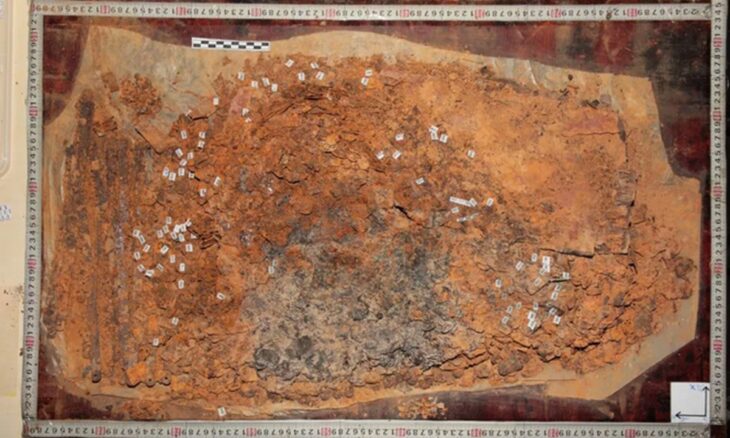
The largest bronze mirror and the largest “dako” iron sword in Japan were discovered at the Tomio Maruyama burial mound in Nara.
Experts say the twin discoveries from the Tomio Maruyama Tumulus last November can be classified as national treasures, with the shield-shaped mirror being the first of its kind.
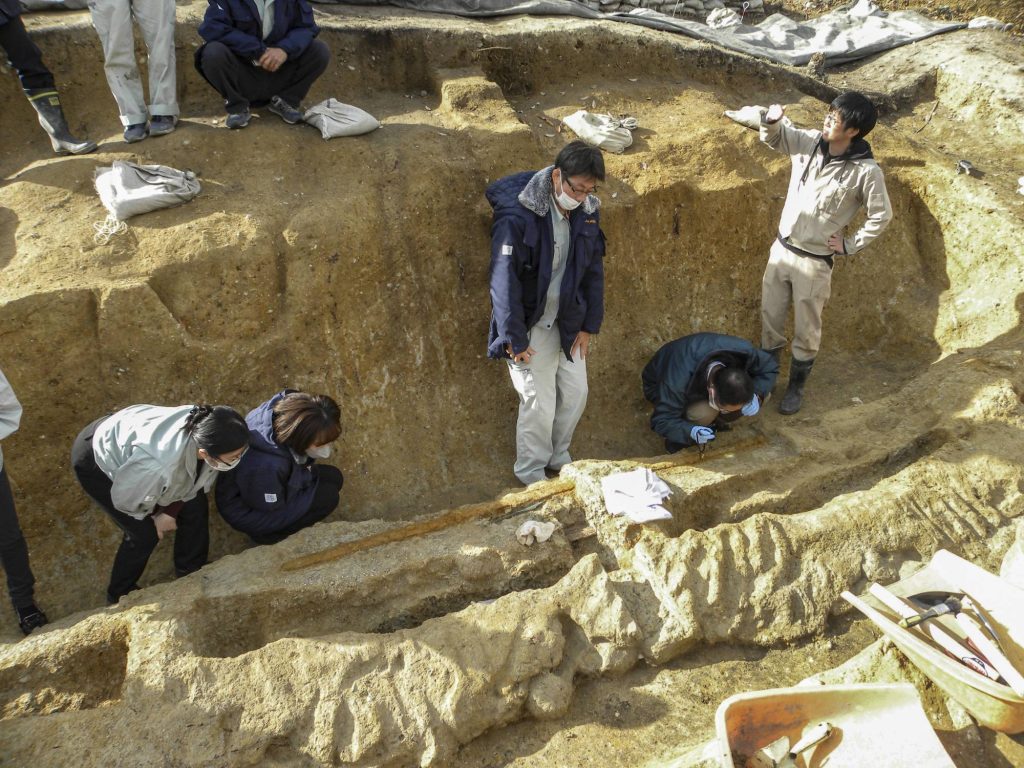
The Nara Municipal Buried Cultural Properties Research Center, which excavates and researches Tomiomaruyama kofun, and the Nara Prefectural Archaeological Institute of Kashihara, which assists in the excavation, announced the discoveries on Jan. 25.
