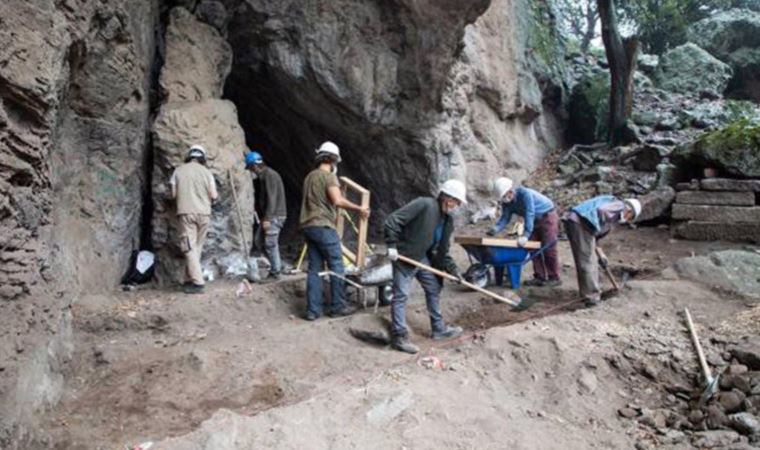
During the rescue excavation carried out in a cave in Dikili, İzmir, in western Turkey, 14 thousand-year-old stone tools and bone remains belonging to the Late Paleolithic Age were found.
Turkish and German scientists who carried out the studies revealed that the cave was also used as a cult center dedicated to the mother goddess Kybele.
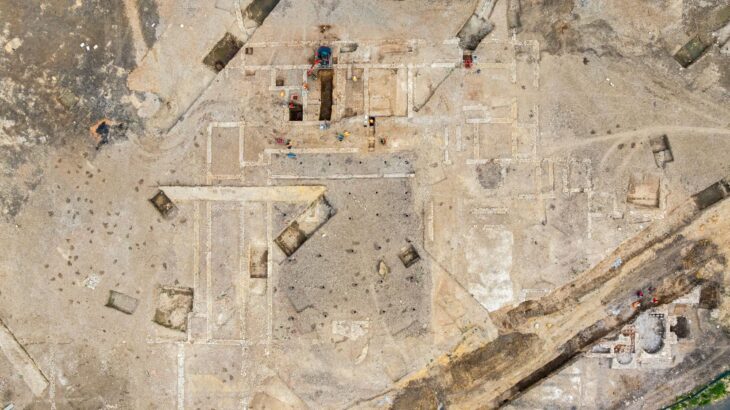
With the permission of the Ministry of Culture and Tourism, General Directorate of Cultural Heritage and Museums, a 6-week rescue excavation was carried out in a cave in Dikili under the direction of Bergama Museum in the autumn of 2021.
The teams of the German Archaeological Institute and Ankara University Faculty of Language, History, and Geography, experts led by Archeology Department Professor Dr. Harun Taşkıran participated in the excavation work.
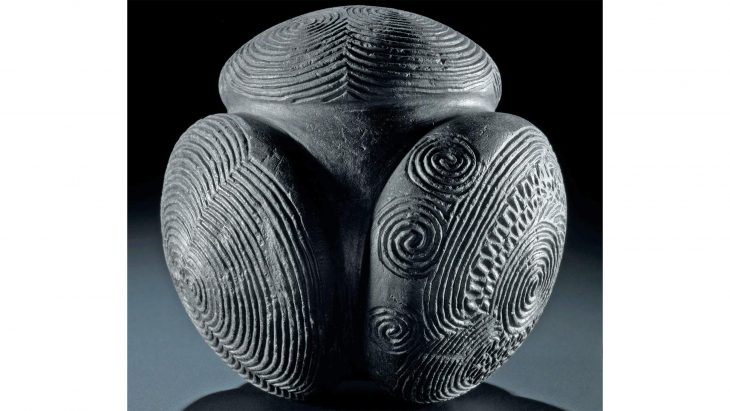
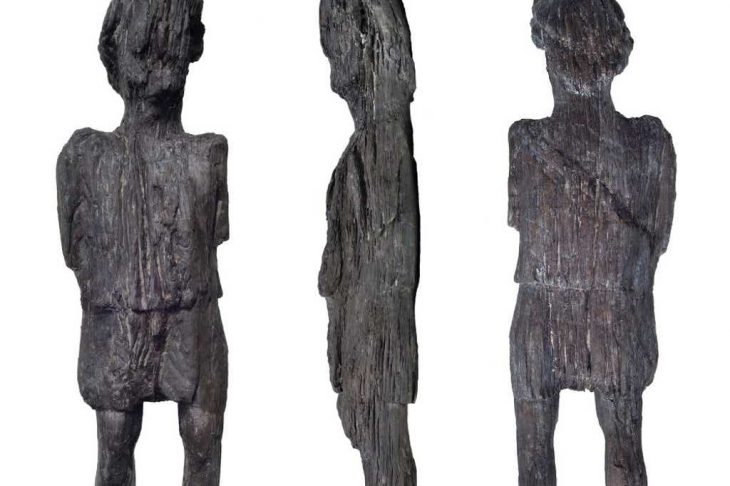
The team of Turkish and German scientists revealed that the cave was used as a cult center dedicated to the mother goddess Cybele from the 6th century BC to the Roman Period, using the information they obtained from the ancient layers.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
