An international team led by The University of Vienna and the Ulsan National Institute of Science and Technology in collaboration with the National Museum of Korea has successfully sequenced and studied the whole genome of eight 1,700-year-old individuals dated to the Three Kingdoms period of Korea (approx. 57 BC-668 AD).
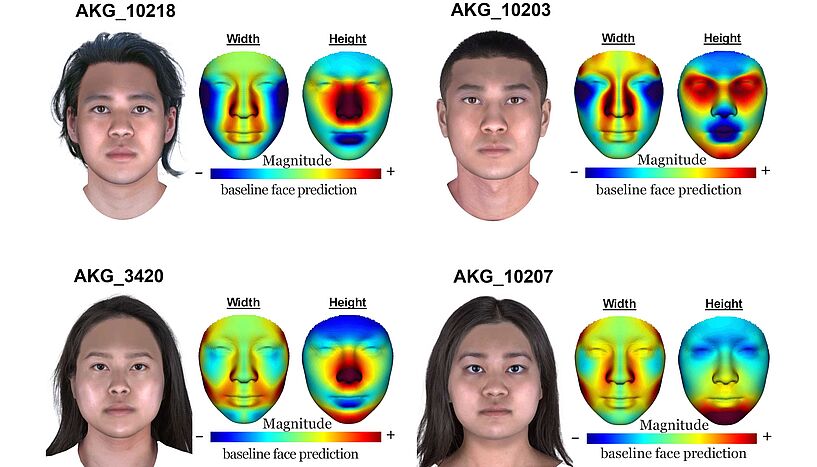
The team also performed a detailed DNA-based facial feature prediction for the eight genomes, showing that Koreans from the Three Kingdoms period were similar to modern Koreans.
This is the first instance of publishing an ancient individual’s face prediction using DNA-only in a scientific journal. This approach may create a precedent for other ancient genome studies to predict facial features when the skulls are extremely degraded.
The study, published in Current Biology, showed that ancient Koreans from the Gaya confederacy were more diverse than the present-day Korean population.

The first published genomes from this period in Korea bring key information for the understanding of Korean population history. The Team has been led by Pere Gelabert and Prof. Ron Pinhasi of the University of Vienna together with Prof. Jong Bhak and Asta Blazyte from the UNIST and Prof. Kidong Bae from the National Museum of Korea.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
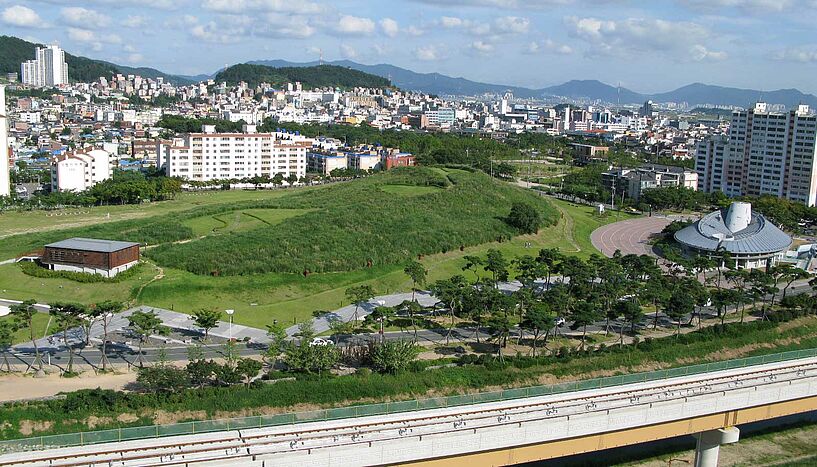
The eight ancient skeletal remains used for DNA extraction and bioinformatic analyses came from the Daesung-dong tumuli, the iconic funerary complex of the Gaya confederacy, and from Yuha-ri shell mound; both archeological sites located in Gimhae, South Korea. Some of the eight studied individuals were identified as tomb owners, others as human sacrifices, and one, a child, was buried in a shell mound, a typical funerary monument of Southeast Asia that is not related to privileged individuals. All burial sites are typical for the Gaya region funerary practices in AD 300-500.
“The individual genetic differences are not correlated to the grave typology, indicating that the social status in the Three Kingdoms Korea would not be related to genetic ancestry. We have observed that there is no clear genetic difference between the grave owners and the human sacrifices” explains Anthropologist Pere Gelabert.

Six out of eight ancient individuals were genetically closer to modern Koreans, modern Japanese, Kofun Japanese (Kofun genomes are contemporaneous with individuals from our study), and Neolithic Koreans. The genomes of the remaining two were slightly closer to modern Japanese and ancient Japanese Jomons. “This means that in the past, the Korean peninsula showed more genetic diversity than in our times” says Gelabert.
Modern Koreans, on the other hand, appear to have lost this Jomon-related genetic component owing to the relative genetic isolation that followed the Three Kingdoms period. These results support a well-documented post- Three Kingdoms period of Korean history, suggesting that Koreans of that time were intermixing within the peninsula, and their genetic differences were diminishing until the Korean population became homogeneous as we know it today.
Cover Photo: Facial reconstruction of four Ancient Korean individuals based on Ancient DNA data. Photo: Current Biology