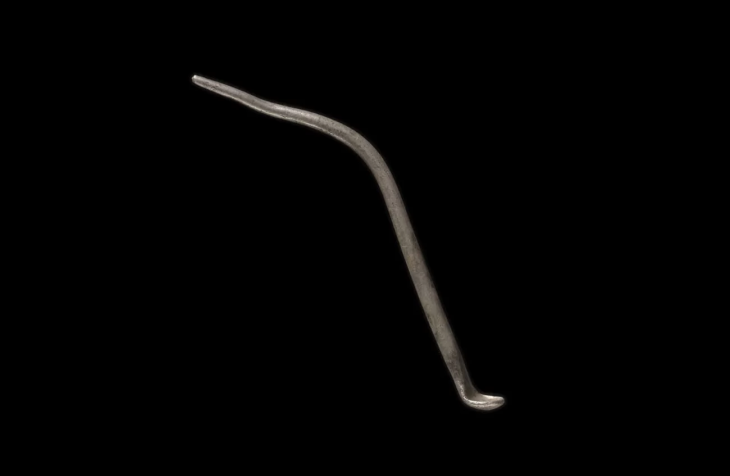
The 2.3-meter sword with a meandering blade is also the largest iron sword made in that period in East Asia.
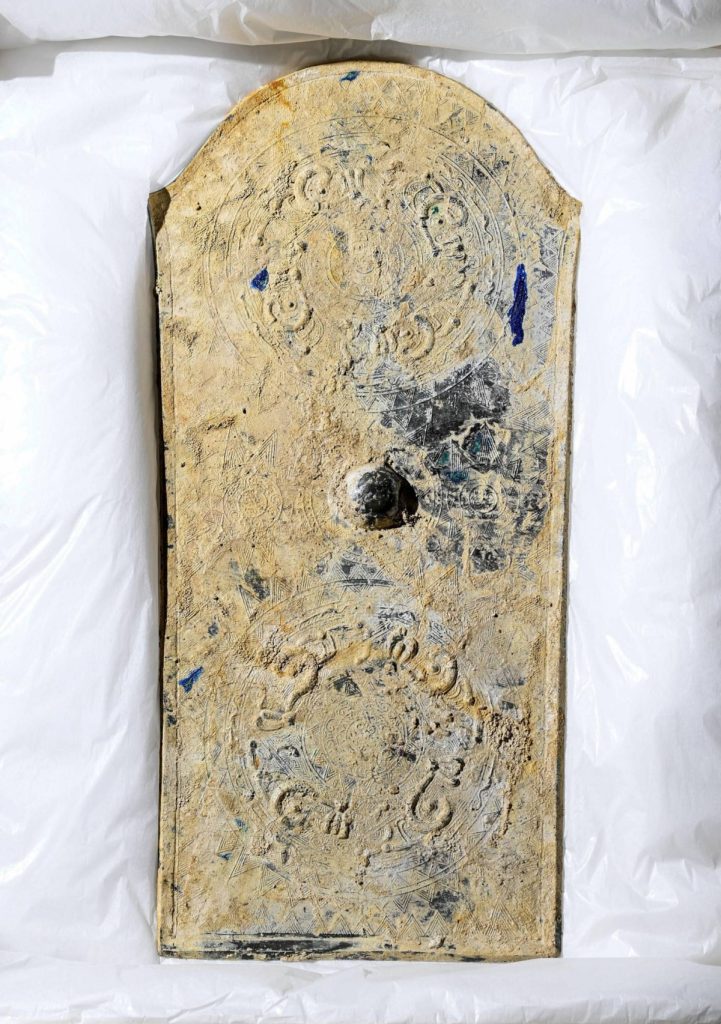
The patterned surface of the mirror carries the designs of two more common “daryu” mirrors, distinctive with its designs based on imaginative creatures, which have been found mainly in western Japan.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!

The shield-shaped mirror is 64 cm in length, 31 cm in width at most, and weighs 5.7 kilograms. Typically, bronze mirrors that are found at archaeological sites are rounded, but this one is shield-shaped.
The sword is the oldest of the dako swords, distinguished by their wavy, snake-like shapes, which give rise to their name. As burial goods, more than 80 other dako swords have been discovered throughout Japan.
The latest sword has markings of a sheath and handle, and together, its length measures 2.6 meters, more than dominating the last longest dako sword discovered at around 85 cm.
“(These discoveries) indicate that the technology of the Kofun period (300-710 AD) are beyond what had been imagined, and they are masterpieces in metalwork from that period,” said Kosaku Okabayashi, the deputy director for Nara Prefecture’s Archaeological Institute of Kashihara.

Mirror and shields are considered to be tools to protect the dead from evil spirits. The sword is thought to have been enlarged to increase its power, and the possibility of its use as a battle tool is low, researchers said.
The 109-m-diameter Tomio Maruyama burial mound, the largest in Japan and dating to the late 4th century, is believed to have belonged to a significant person who supported the Yamato rulers at the time.
The burial chamber where the discoveries were made is thought to have belonged to someone close to that person, according to Naohiro Toyoshima, an archaeology professor at Nara University. He also said that the ritualistic sword and the shield-shaped mirror may indicate that the individual was involved in military and ritualistic matters.
Cover Photo: Photo taken on Dec. 5, 2022, shows a sword discovered at the Tomio Maruyama burial mound in Nara, western Japan. (Photo courtesy of Nara city board of education)(Kyodo)