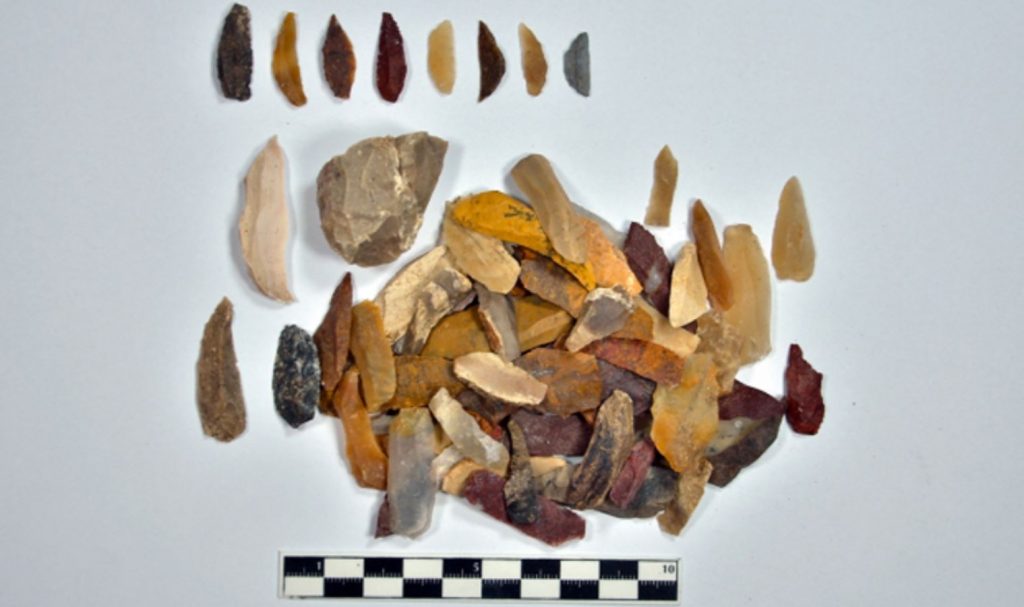

During the surveys carried out in parallel with the Pergamon excavations carried out by the German Archaeological Institute, layers belonging to the Epipaleolithic Period were found in the region.
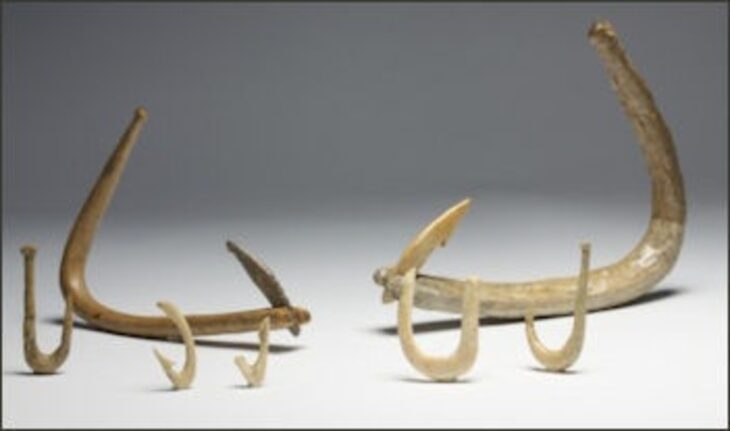
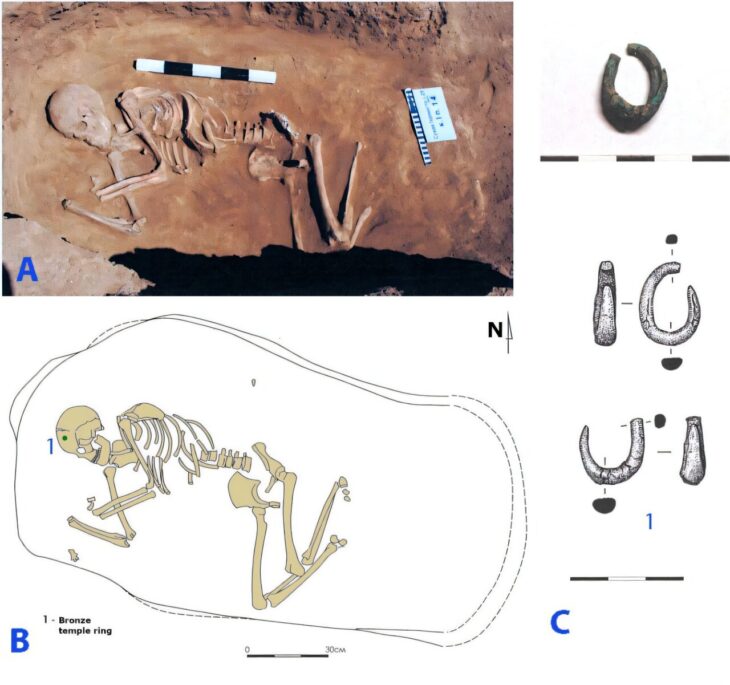
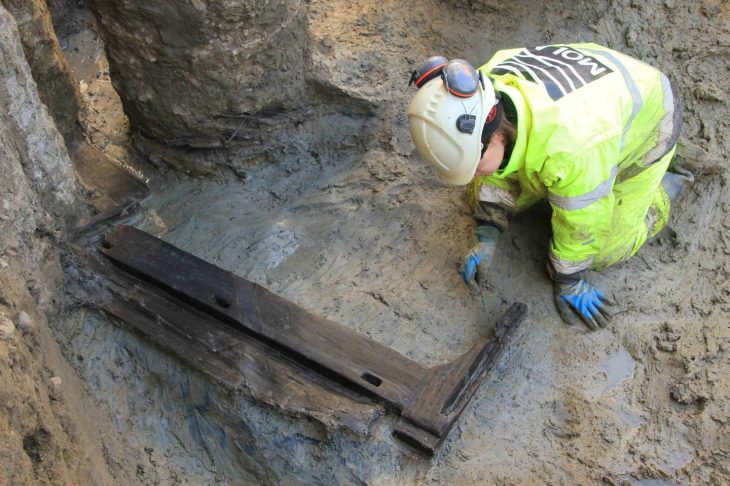
Stone tools and bones were unearthed in these layers.
As a result of the examinations made in the laboratories with the radiocarbon dating method, it was determined that the stone tools and bones belonged to 14 thousand years ago.
A NEW PAGE IN THE HISTORY OF WESTERN ANATOLIA
Director of the German Archaeological Institute Prof. Felix Pirson said that within the scope of the rescue excavation, the first remains belonging to the Epipalaeotic Period were discovered in Western Anatolia.
Pointing out that Anatolia is the lands that unite the east and the west in the developments and events throughout history, Pirson said:
The excitement created by the latest Göbeklitepe finds is one of the examples in this context. At Göbeklitepe, mankind created the first monumental architectural and plastic works in 10,000 years BC. Although the Neolithic Age, which includes Göbeklitepe in its early stages, is relatively known; The previous Paleolithic Age is less known. To date, a few Paleolithic finds have been identified and are still being excavated in Southern and Southeastern Anatolia. However, although surface finds belonging to some periods of the Paleolithic Age are known in Western Anatolia, that is, in the Aegean coasts and the transition region to Europe, no find site could not be detected in an archaeological filling belonging to the Paleolithic Period or the transitional phases to the Neolithic Period.” he said.
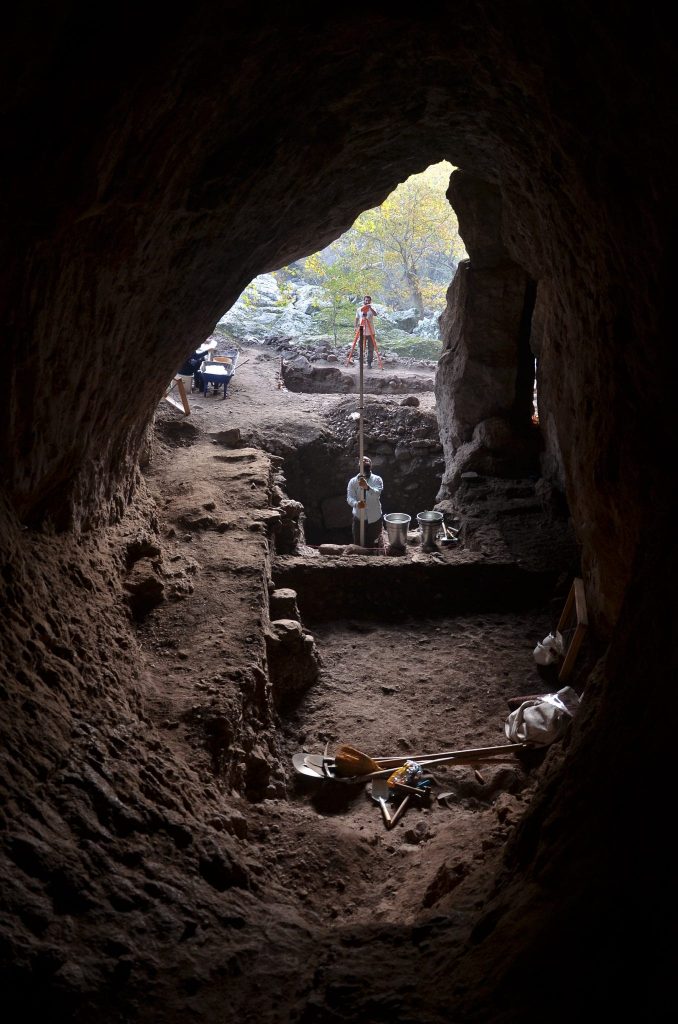

Noting that it was a great surprise to find 14 thousand-year-old layers from the Late Paleolithic Age in a cave discovered between Dikili and Bergama during the surveys carried out in parallel with the Pergamon excavations carried out by the German Archaeological Institute, Pirson said, “Stone tools and bones were found in the layers unearthed by the cleaning of the profiles. Examining the stone tools by experts and dating the bone finds with the radiocarbon method in laboratories, it was understood that they belonged to 14 thousand years ago.” used the phrases.
Pointing out that the cave was used as a short-term settlement or a seasonal campsite visited by Epi-paleolithic hunter-gatherer groups rather than a permanent settlement, Pirson gave the following information:
“Tools made of flint from this period were recovered. Flint cores, technological pieces, and production residues found in the archaeological filings reveal that the flaking process was carried out in the cave. Although the possibility that the flint raw material was collected from the creek bed in front of the cave can be considered, the question of where exactly people obtained the flint stone has not yet been answered.”
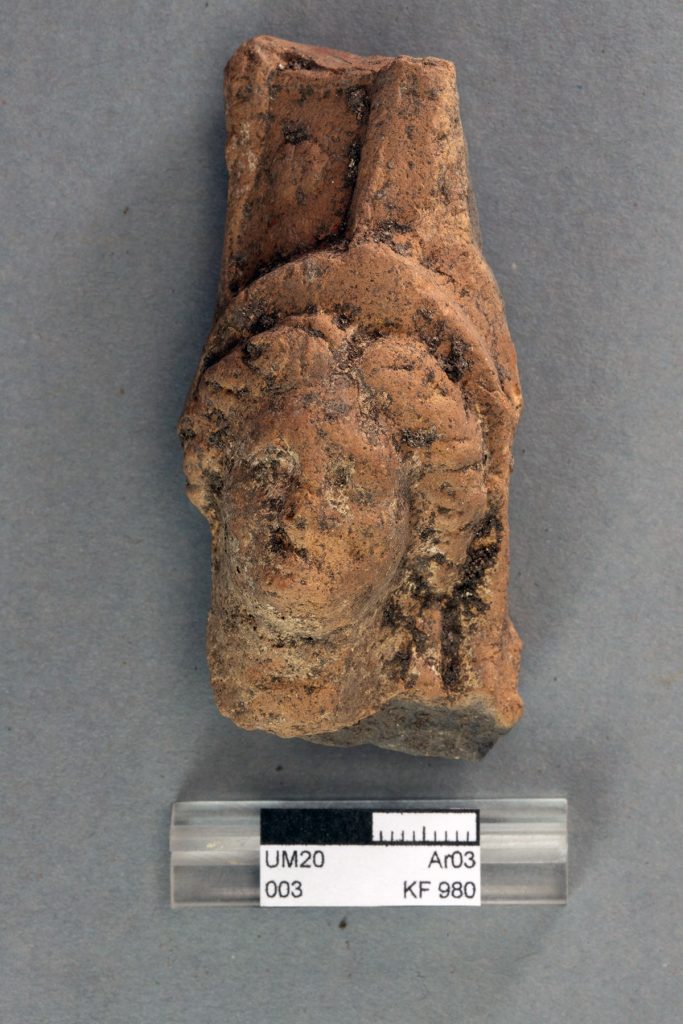

USED AS KYBELE CULT CENTER
Prof. Felix Pirson informed that the cave was used as a cult center dedicated to the mother goddess Kybele from the 6th century BC to the Roman Period and that the latest finds found in the cave belong to the Byzantine and Ottoman periods.
The investigation of the finds unearthed during the excavations under the direction of Pergamon Museum Director Nilgün Ustura is carried out within the scope of a long-term project titled the transformation of Pergamon micro geography between the Hellenistic and Roman Periods, financed by the German Research Institute (DFG).
Experts from the German Archeology Institute and Ankara University, Manisa Celal Bayar University and Sinop University, Berlin Frei University, and TÜBİTAK Marmara Research Center are participating in the rescue excavation and evaluation of the finds.